- Summary list for topic 5.3 Classification of biodiversity
- Mindmaps
- Stretch your skills
- Model answer
- Model answer
- 5.3 Classification of Biodiversity 1/1

Learn and test your biological vocabulary for 5.3 Classification of biodiversity using these flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
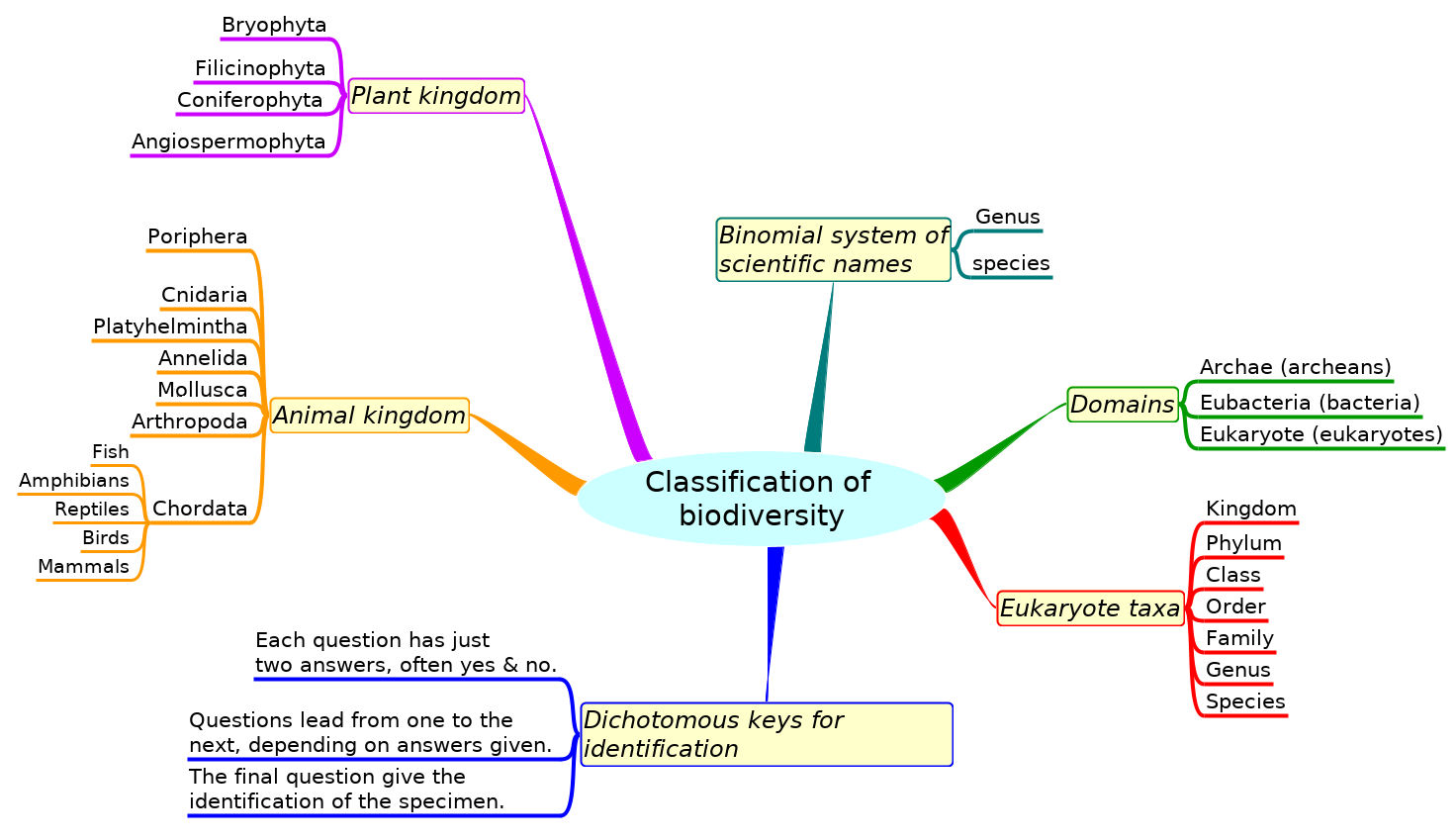
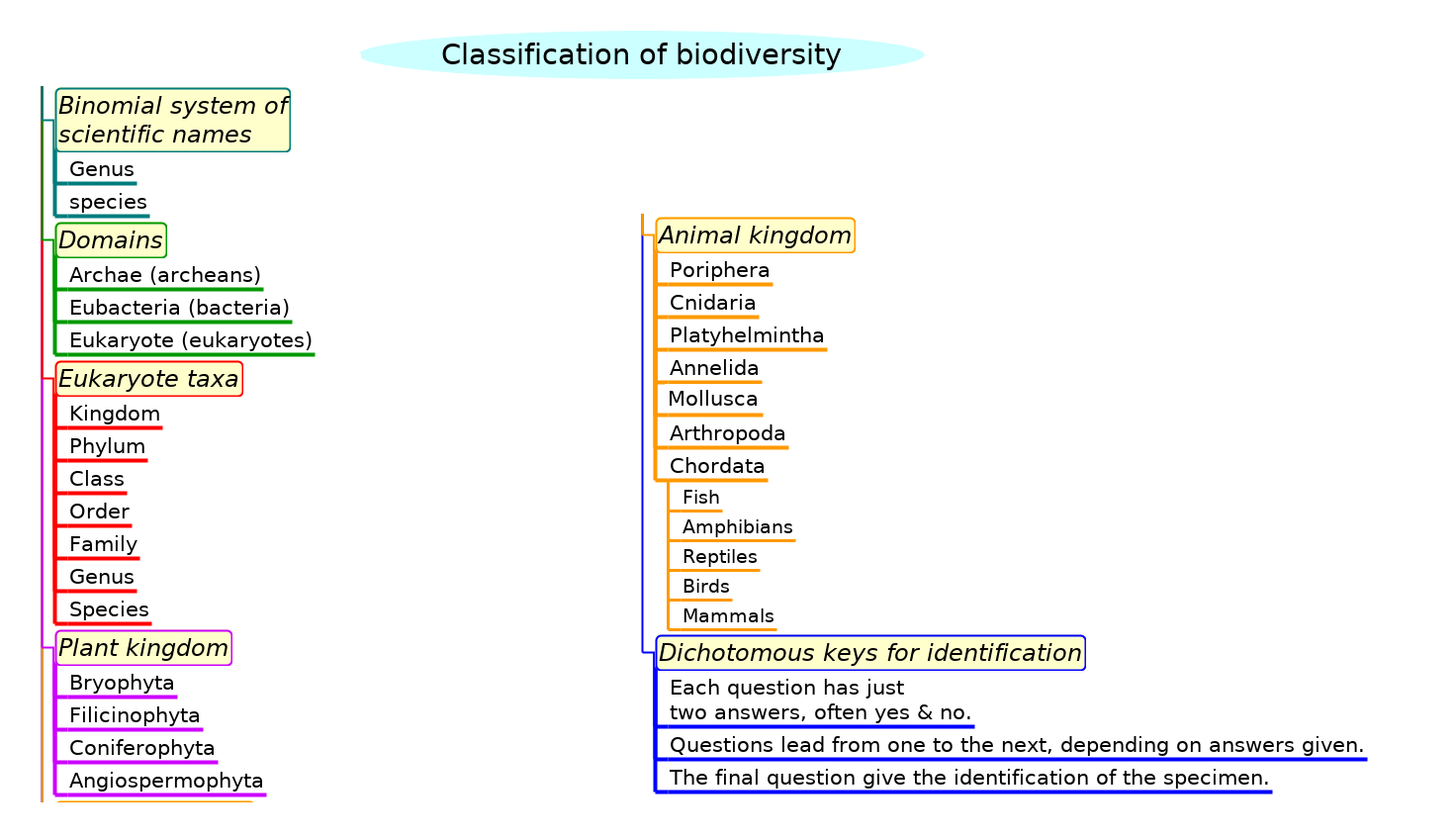
Summary list for topic 5.3 Classification of biodiversity
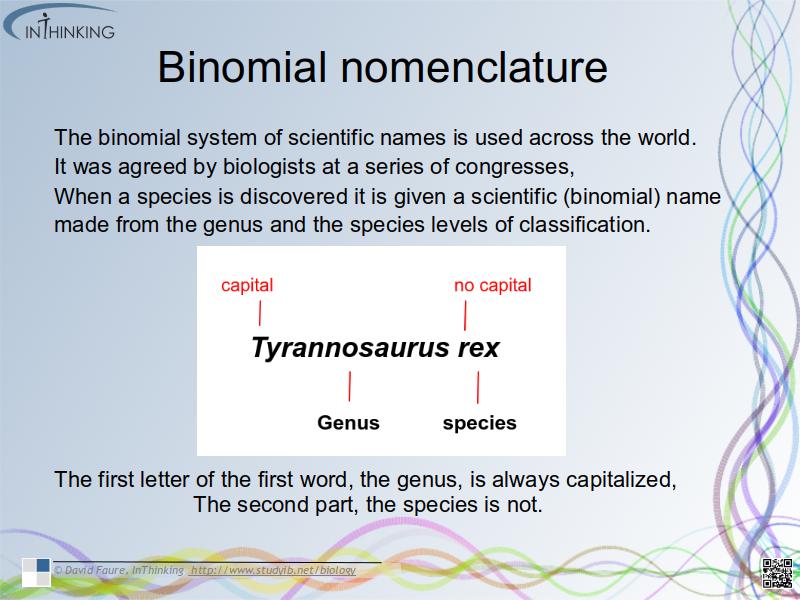
- The binomial system of scientific names is used across the world. It was agreed by biologists at a series of congresses,

- When a species is discovered it is given a scientific (binomial) name.
- Taxonomists classify species using a hierarchy of taxa.
- All organisms are classified into three domains; Archaea (called archaeans), eubacteria (bacteria) and eukaryote (eukaryotes). Note: Viruses are not classified as living.
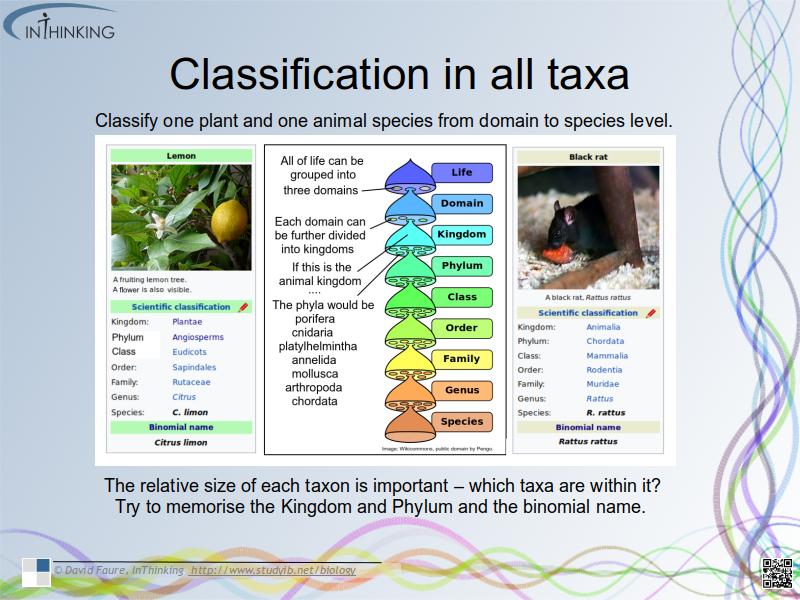
- Eukaryotes are classified into the main taxa: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
- In a natural classification, the genus and accompanying higher taxa consist of all the species that have evolved from one common ancestral species.
- This natural classification helps identification of species and the prediction of shared characteristics by related species.
- Taxonomists sometimes reclassify groups of species when new evidence about evolution appears.
Skills (can you ....)
- Classify one plant and one animal species from domain to species level.
- Remember and recognise the main features of:
- bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and angiospermophyta.(including vascular tissue)
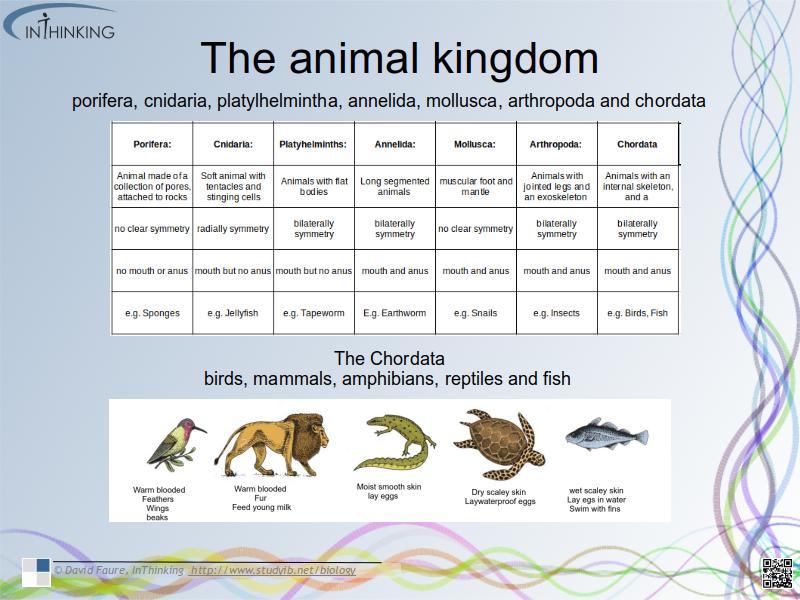
- porifera, cnidaria, platylhelmintha, annelida, mollusca, arthropoda and chordata.
- birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles and fish.
- Construct a dichotomous key for use in identifying specimens.
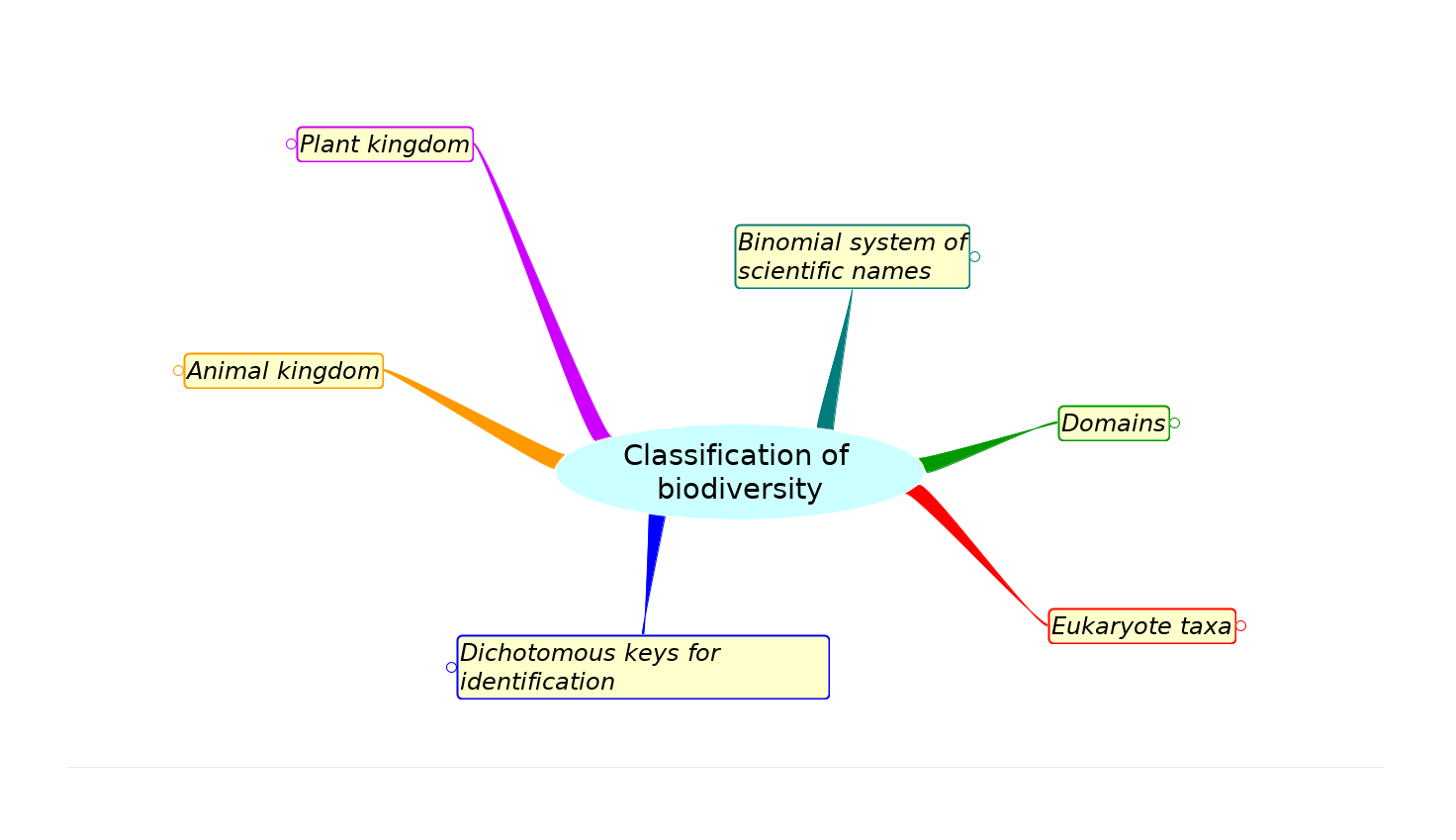
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 5.3 Classification of biodiversity.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map, from memory if you can.
Stretch your skills
Can you recognise the features of the main classification groups?
Test yourself using these cards.
This question requires knowledge of how organisms are classified and of the classification features of the Class Mammalia
A new species of mouse lemur was discovered in Madagascar in 2021. It is a small tree dwelling primate in the class Mammalia. It was given the binomial name of Microcebus jonahi.

a) List two characteristics that the mouse lemur possesses that classify it in class Mammalia (2 marks)
i…………………………………………………………….
ii……………………………………………………………
b) Explain what is meant by the term “binomial name” (2 marks)
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
c) Microcebus is the name given to all the mouse lemurs. Besides physical characteristics, what other types of evidence may have been used by taxonomists to decide that Microcebus jonahi was a new species? (2 marks)
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
d) Dr Jonah Ratsimbazafy discovered this lemur, and it was named after him by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Suggest why this body approves the generic name of a newly discovered mammal (1 marks)
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
........................................................................ ..................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
The organism shown in the picture is a female Griffon vulture (Gyps fulvis) with two chicks.
Drag the correct term into the gap to outline the classification of this organism.

Gyps feathers Gyps ruepelli fulvis hair shelled external Fulvis gyps legs internal forelimbs gyps ruepelli
The Griffon vulture is in the Class Aves because they have covering their body, scales on their only and modified into wings. They lay eggs and have fertilisation.
The binomial name of the Griffon vulture indicates the genus ( ) and the species ( ).
Ruppell's vulture is a related species, the binomial name is .
You need to know the binolmial system of nomenclature and the characteristics of certain groups.
Click the '+' symbol to open the next explanation.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Classification terms card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Classification of biodiversity 5.3 have you understood?

























 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn