These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 6.2 Blood system
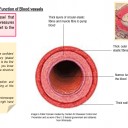
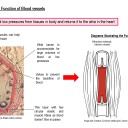
- Arteries carry blood at high pressure from the ventricles of the heart to the tissues of the body.
- Arteries have muscle cells and elastic fibres in their walls.which maintain blood pressure between ventricle contractions.
- Capillaries carry blood through tissues and have permeable walls to allow exchange between tissue cells and the blood.
- Veins carry blood at low pressure from the tissues to the atria of the heart.
- Valves in veins and the heart prevent back-flow.
- There is a separate circulation for the lungs.
- The sinoatrial node (SA node) initiates heart beat
- The SA node is made of specialised muscle cells in the right atrium which act as a pacemaker.
- The sinoatrial node sends out an electrical signal which is propagated through the walls of the atria and ventricles.
- The heart rate is controlled by impulses brought to the heart through two nerves from the medulla of the brain.
- Epinephrine (adrenalin) increases the heart rate.
Skills
- Outline your knowledge of William Harvey’s discovery of the circulation of the blood with the heart acting as the pump.
- Interpret pressure changes in the left atrium, left ventricle and aorta during the cardiac cycle.
- Link causes and consequences of occlusion of the coronary arteries.
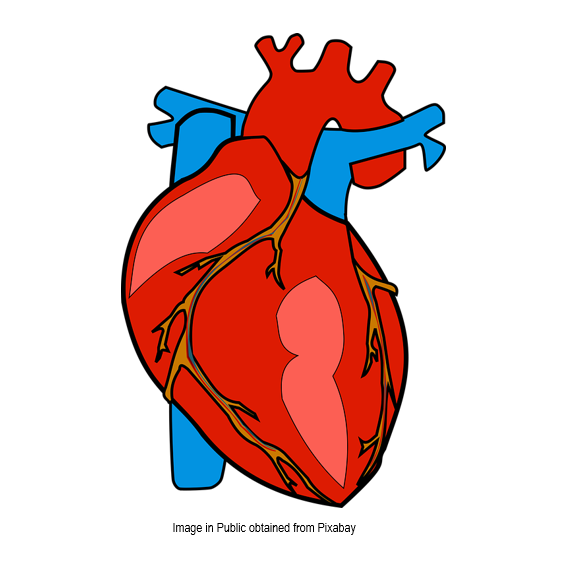
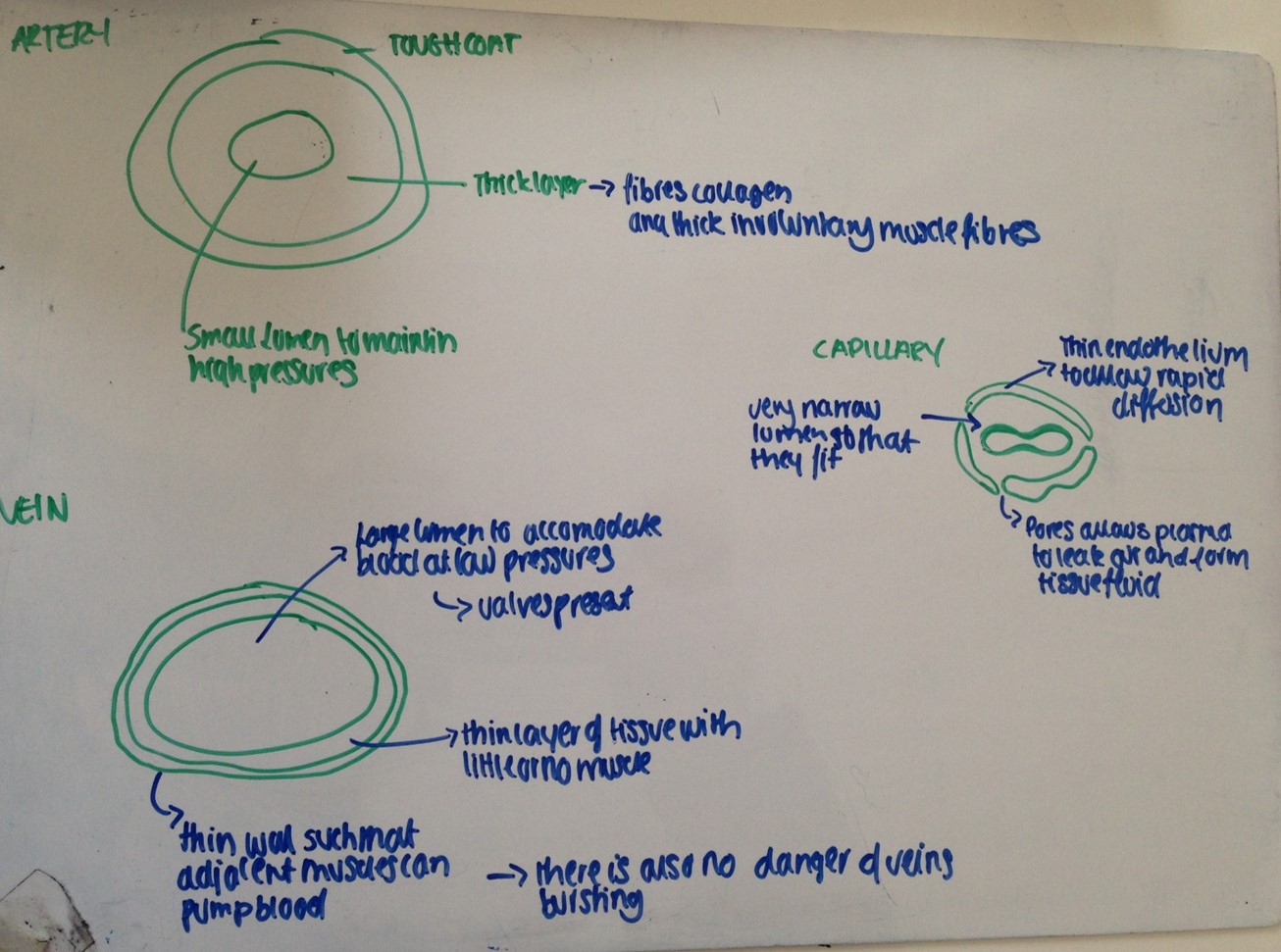
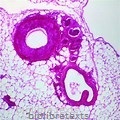
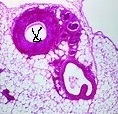
- Identify arteries, capillaries or veins from the structure of their walls.
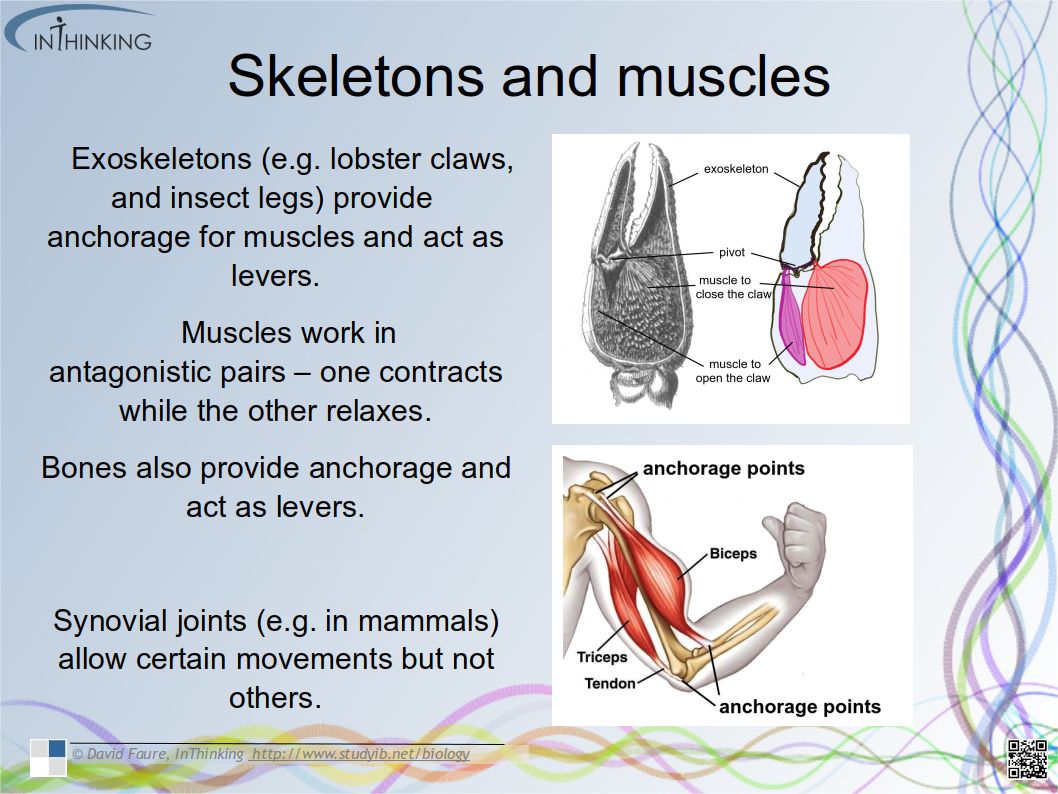
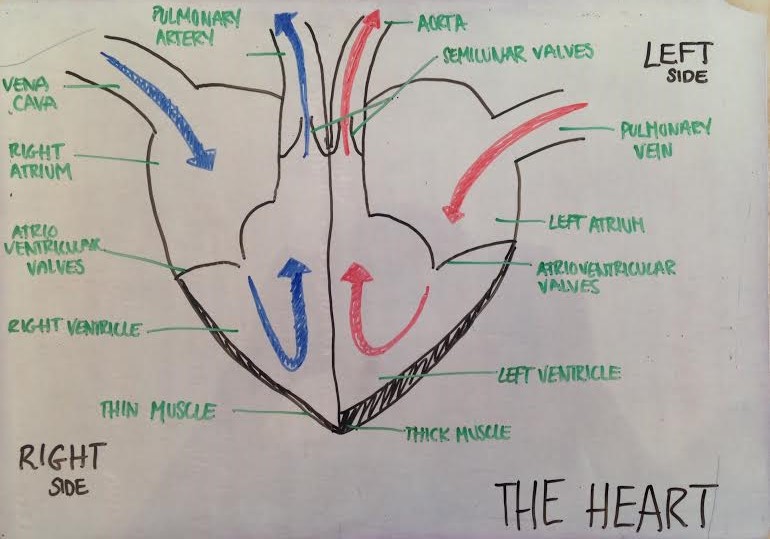
- Recognise the four chambers and valves of the heart and the blood vessels connected to it in a dissected heart or in diagrams of heart structure.
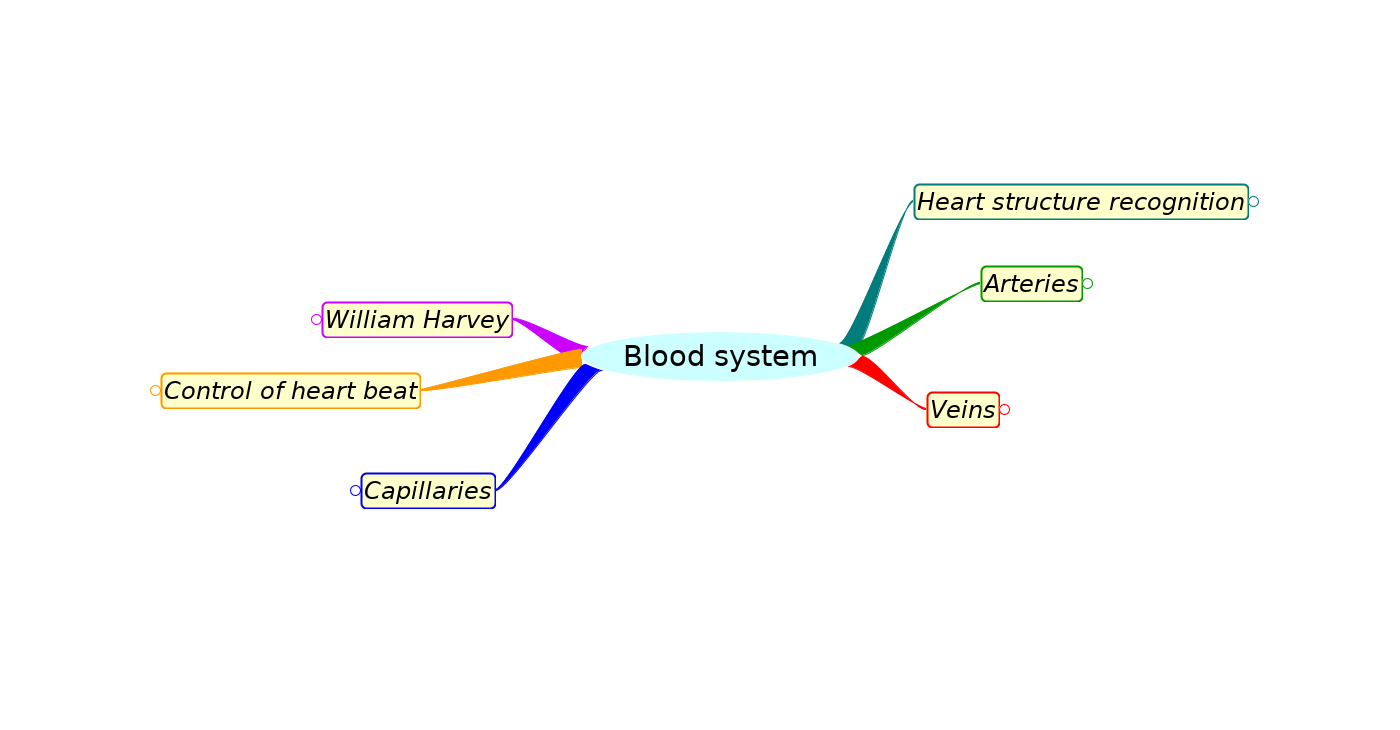
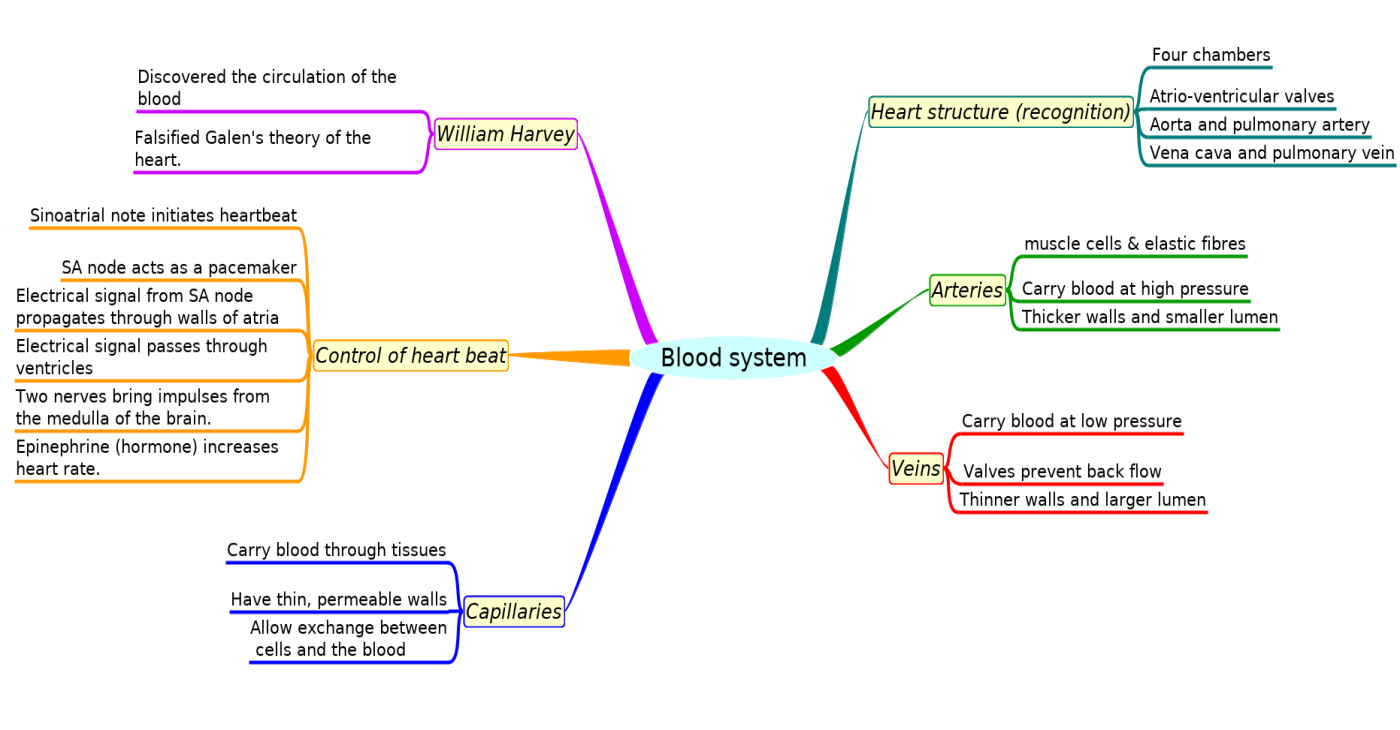
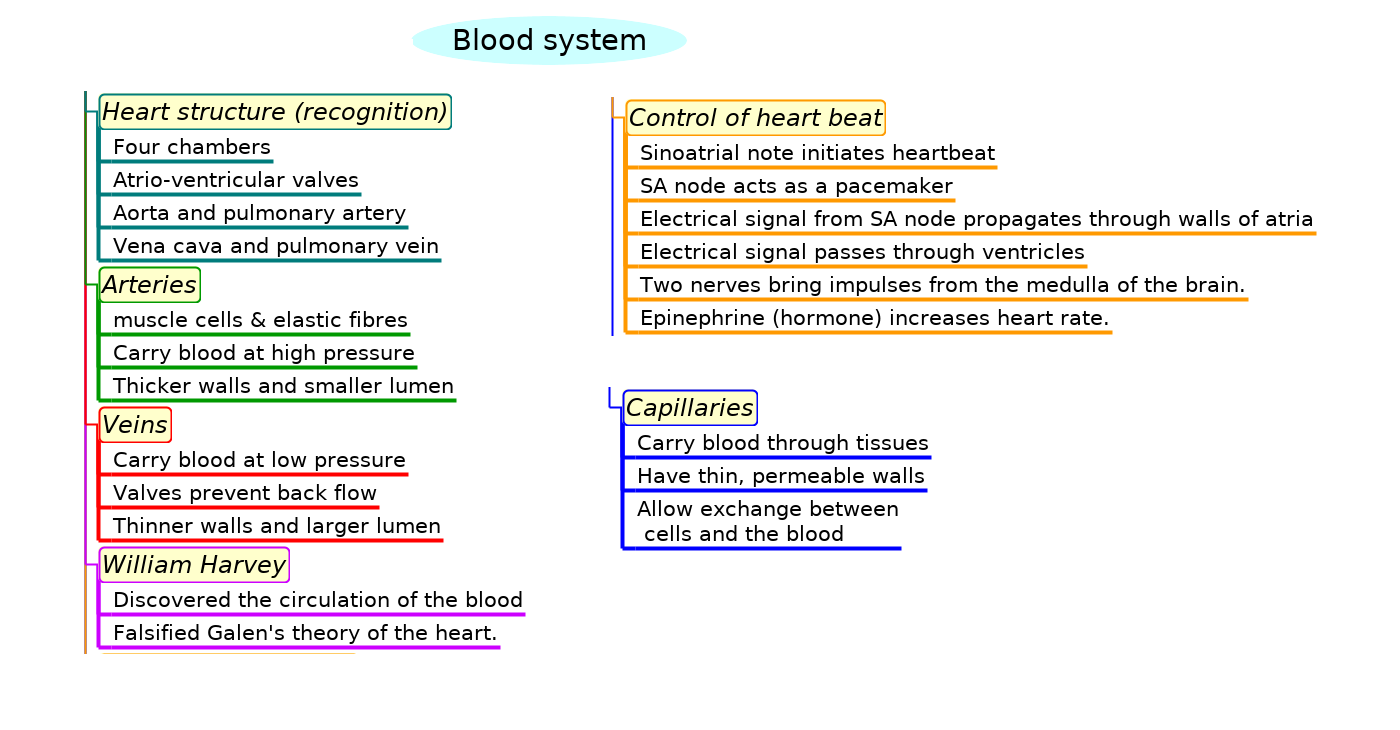
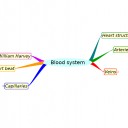
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 6.2.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Revision Exercise - Whiteboards
Do you really need to revise but you don't feel like copying out all your notes?
Want something quicker and more effective? All you need is a small whiteboard and pen.
Instead of laboriously writing out all of your notes (particularly diagrams!) try sketching. This technique is not only faster than writing on paper but also allows you to easily make changes, rub things out or add things you may have forgotten.
Doesn't have to be that neat either! But don't forget to take a picture of all of your whiteboard "pages".
They can be useful revision notes to come back to later! Check out two examples below..
Exam style question about pressure changes in the heart
Explaining the flow of blood through the heart and the opening and closing of valves is an important skill in this topic.
Answer the question below, on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
The image shows a diagram of the heart in one stage of the cardiac cycle.
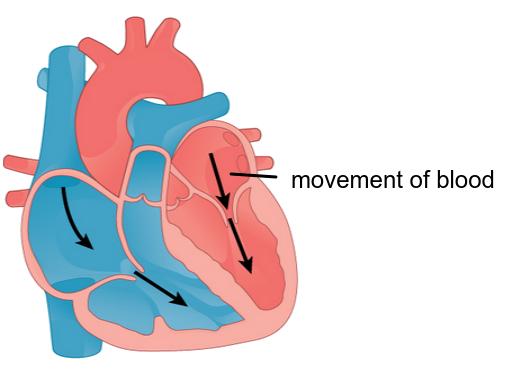
Outline how the contraction and relaxation of muscles in the heart causes different pressures of blood in different chambers leading to blood flow and valve movements in this heart [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
The heart beat is controlled by the pacemaker but the rate can be increased or decreased depending upon the needs of the body.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to describe the control of the heart rate.
increase increased pacemaker normal heart rate slow cardiovascular centre accelerans fear ventricles sinoatrial node contraction involuntarily contraction right voluntarily left atrium epinephrine
Heart muscle is myogenic, it contracts without stimulation. The heart has a in the atrium which generates the at approximately 72 beats per minute without nervous or hormonal control.
The pacemaker, the , initiates the heart beat and of the heart muscle starting from the right atrium, passing through the and then to the causing of the heart muscle in the correct sequence.
The rate of the heartbeat can be or decreased by the of the medulla oblongata in the hind brain utilizing the vagus nerve to the heart (rest) and the nerve to the heart rate (exercise).
The hormone, , which is released in a stress or situation to stimulate the “fight or flight” response also increases the heart rate.
The heart beat is controlled by the sinoatrial node pacemaker but the rate can be increased or decreased by nerves and hormones to suit the needs of the body.
This is a little bit of fun. You can choose your favourite game.
If you can't see the content below please click this direct link to Blood system card matching game.
How much of Blood system 6.2 have you understood?



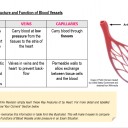

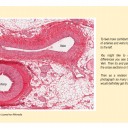




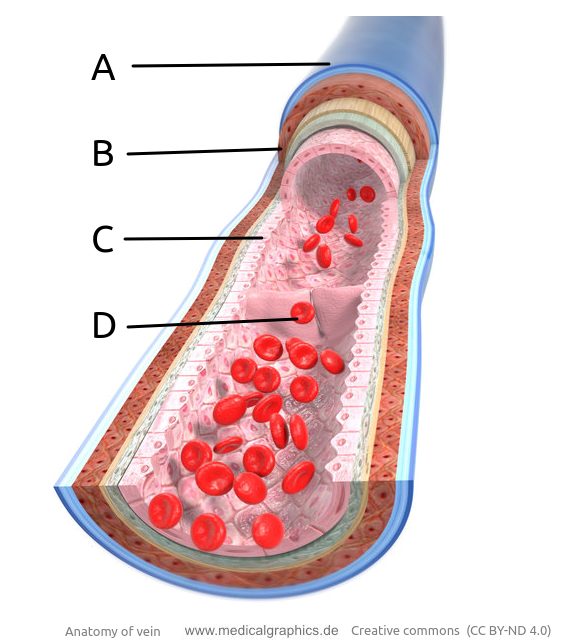 he image shows a model of a vein.
he image shows a model of a vein.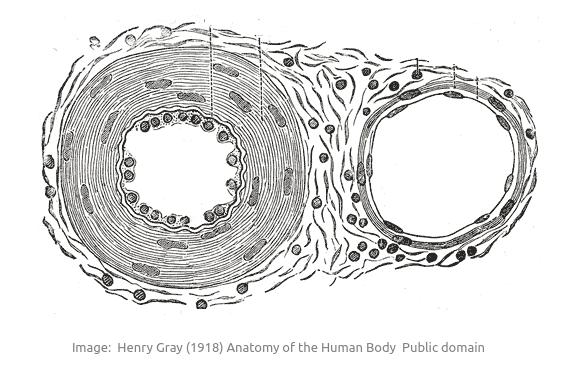
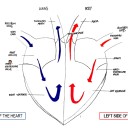
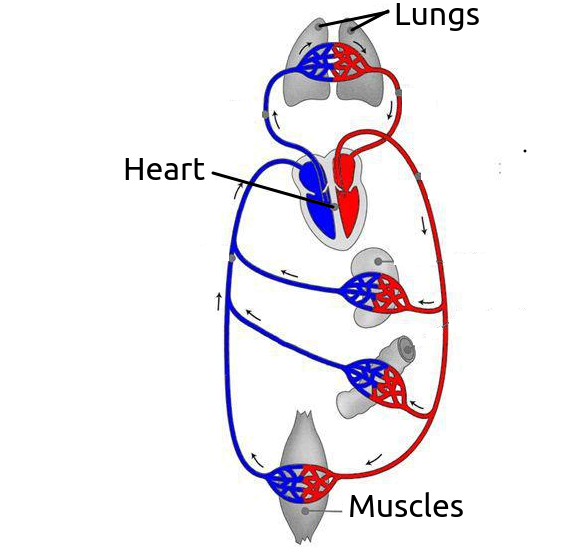 The image shows a simplified diagram of the human circulatory system.
The image shows a simplified diagram of the human circulatory system. Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn