
SL Paper 1
A particle of mass m is a distance R from the surface of Earth of mass M. The force acting on the particle is F. Which of the following is the gravitational field strength at R?
A. \(\frac{{Gm}}{{{R^2}}}\)
B. \(\frac{{GmM}}{{{R^2}}}\)
C. \(\frac{F}{m}\)
D. \(\frac{F}{M}\)
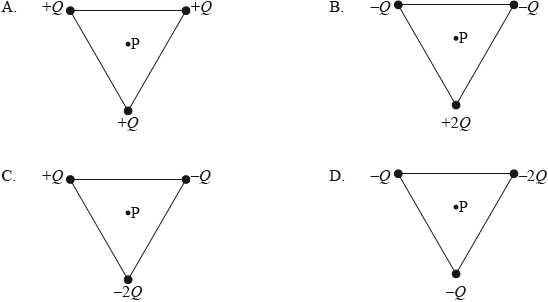
Which arrangement of three point charges at the corner of an equilateral triangle will result in a zero electric field strength at the centre of the triangle, point P?
A positive point charge P and a negative point charge Q of equal magnitude are held at fixed positions. Y is midway between P and Q.
Which of the following gives the direction of the electric field due to the charges at X, Y and Z?
A point charge of magnitude \(2.0{\text{ }}\mu {\text{ C}}\) is moved between two points X and Y. Point X is at a potential of \( + 6.0{\text{ V}}\) and point Y is at a potential of \( + 9.0{\text{ V}}\). The gain in potential energy of the point charge is
A. \(0.20{\text{ }}\mu {\text{J.}}\)
B. \(1.5{\text{ }}\mu {\text{J.}}\)
B. \(6.0{\text{ }}\mu {\text{J.}}\)
B. \(30{\text{ }}\mu {\text{J.}}\)
The gravitational field strength at a point X in a gravitational field is defined as the force
A. per unit mass on a mass placed at X.
B. on a mass placed at X.
C. per unit mass on a small point mass placed at X.
D. on a small point mass placed at X.
The electric field strength between two oppositely charged parallel plates
A. has the same value everywhere between the two plates.
B. decreases from the positive plate to the negative plate.
C. is larger at the edges than in the center.
D. is smaller at the edges than in the center.
A particle has charge and mass. Which types of field cause a force to be exerted on the particle when it is moving in the direction of the field?
A. Electric, gravitational and magnetic fields
B. Electric and magnetic fields only
C. Gravitational and magnetic fields only
D. Electric and gravitational fields only
An electron of mass me and charge e accelerates between two plates separated by a distance s in a vacuum. The potential difference between the plates is V.
What is the acceleration of the electron?
A. \(\frac{{{m_e}ev}}{s}\)
B. \(\frac{{{m_e}v}}{{es}}\)
C. \(\frac{{eV}}{{{m_e}s}}\)
D. \(\frac{V}{{{m_e}es}}\)
Three positive point charges +Q are fixed in position at the vertices of an isosceles triangle. P is the mid point between two of the charges.
Which arrow correctly identifies the direction of the electric field at point P?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
Four point charges of equal magnitude W, X, Y and Z are each fixed to a corner of a square.
W is a positive charge and X is a negative charge. The arrow shows the direction of the resultant electric field at the centre of the square. What are the correct signs of charge Y and of charge Z?
What field pattern can be produced by two point charges?
An electron is held close to the surface of a negatively charged sphere and then released. Which describes the velocity and the acceleration of the electron after it is released?
Which diagram shows the electric field pattern surrounding two equal positive point charges?