
SL Paper 2
Ethene belongs to the homologous series of the alkenes.
A bromoalkane, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\), reacts with a warm, aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH.
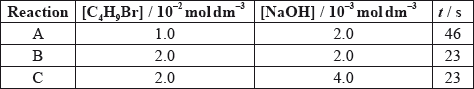
The time taken to produce a certain amount of product using different initial concentrations of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\) and NaOH is measured. The results are shown in the following table.
Outline three features of a homologous series.
Describe a test to distinguish ethene from ethane, including what is observed in each case.
Bromoethane can be produced either from ethene or from ethane. State an equation for each reaction.
State the equation for the reaction of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\) with NaOH.
Suggest what would happen to the pH of the solution as the reaction proceeds.
Deduce the effect of the concentration of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\) and NaOH on the rate of reaction.
C4H9Br:
NaOH:
Suggest why warm sodium hydroxide solution is used.
Deduce whether C4H9Br is a primary or tertiary halogenoalkane.
Determine the structural formula of C4H9Br.
Describe, using an equation, how \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\) can be converted into \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\).
Explain the mechanism for the reaction in (c) of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{Br}}\) with NaOH, using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs.
Electrolysis is an important industrial process used to obtain very reactive elements from their common ores.
Molten magnesium chloride can be electrolysed using inert graphite electrodes at 800 °C.
Describe, using a labelled diagram, the essential components of this electrolytic cell.
Molten magnesium chloride can be electrolysed using inert graphite electrodes at 800 °C.
Deduce the half-equations, including state symbols, for the reactions occurring at each electrode. (The melting points of MgCl2 and Mg are 714 °C and 649 °C respectively.)
Positive electrode (anode):
Negative electrode (cathode):
Outline why solid magnesium chloride does not conduct electricity.
Aluminium can also be obtained by electrolysis. Suggest one reason why aluminium is often used instead of iron by engineers.