Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 10.1 Meiosis flashcards
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 10.1 Meiosis
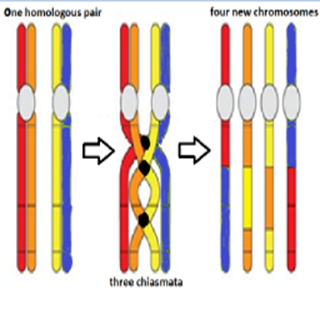
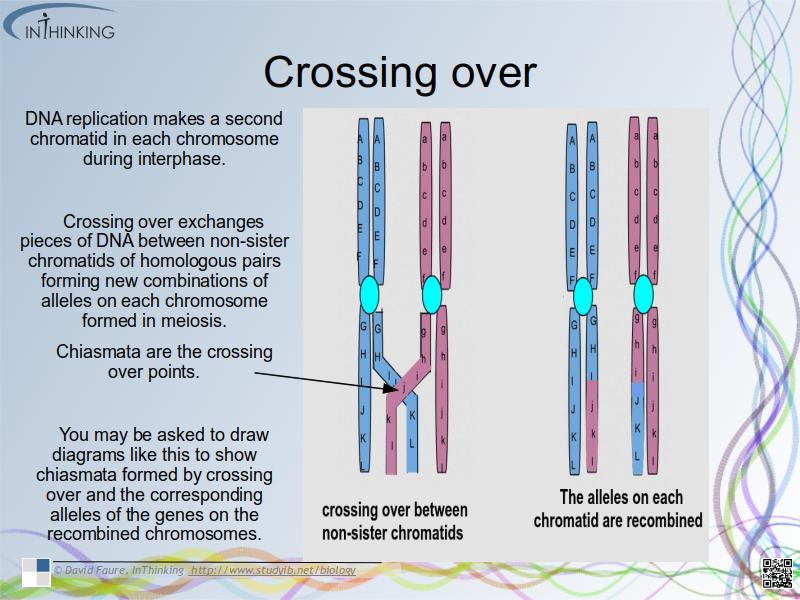
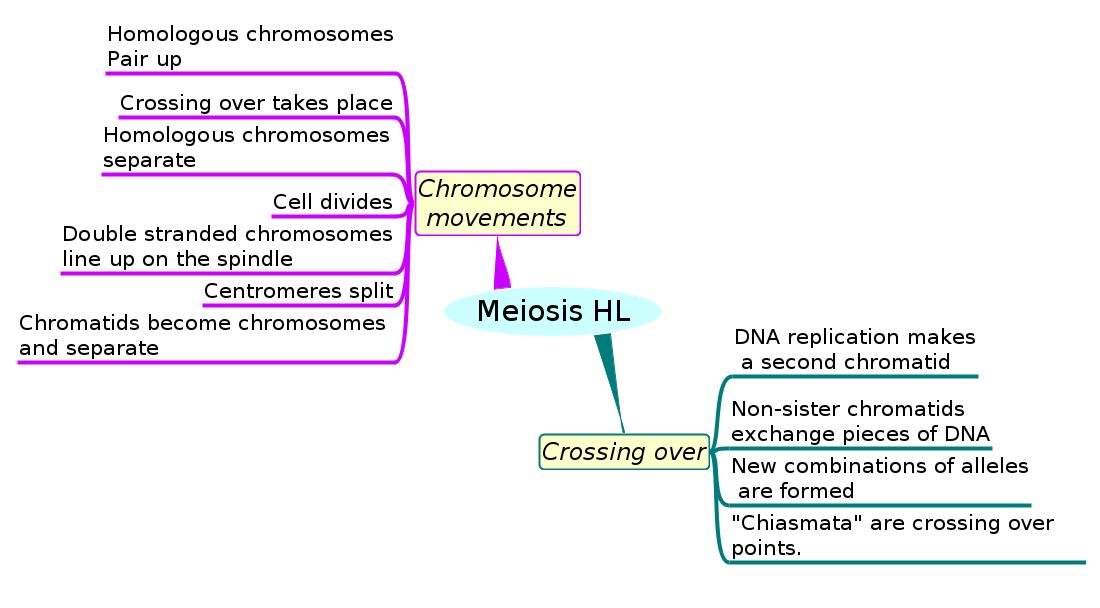
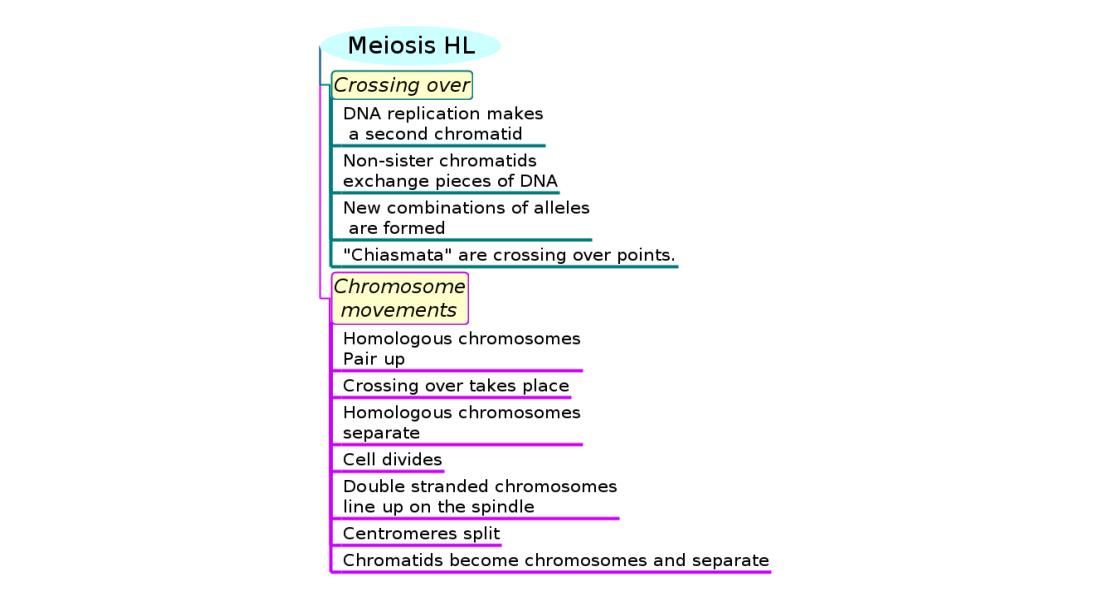
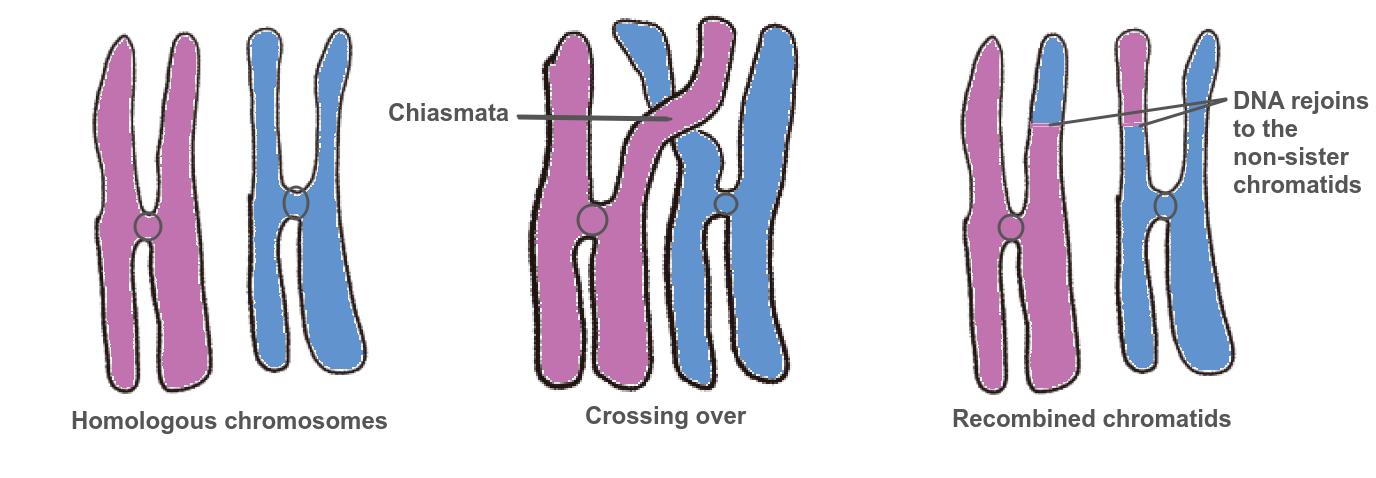
Crossing over
- DNA replication makes a second chromatid in each chromosome in interphase before meiosis.
- Crossing over exchanges pieces of DNA between non-sister homologous chromatids and forms new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes formed in meiosis.
- Chiasmata are the crossing over points.
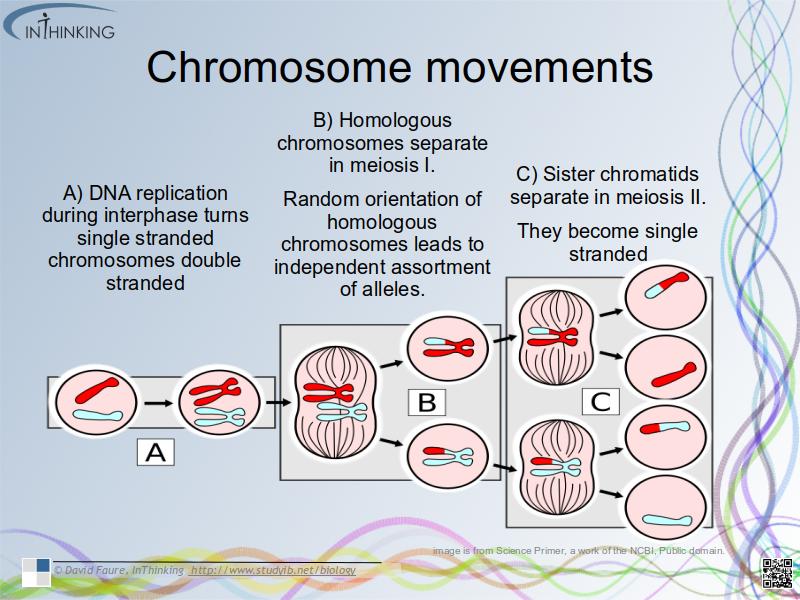
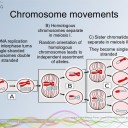
Chromosomes movements
- Details of chromosome movements in meiosis.
- Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I.
- Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II.
- Random orientation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I leads to independent assortment of alleles.
Student skills and applications
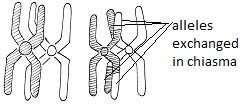
- Drawing diagrams to show chiasmata formed by crossing over.
- show sister chromatids still closely aligned, except at the point where crossing over occurred and a chiasma was formed.
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 10.1.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about meiosis
Explaining the movement of chromosomes is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below, on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Describe crossing over and the formation of a chiasma. Credit will be given to labelled diagrams. [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
.
.
.
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Independent assortment during meiosis creates genetic variation.
Drag an drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to outline how independent assortment occurs.
Prophase 1 equator second centromere randomly Prophase II sister centre separated gamete homologous
In of meiosis, chromosomes pair and become attached by their . The pairs of homologous chromosomes then associate into a bivalent of chromosomes.
In Metaphase 1 of meiosis, the bivalents line up on the spindle at the . Each tertrad orientates and independently of any other set of bivalents.
In Anaphase 1, the bivalents are , any pair can be drawn to either pole independently. The pairs of chromatids later separate during the division of meiosis giving different combinations of chromatids in the .
Homologous chromosomes have identical alleles, inherited from on of the parents. Sister chromosomes have identical genes but may have different alleles and are inherited from the other parent.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this meiosis card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Meiosis 10.1 HL have you understood?









 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn