
HL Paper 1
When a nucleus undergoes radioactive \({\beta ^ + }\) decay, the change in the number of particles in the universe is
A. 0.
B. 1.
C. 2.
D. 3.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A number of candidates neglected the neutrino accompanying \({\beta ^ + }\) decay. Some candidates may have over-complicated the question by considering subsequent reactions (such as pair annihilation), following the \({\beta ^ + }\) decay.
The diagram shows four possible electron energy levels in the hydrogen atom.

The number of different frequencies in the emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen that arise from electron transitions between these levels is
A. 0.
B. 2.
C. 4.
D. 6.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
All the energy levels in a simple model of an atom are shown.
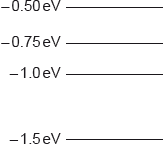
The atom is excited so that an electron is promoted to the \( - {\text{0.50 eV}}\) energy level. How many different frequencies will be observed in the emission spectrum?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
More than half of the candidates chose A, suggesting that they did not understand that the emission spectrum contained evidence of all possible electron transitions. Normally with four energy levels this would involve 6 transitions, but in this case some of the transitions were identical – a fact that escaped most candidates even the most able.
A nucleus of the isotope potassium-40 decays to a nucleus of the isotope argon-40. The reaction equation for this decay may be written as
\[_{{\text{19}}}^{{\text{40}}}{\text{K}} \to _{\;Z}^{{\text{40}}}{\text{Ar}} + {\text{X}} + \nu \]
Which of the following correctly identifies the proton number of argon-40 and the particle X?
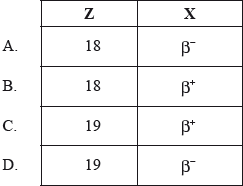
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which of the following lists the particles emitted during radioactive decay in order of increasing ionizing power?
A. γ, β, α
B. β, α, γ
C. α, γ, β
D. α, β, γ
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
What is correct about the Higgs Boson?
A. It was predicted before it was observed.
B. It was difficult to detect because it is charged.
C. It is not part of the Standard Model.
D. It was difficult to detect because it has no mass.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
\(_{\;{\text{6}}}^{{\text{11}}}{\text{C}}\) undergoes \({\beta ^ + }\) decay. The products of this decay are the \({\beta ^ + }\) particle, X and Y. What are X and Y?
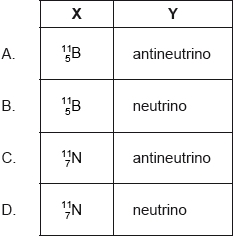
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which of the following leads to a paradigm shift?
A. Multi-loop circuits
B. Standing waves
C. Total internal reflection
D. Atomic spectra
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Which of the following would decrease the initial activity of a sample of plutonium?
A. Placing the sample in a lead container
B. Placing the sample in a dark room
C. Decreasing the mass of the sample
D. Decreasing the temperature of the sample
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Which of the following gives evidence to support the existence of atomic energy levels?
A. Alpha particle scattering
B. Absorption spectra
C. The existence of isotopes
D. Beta decay
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which of the following is a correct list of particles upon which the strong nuclear force may act?
A. protons and neutrons
B. protons and electrons
C. neutrons and electrons
D. protons, neutrons and electrons
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
This was outside the requirements of the syllabus, as many teachers observed, and the question was discounted.
All isotopes of uranium must have the same
A. chemical properties.
B. mass.
C. half-life.
D. decay constant.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Identify the conservation law violated in the proposed reaction.
p+ + p+ → p+ + n0 + μ+
A. Strangeness
B. Lepton number
C. Charge
D. Baryon number
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Patterns in graphs help scientists make predictions. What can be deduced from a graph of neutron number versus proton number for all stable nuclides?
A. The short-range nature of the strong nuclear force
B. The increase of the binding energy per nucleon with proton number
C. The existence of quarks and leptons
D. The existence of alpha decay
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A pure sample of nuclide A and a pure sample of nuclide B have the same activity at time t = 0. Nuclide A has a half-life of T, nuclide B has a half-life of 2T.
What is \(\frac{{{\text{activity of A}}}}{{{\text{activity of B}}}}\) when t = 4T?
A. 4
B. 2
C. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
D. \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Protons and neutrons are held together in the nucleus by the
A. electrostatic force.
B. gravitational force.
C. weak nuclear force.
D. strong nuclear force.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A radioactive isotope has an initial activity \({A_0}\) and a half-life of 1 day. The graph shows how the activity \(A\) varies with time.
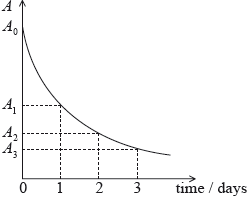
The ratio \(\frac{{{A_0}}}{{{A_2}}}\) is equal to which of the following?
A. \(\frac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_3}}}\)
B. \(\frac{{{A_0}}}{{{A_3}}}\)
C. \(\frac{{{A_0}}}{2}\)
D. \(\frac{{{A_3}}}{3}\)
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The diagram was not drawn strictly to scale, but this did not confuse the majority of the students.
A pure sample of a known element has a very long half-life. What measurement(s), together with the initial activity of the sample, must be made in order to measure the half-life of the element?
A. The activity of the sample after a given period of time.
B. The mass of the sample after a given period of time.
C. The activity and the mass of the sample after a given period of time.
D. The mass of the sample.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Well over 50% of the candidates chose A and seemed unaware that if we say that an element has a ‘very long half-life’ then we are, in all likelihood talking about timespans that far exceed the length of a human life. Hence it is not possible to come back later and hope to see a noticeable diminution of the activity of the sample. The syllabus guide clearly invites teachers to consider how to measure very long half-lives and this can only be done without reference to time. Hence it must be D. Note that the stem does specify that the sample is pure.
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is equal to the wavelength of a photon that has energy E. What is the momentum of the electron?
A. \(\frac{E}{c}\)
B. \(\frac{E}{hc}\)
C. \(\frac{hc}{E}\)
D. \(\frac{{{m_e}{c^2}}}{{hE}}\)
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A is the only answer with the correct units. So the rest can be discounted.
A unit in which mass defect can be measured is
A. MeV.
B. MeV c–1.
C. MeV c–2.
D. MeV per nucleon.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
It must be known that a unit for mass that is convenient in atomic and nuclear physics is
MeVc–2.
The nuclear reaction represented by
\[{}_0^1{\rm{n + }}{}_{92}^{235}{\rm{U}} \to {}_{56}^{141}{\rm{Ba + }}{}_{36}^{92}{\rm{Kr + 3}}{}_0^1{\rm{n}}\]
is an example of
A. nuclear fusion.
B. nuclear fission.
C. artificial transmutation.
D. radioactive decay.
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A proton decays to a neutron. The other products of the decay are a
A. positron and neutrino.
B. positron and antineutrino.
C. electron and neutrino.
D. electron and antineutrino.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Evidence for the existence of isotopes can come from analysis of
A. the closest approach distance from charged particle scattering experiments.
B. the discrete energies of alpha particles from a given nuclide.
C. the range of energies of beta particles from a given nuclide.
D. the paths taken by ions in a Bainbridge mass spectrometer.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 20s. What fraction of the original sample will have decayed in one minute?
A. \(\frac{1}{8}\)
B. \(\frac{1}{4}\)
C. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
D. \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Far too many candidates selected response A, indicating that they had not carefully read the question.
The energies of alpha particles and of gamma-rays emitted in radioactive decay are discrete. This observation is evidence for
A. atomic energy levels.
B. nuclear energy levels.
C. nuclei having more neutrons than protons.
D. the existence of isotopes.
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A radioactive nuclide decays to a stable daughter nuclide. Initially the sample consists entirely of atoms of the radioactive nuclide. What fraction of the sample consists of the daughter nuclide after four half-lives?
A. \(\frac{{15}}{{16}}\)
B. \(\frac{{1}}{{16}}\)
C. \(\frac{{1}}{{8}}\)
D. \(\frac{{7}}{{8}}\)
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A simple diagram showing the depletion of the sample with increasing half-lives is needed. Those who chose B were perhaps jumping to conclusions without such a visual image.
The lowest four energy levels of a particular atom are represented in the energy level diagram below.
Planck’s constant is h. What is the highest frequency in the atom’s emission spectrum that is associated with these levels?
A. \(\frac{{{E_3}}}{h}\)
B. \(\frac{{{E_0}}}{h}\)
C. \(\frac{{{E_3} - {E_0}}}{h}\)
D. \(\frac{{{E_3} - {E_2}}}{h}\)
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation with time t of the activity A of a radioactive sample. The energy released in each decay is E. The shaded area is equal to S.
What does the quantity S \( \times \) E represent?
A. Average energy produced in 2 s.
B. Average power produced in 2 s.
C. Total energy produced in 2 s.
D. Maximum power produced in 2 s.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The diagram shows three electron energy levels of an atom. Which transition results in the emission of a photon of the longest wavelength?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
When compared with beta particles and gamma-ray photons, alpha particles have the greatest
A. mass.
B. penetrating power.
C. range in air.
D. speed.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
An alpha particle is directed head-on towards a nucleus of an isotope of iron. A second alpha particle, with the same energy as the first, is directed head-on towards a different isotope of iron.
Which of the following is a comparison of the distances of closest approach of the two alpha particles and the forces experienced by the alpha particles at the point of closest approach?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
There was much discussion of this question on the G2’s. Candidates are expected to choose the best answer and to discount factors that are negligible. The evidence would suggest that many candidates were randomly guessing the answer.
If the difference in the situations is that two isotopes of iron are used, then we can assume the charge is the same and that the distance and force remain unchanged. The slight difference in mass will not affect this.
In the nuclear reaction X + Y → Z + W, involving nuclides X, Y, Z and W, energy is released. Which is correct about the masses (M) and the binding energies (BE) of the nuclides?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
What is the charge on an electron antineutrino and during what process is an electron antineutrino produced?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The arrows below indicate transitions involving three energy levels of an atom. The wavelength of the photon emitted in each transition is indicated.
Which of the following relationships between the wavelengths is correct?
A. \({\lambda _1} = {\lambda _2} + {\lambda _3}\)
B. \({\lambda _1} = {\lambda _3} - {\lambda _2}\)
C. \(\frac{1}{{{\lambda _1}}} = \frac{1}{{{\lambda _2}}} + \frac{1}{{{\lambda _3}}}\)
D. \(\frac{1}{{{\lambda _1}}} = \frac{1}{{{\lambda _2}}} - \frac{1}{{{\lambda _3}}}\)
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Candidates do not need to work through the algebra to generate the correct answer. They should know that the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength (so A and B are incorrect) – and that it is the energies that need to add up. So D must also be incorrect.
A fission reaction for uranium is
\[{}_{92}^{235}{\rm{U}} + {\rm{n}} \to {}_{56}^{141}{\rm{Ba}} + {}_Z^A{\rm{Kr}} + 3{\rm{n}}\]
where n is the neutron. Which of the following gives the value of the nucleon number A and proton number Z for the krypton (Kr)?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The diagram below shows some of the energy levels available to an electron in a caesium atom.
Photons of energy 0.9eV pass through a sample of low pressure caesium vapour. Which of the following gives the energy transition of the electron when a photon is absorbed?
-
From -3.9eV to 0
-
From -2.5eV to -1.6eV
-
From -1.6eV to -2.5eV
-
From 0 to -3.9eV
Markscheme
Examiners report
The nuclei in a sample of a radioactive isotope decay by emitting α and γ particles. Which of the following is correct for the energies of the α particles and for the energies of the γ particles?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
C was a popular, yet incorrect, response. Candidates need to know that the nucleus has its own discrete energy levels, which are revealed in the emission of a Ɣ-particle.
The graph shows the relationship between binding energy per nucleon and nucleon number. In which region are nuclei most stable?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The diagram shows the three lowest energy levels of an atom.
Which diagram shows the emission line spectrum associated with electron transitions from energy level X?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A number of candidates opted for B, seemingly forgetting the reciprocal relationship between energy and the wavelength of the photos emitted.
Some of the energy levels for a hydrogen atom are shown in the diagram.
The table shows four photons with their corresponding energies.
Each photon is incident on a hydrogen atom in its ground state. Which photons could be absorbed by the atom?
A. W only
B. X and Y only
C. Y and Z only
D. X, Y and Z only
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The diagram shows four energy levels W, X, Y and Z of an atom.
Which electron transition will produce a photon of the longest wavelength and which transition will produce a photon with the highest frequency?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
In a fission reaction, the total mass and the total binding energy before the reaction are Mi and Ei respectively, where the binding energy is defined as a positive quantity. After the reaction the total mass is Mf and the total binding energy is Ef . Which of the following correctly compares the total masses and the total binding energies?
Markscheme
Examiners report
The diagram shows three energy levels of the hydrogen atom and some of the associated electron transitions between the levels.
Which labelled electron transition gives rise to the photon with the greatest wavelength and which gives rise to the photon with the smallest wavelength?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The structure of the atom was investigated by firing alpha particles from a source at a thin foil of gold. The basic set-up of the apparatus is shown.
Which graph shows the variation in the number of scattered alpha particles with scattering angle \(\theta \)?
Markscheme
C