
HL Paper 1
In which reaction will the entropy of the system increase significantly?
A. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{CaO(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
C. \({\text{HCl(g)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{Cl(s)}}\)
D. \({\text{NaOH(aq)}} + {\text{HCl(aq)}} \to {\text{NaCl(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
Consider the values of \(\Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\) À for the reaction of nitrogen with oxygen at 298 K.
\({{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2NO(g)}}\) \(\Delta {H^\Theta } = + 181{\text{ kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\)
\(\Delta {S^\Theta } = + 25{\text{ J}}\,{{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\)
Which statement is correct for this reaction?
A. \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) is positive at all temperatures.
B. \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) is negative at all temperatures.
C. \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) is positive at high temperatures.
D. \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) is positive at low temperatures.
What is the standard enthalpy of formation, in kJ mol–1, of IF (g)?
IF7 (g) + I2 (s) → IF5 (g) + 2IF (g) ΔH\(^\theta \) = –89 kJ
ΔH\(_f^\theta \) (IF7) = –941 kJ mol–1
ΔH\(_f^\theta \) (IF5) = –840 kJ mol–1
A. –190
B. –95
C. +6
D. +95
Which is a correct definition of lattice enthalpy?
A. It is the enthalpy change that occurs when an electron is removed from 1 mol of gaseous atoms.
B. It is the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of a compound is formed from its elements.
C. It is the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of solid crystal changes into a liquid.
D. It is the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of solid crystal is formed from its gaseous ions.
Which equation corresponds to the lattice enthalpy for silver iodide, AgI?
A. \({\text{AgI(s)}} \to {\text{Ag(s)}} + {\text{I(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{AgI(s)}} \to {\text{Ag(s)}} + \frac{1}{2}{{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{AgI(s)}} \to {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{I}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
D. \({\text{AgI(s)}} \to {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{I}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
Which reaction has the largest increase in entropy?
A. \({{\text{H}}_2}({\text{g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}({\text{g)}} \to {\text{2HCl(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{Al(OH}}{{\text{)}}_3}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{NaOH(aq)}} \to {\text{Al(OH)}}_4^ - {\text{(aq)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3}({\text{s)}} + 2{\text{HCl(aq)}} \to {\text{2NaCl(aq)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}({\text{g)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
D. \({\text{BaC}}{{\text{l}}_2}({\text{aq)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}({\text{aq)}} \to {\text{BaS}}{{\text{O}}_4}({\text{s)}} + 2{\text{NaCl(aq)}}\)
Which reaction has the greatest increase in entropy?
A. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S(g)}} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} + {\text{3S(s)}}\)
B. \({\text{CaO(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(s)}}\)
C. \({\text{Ca}}{{\text{C}}_2}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{Ca(OH}}{{\text{)}}_2}{\text{(s)}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({{\text{N}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2NO(g)}}\)
Which equation represents enthalpy of hydration?
A. Na(g) → Na+(aq) + e−
B. Na+(g) → Na+(aq)
C. NaCl(s) → Na+(g) + Cl−(g)
D. NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
Which ionic compound has the most endothermic lattice enthalpy?
A. NaCl
B. KCl
C. NaF
D. KF
Which statement is correct?
A. If ΔH < 0, reaction is always spontaneous.
B. If ΔH > 0, reaction is never spontaneous.
C. If ΔS < 0, reaction can be spontaneous if temperature is low enough.
D. If ΔS < 0, reaction can be spontaneous if temperature is high enough.
Which step(s) is/are endothermic in the Born-Haber cycle for the formation of LiCl?
A. \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{Cl(g)}}\) and \({\text{Li(s)}} \to {\text{Li(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{Cl(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\) and \({\text{Li(g)}} \to {\text{L}}{{\text{i}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - }\)
C. \({\text{L}}{{\text{i}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{LiCl(s)}}\)
D. \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{Cl(g)}}\) and \({\text{Cl(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
Which ion’s hydration energy is the most exothermic?
A. Li+
B. Na+
C. Br–
D. I–
Which value represents the lattice enthalpy, in kJ mol−1, of strontium chloride, SrCl2?
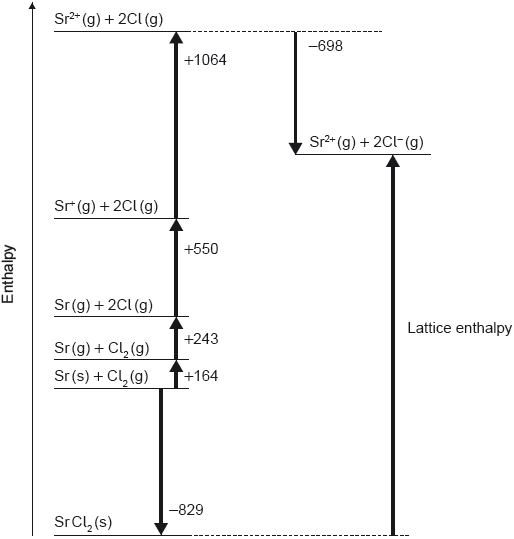
A. – (–829) + 164 + 243 + 550 + 1064 – (–698)
B. –829 + 164 + 243 + 550 + 1064 – 698
C. – (–829) + 164 + 243 + 550 + 1064 – 698
D. –829 + 164 + 243 + 550 + 1064 – (–698)
Which change will not increase the entropy of a system?
A. Increasing the temperature
B. Changing the state from liquid to gas
C. Mixing different types of particles
D. A reaction where four moles of gaseous reactants changes to two moles of gaseous products
Which reaction has the greatest increase in entropy?
A. \({{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_8}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{3C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}}\)
B. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2HCl(g)}}\)
C. \({{\text{N}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_6}{\text{(g)}}\)
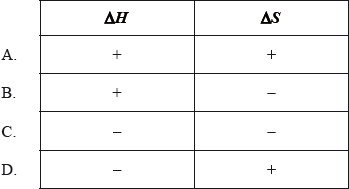
Which combination of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) signs will always result in a spontaneous reaction at all temperatures?
Which compound has the most positive lattice enthalpy of dissociation?
A. NaCl
B. NaBr
C. \({\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{MgB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which transition represents an enthalpy of hydration?
C. K+(s)→K+(aq)
D. K+(g)→K+(aq)
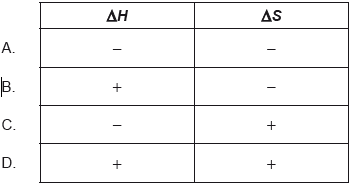
Which combination of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) values corresponds to a non-spontaneous reaction at all temperatures?
Which reactions/processes have a positive entropy change, \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\)?
I. \({\text{NaCl(s)}} \to {\text{NaCl(aq)}}\)
II. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{2HCl(aq)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2NaCl(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
III. \({\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{NaCl(aq)}} \to {\text{AgCl(s)}} + {\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which change leads to an increase in entropy?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(s)}}\)
B. \({\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_6}({\text{g)}} \to {\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_6}({\text{l)}}\)
C. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(s)}}\)
D. \({\text{NaCl(s)}} \to {\text{NaCl(aq)}}\)
Which ionic compound has the most endothermic lattice enthalpy?
A. Sodium chloride
B. Sodium oxide
C. Magnesium chloride
D. Magnesium oxide
Which factors will increase the entropy of this system?
\[{\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(s)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{CaO(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\]
I. Increasing the temperature without changing the volume of the container.
II. Decreasing the concentration of the gas without changing the volume of the container.
III. Increasing the pressure without changing the volume of the container.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which system has the most negative entropy change, ΔS, for the forward reaction?
A. N2(g) + 3H2(g) \( \rightleftharpoons \) 2NH3(g)
B. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
C. 2S2O32−(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I–(aq)
D. H2O(l) → H2O(g)
Which change must be negative when a reaction occurs spontaneously?
A. \(\Delta H\)
B. \(\Delta G\)
C. \(\Delta S\)
D. \(\Delta T\)
Which statements are correct for ionic compounds?
I. Lattice energy increases as ionic radii increase.
II. Within the same group, the melting point of salts tends to decrease as the radius of the cation increases.
III. Solubility in water depends on the relative magnitude of the lattice energy compared to the hydration energy.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which processes have a negative value for \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\)?
I. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(s)}}\)
II. \({\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(l)}} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} + {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
III. \({\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(g)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which processes are predicted to have a positive entropy change, \(\Delta S\)?
I. \({{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(s)}}\)
II. \({\text{4N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{4NO(g)}} + {\text{6}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}}\)
III. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH(l)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH(g)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which equation represents the lattice enthalpy of magnesium sulfide?
A. MgS (s) → Mg (g) + S (g)
B. MgS (s) → Mg+ (g) + S– (g)
C. MgS (s) → Mg2+ (g) + S2– (g)
D. MgS (s) → Mg (s) + S (s)
Which equation represents the second electron affinity of oxygen?
A. \(\frac{1}{2}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{e}}^ - } \to {{\text{O}}^{2 - }}{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{O(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{e}}^ - } \to {{\text{O}}^{2 - }}{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{2}}{{\text{O}}^{2 - }}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {{\text{O}}^{2 - }}{\text{(g)}}\)
Which combinations of values will result in a spontaneous reaction?
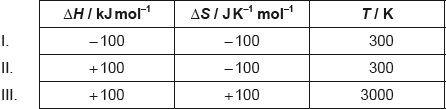
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What are the signs for the entropy changes associated with this reaction?
H2O(g) → H2O(l)
Which combination of ΔH θ and ΔS θ will result in a non-spontaneous reaction at all temperatures?
The combustion of glucose is exothermic and occurs according to the following equation:
C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) → 6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g)
Which is correct for this reaction?
The Born-Haber cycle for potassium oxide is shown below:
Which expression represents the lattice enthalpy in kJ mol–1?
A. –361 + 428 + 838 + 612
B. –(–361) + 428 + 838 + 612
C. –361 + 428 + 838 – 612
D. –(–361) + 428 + 838 – 612
What is the correct order for increasing lattice enthalpy?
A. \({\text{MgO}} < {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} < {\text{NaCl}} < {\text{CsCl}}\)
B. \({\text{CsCl}} < {\text{NaCl}} < {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} < {\text{MgO}}\)
C. \({\text{NaCl}} < {\text{CsCl}} < {\text{MgO}} < {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{NaCl}} < {\text{CsCl}} < {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} < {\text{MgO}}\)
Consider the following information:
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{CaO(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}} \\ {\Delta H = + 179{\text{ kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}} \\ {\Delta S = + 161.0{\text{ J}}\,{{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}} \end{array}\]
What happens to the spontaneity of this reaction as the temperature is increased?
A. The reaction becomes more spontaneous as the temperature is increased.
B. The reaction becomes less spontaneous as the temperature is increased.
C. The reaction remains spontaneous at all temperatures.
D. The reaction remains non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
Which equation represents the lattice enthalpy of calcium chloride?
A. \({\text{CaCl(s)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{a}}^{{\text{2}} + }}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{a}}^{{\text{2}} + }}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{a}}^{{\text{2}} + }}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
Which ionic compound has the greatest lattice enthalpy?
A. MgO
B. CaO
C. NaF
D. KF
A reaction has a standard enthalpy change, \(\Delta {H^\Theta }\), of \({\text{ +10.00 kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\) at 298 K. The standard entropy change, \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\), for the same reaction is \({\text{ +10.00 J}}\,{{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\). What is the value of \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) for the reaction in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\)?
A. +9.75
B. +7.02
C. –240
D. –2970
Which process would be expected to have a \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\) value which is negative?
A. \({\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{NaCl(s)}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2HI(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{O}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}} \to {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2HF(g)}}\)
The reaction between but-1-ene and water vapour produces butan-1-ol.
\[{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}} \to {{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_9}{\text{OH(l)}}\]
The standard entropy values \({\text{(}}{S^\Theta }{\text{)}}\) for but-1-ene, water vapour and butan-1-ol are 310, 189 and \({\text{228 J}}\,{{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\) respectively. What is the standard entropy change for this reaction in \({\text{J}}\,{{\text{K}}^{ - 1}}{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\)?
A. –271
B. +271
C. –107
D. +107
Which combination of enthalpy change and entropy change produces a non-spontaneous reaction at all temperatures?
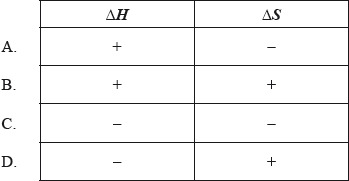
When hydrogen peroxide decomposes, the temperature of the reaction mixture increases.
\[{\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(aq)}} \to {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}}\]
What are the signs of \(\Delta H\), \(\Delta S\) and \(\Delta G\) for this reaction?
Which ionic compound has the largest value of lattice enthalpy?
A. MgS
B. MgO
C. CaBr2
D. NaF
Which reaction has the greatest increase in entropy?
A. \({\text{2C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH(l)}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
B. \({{\text{N}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{2HCl(aq)}} + {\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{HCl(g)}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{Cl(s)}}\)
Which species are arranged in order of increasing entropy?
A. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{(g) < C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH(l) < Hg(l) < Na(s)}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH(l) < }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{(g) < Hg(l) < Na(s)}}\)
C. \({\text{Na(s) < Hg(l) < C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH(l) < }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{Na(s) < Hg(l) < }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{(g) < C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH(l)}}\)
Which equation represents the electron affinity of chlorine?
A. \({\text{Cl(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{Cl(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{Cl(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}({\text{g)}} + 2{{\text{e}}^ - } \to 2{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }({\text{g)}}\)
D. \({\text{Cl(g)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ - }\)
What is the correct definition of lattice enthalpy?
A. Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is separated into gaseous ions.
B. Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is separated into its ions in their standard state.
C. Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from gaseous elements.
D. Enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from the elements in their standard states.
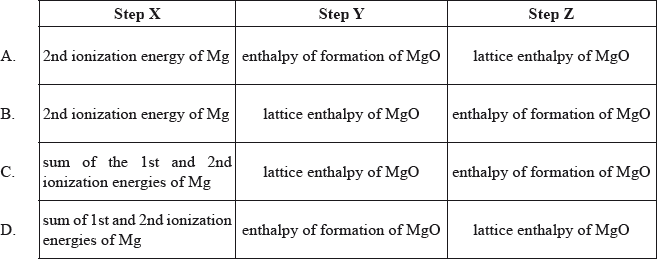
The Born-Haber cycle for the formation of magnesium oxide is shown below.

What is a correct description of the steps X, Y and Z in this cycle?
Which combination of ions will give the greatest absolute lattice enthalpy?
A. A small positive ion with a high charge and a small negative ion with a high charge
B. A small positive ion with a low charge and a small negative ion with a low charge
C. A large positive ion with a high charge and a large negative ion with a high charge
D. A large positive ion with a low charge and a small negative ion with a low charge
The rate expression for the reaction between iodine and propanone with an acid catalyst is found to be:
\[{\text{rate}} = k{{\text{[}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{]}}^1}{{\text{[}}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{]}}^0}{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{]}}^1}\]
What is the overall order of the reaction?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
\(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) calculations predict that a reaction is always spontaneous for which of the following combinations of \(\Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\)?
A. \( + \Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \( + \Delta {S^\Theta }\)
B. \( + \Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \( - \Delta {S^\Theta }\)
C. \( - \Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \( - \Delta {S^\Theta }\)
D. \( - \Delta {H^\Theta }\) and \( + \Delta {S^\Theta }\)
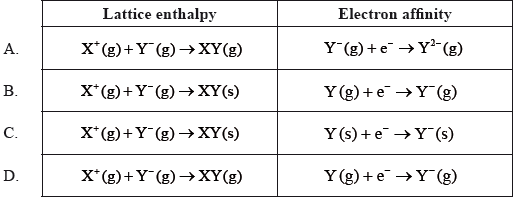
Which row of the table correctly represents the equations for the lattice enthalpy of substance XY and the electron affinity of atom Y?
What is the standard entropy change, \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\), for the following reaction?
\[{\text{2CO(g)}} + {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\]
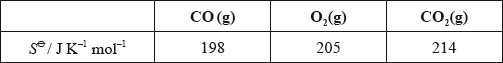
A. –189
B. –173
C. +173
D. +189
What is the enthalpy of solution of MgF2(s) in kJ mol−1?
Lattice enthalpy of MgF2(s) = 2926 kJ mol−1
Hydration enthalpy of Mg2+(g) = −1963 kJ mol−1
Hydration enthalpy of F−(g) = −504 kJ mol−1
A. 2926 − 1963 + 2(−504)
B. 2926 − 1963 − 504
C. −2926 − (−1963) − (−504)
D. −2926 − (−1963) − 2(−504)
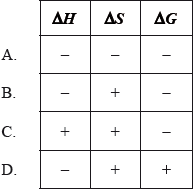
When solid potassium chlorate, \({\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\), dissolves in distilled water the temperature of the solution decreases. What are the signs of \(\Delta {H^\Theta }\), \(\Delta {S^\Theta }\) and \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) for this spontaneous process?
Which represents the enthalpy change of hydration of the chloride ion?
During which process is there a decrease in the entropy of the system?
A. \({\text{Ag(s)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{NO}}_3^ - {\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{Ba(OH}}{{\text{)}}_2}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{BaO(s)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_3}({\text{g)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}({\text{g)}} \to {\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_5}({\text{g)}}\)
D. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(s)}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)