- Summary list for 11.1 Antibody production & vaccination
- Mindmaps
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 11.1 Antibodies quiz 1/1
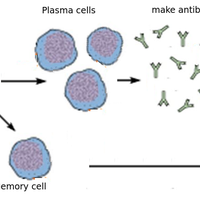
This topic covers the role of antigens in challenging the immune system leading to antibody production. There are many details required including knowledge of B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, memory cells and plasma cells. Vaccination as a method of promoting antibody production leading to immunity is an important concept in this topic as is the production of mono-clonal antibodies.
Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 11.1 Antibodies and vaccination flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary
Summary list for 11.1 Antibody production & vaccination
Cells & pathogens
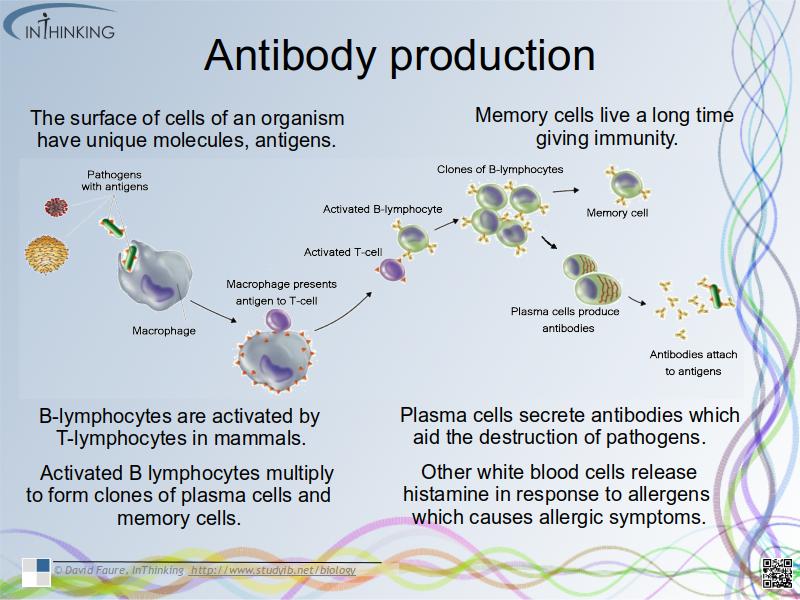
- The surface of cells of an organism has unique molecules.
- Pathogens can be species-specific or can cross species barriers.
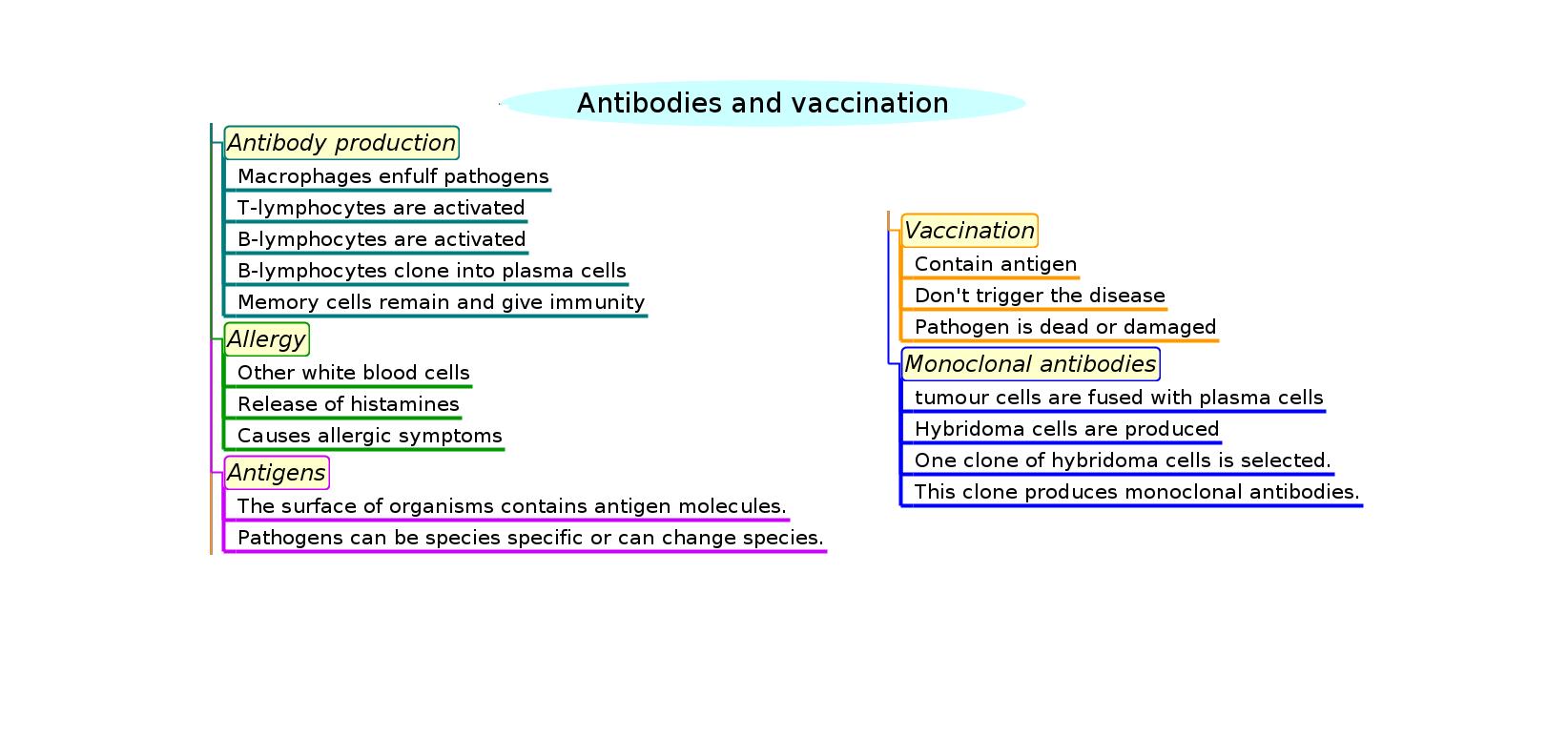
Antibody production involves the following:
- B lymphocytes are activated by T lymphocytes in mammals.
- Activated B lymphocytes multiply to form clones of plasma cells and memory cells (giving immunity).
- Plasma cells secrete antibodies which aid the destruction of pathogens.
- Other white blood cells release histamine in response to allergens which causes allergic symptoms.
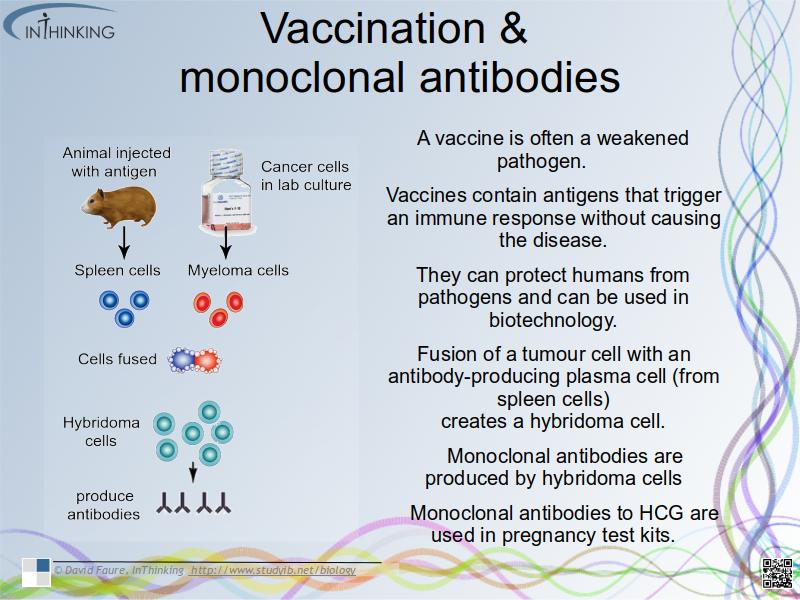
Vaccination and monoclonal antibodies
- Vaccines contain antigens that trigger an immune response without causing the disease.
- Fusion of a tumour cell with an antibody-producing plasma cell creates a hybridoma cell.
- Monoclonal antibodies are produced by hybridoma cells.
- Monoclonal antibodies to HCG are used in pregnancy test kits.
Skills & applications
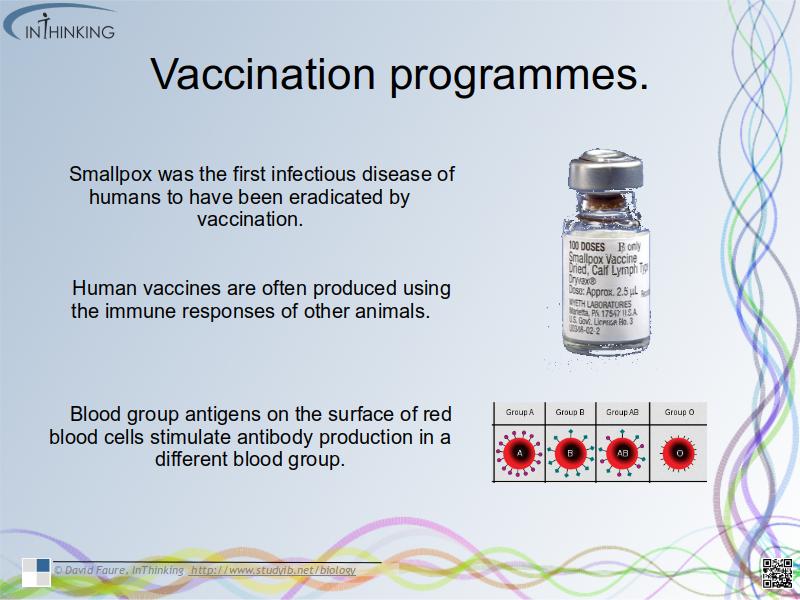
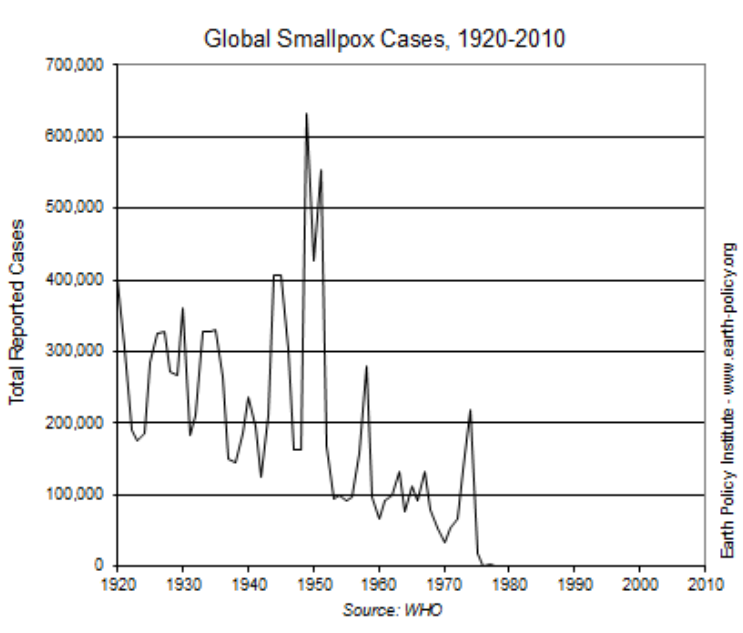
- Smallpox was the first infectious disease of humans to have been eradicated by vaccination.
- Human vaccines are often produced using the immune responses of other animals
- Blood group antigens on the surface of red blood cells stimulate antibody production in a different blood group.
- Skills to analyse epidemiological data related to vaccination programmes.
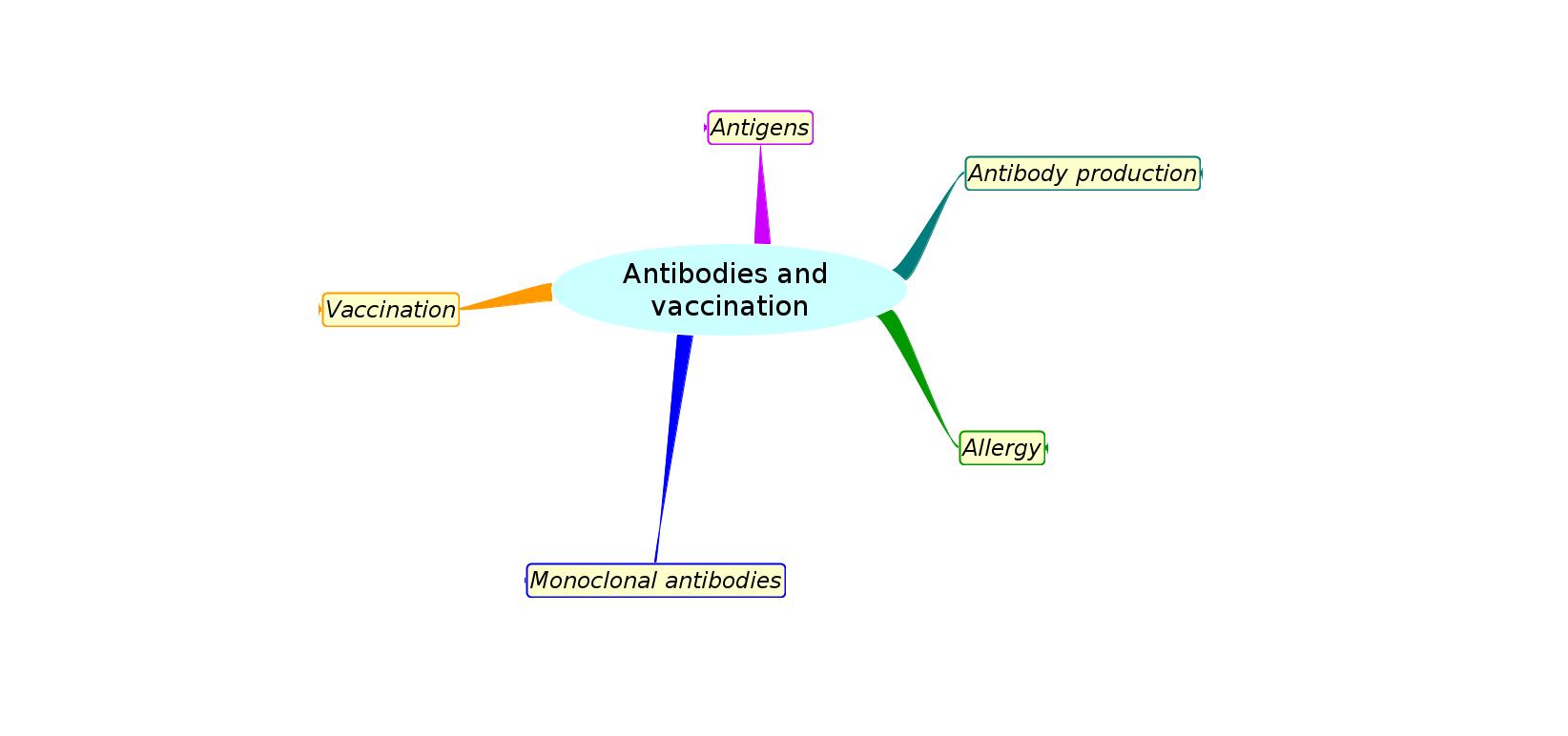
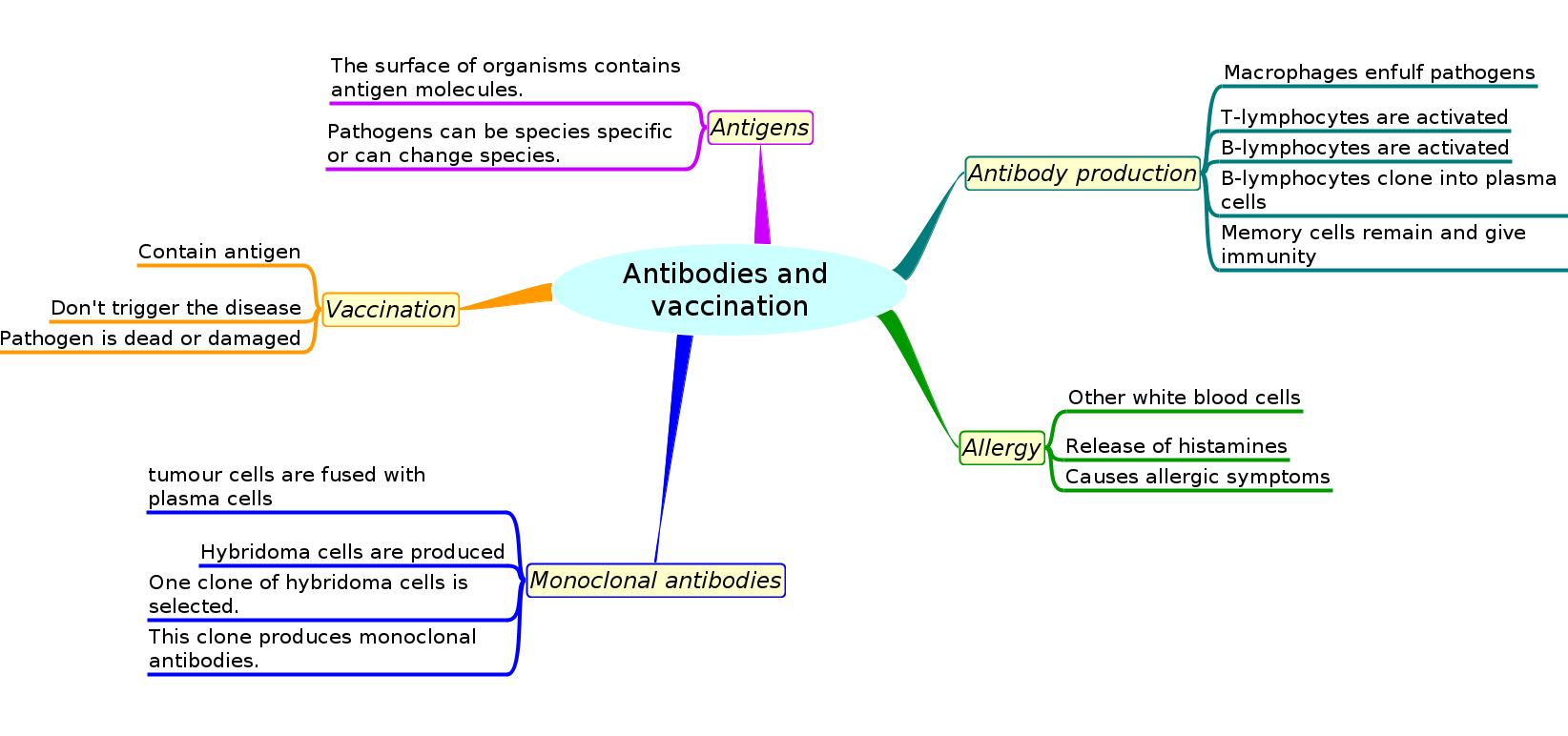
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 11.1 about antibodies and vaccination.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Antibodies: Explaining the processes which lead to immunity following a vaccination is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Explain how exposure to antigens leads to the production of antibodies by the immune system. [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
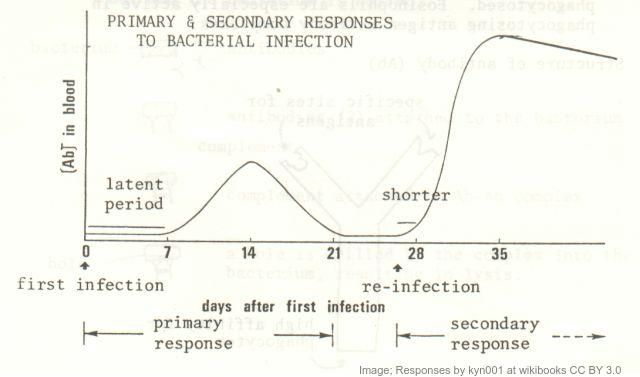
The secondary immune response.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe the secondary immnune reponse.
respond vaccination quickly immunity antigen booster B cells previously blood
A secondary immune response occurs when a person has been exposed to a particular pathogen or has received a .
In the primary immune response to the , memory cells are produced from and these persist in the once the disease is overcome.
These memory cells are already primed to to the specific antigen if it is encountered a second time. They divide to rapidly produce antibodies giving to the disease.
A vaccination has a similar response, enhancing immunity.
The secondary reponse gives immunity as the memory cells immediately recognise the pathogen and respond with great rapidity. The secondary reponse generally produces a greater quantity of antibodies and, subsequently, memory cells to enhance immunity.
How much of Antibody production & vaccination 11.1 HL have you understood?





 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn