
HL Paper 3
The structure of a drug is shown below:
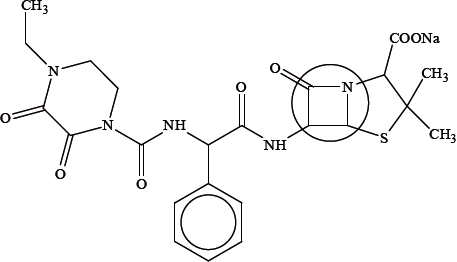
Another drug that can have a similar effect to the one shown in (a) is doxycycline, shown below.
Identify the class of drugs to which this particular drug belongs.
Explain the high reactivity of the part of the drug that is enclosed in the circle.
Suggest why the drug is administered as its sodium salt.
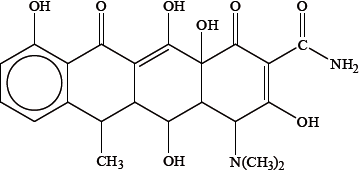
Because it contains several –OH groups and an amine group, doxycycline is slightly polar. Identify the amine group by drawing a circle around it on the structure above and state whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Suggest one way in which the polarity of doxycycline could be substantially increased.
Deduce the number of chiral carbon atoms in doxycycline and explain why chirality is important when considering its action in the body.
Compound X has the molecular formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\) and is found in human perspiration.
Its infrared (IR) spectrum is represented below.
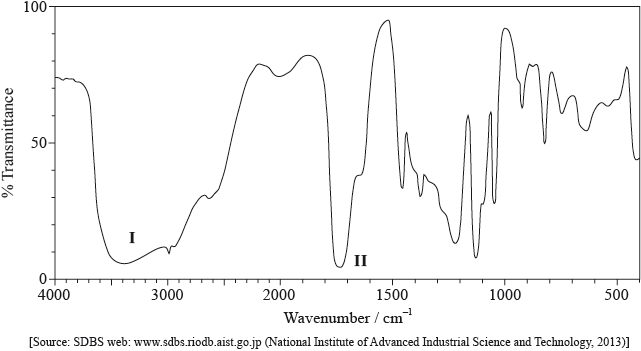
Deduce the bonds responsible for the absorptions labelled I and II.
I:
II:
The \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum recorded showed four peaks with the following chemical shift values (in ppm):
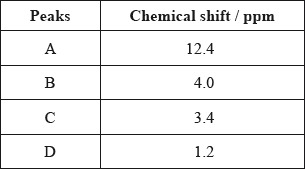
The integration trace for A:B:C:D was found to be 1:1:1:3.
Deduce what information can be obtained about the hydrogen atoms responsible for peak D at 1.2 ppm from the integration trace in the \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of X.
Deduce the fragments in the mass spectrum which correspond to the following \(m{\text{/}}z\) values.
\(m{\text{/}}z = 45\):
\(m{\text{/}}z = 17\):
\(m{\text{/}}z = 15\):
Deduce the structural formula of X.
Y is an isomer of X, which contains the same functional groups. Deduce the structural formula of Y.
(i) Like X, 3-methylbutanoic acid is also a source of body odour. Deduce the \(m{\text{/}}z\) value for the molecular ion peak on the mass spectrum of this compound.
(ii) Ethyl propanoate (ethyl propionate) is an isomer of 3-methylbutanoic acid. Its \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum consists of four peaks.
Deduce the ratios of the areas under each peak in the \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of ethyl propanoate. For each peak, deduce the range of chemical shift values (in ppm), using Table 18 of the Data Booklet, and predict the splitting pattern.
The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 is often given as an example of serendipity in science.
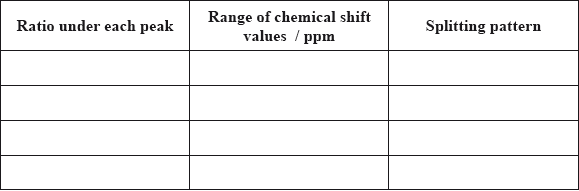
The structure of a particular type of penicillin called dicloxacillin is shown below.
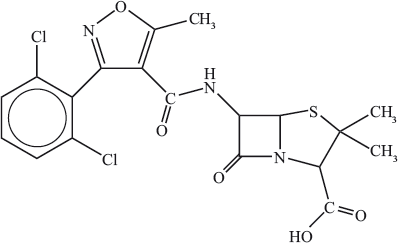
Describe what happens to bacteria when they come into contact with penicillin.
(i) Identify the \(\beta \)-lactam ring by drawing a circle around it.
(ii) Explain why the \(\beta \)-lactam ring is so important in the mechanism of the action
of penicillin.
(iii) State the name of the functional group in dicloxacillin, circled below.
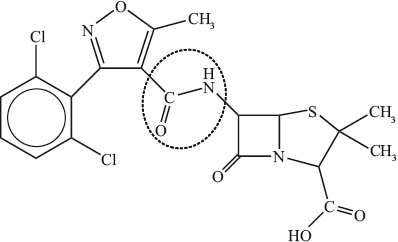
Comment on the fact that many bacteria are now resistant to penicillins.
Aspirin is one of the most widely used drugs in the world.
Aspirin was synthesized from 2.65 g of salicylic acid (2-hydroxybenzoic acid) (Mr = 138.13) and 2.51 g of ethanoic anhydride (Mr = 102.10).
Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds, that would be present in the infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin.
State two techniques, other than IR spectroscopy, which could be used to confirm the identity of aspirin.
Antimony oxide is widely used as a homogeneous catalyst for the reaction of benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid with ethane-1,2-diol in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PETE).
Deduce the repeating unit of the polymer and the other product of the reaction.
State the class of polymer to which PETE belongs.
In recent years several antiviral medications have been produced. One of these medications is oseltamivir (Tamiflu).
Identify the functional group circled in the structure of oseltamivir.
Predict the number of signals and relative integration you would expect to see in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) spectrum for the circled portion in the structure.
Number of signals:
Relative integration:
Oseltamivir is a chiral compound.
(i) Identify an apparatus that can be used to distinguish between its enantiomers.
(ii) Explain how the differentiation between the enantiomers is obtained using this apparatus.
Polymer nanocomposites often have better structural performance than conventional materials. Lithographic etching and metal coordination are two methods of assembling these nanocomposites.
Dendrimers are highly branched nanoparticles with a wide range of usage. One such dendrimer is PAMAM, or polyamidoamine.
The first step in the synthesis is to make the core by reacting ethane-1,2-diamine with methylpropenoate.
Estimate the atom economy of this first step.
Suggest, giving one reason, whether this is an addition or condensation reaction.
Subsequent steps proceed under differing conditions, forming the dendrimer polymer with the following repeating unit.
State the name of one functional group in this repeating unit.