Topic 3: Genetics SL 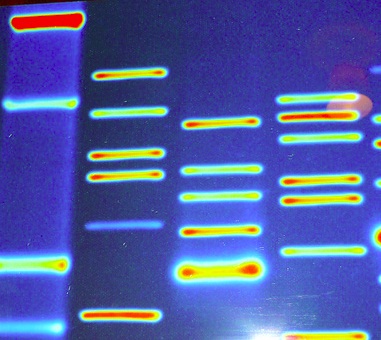
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about genetics.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Genetics SL revision resources
This is an introduction to the SL genetics topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 3 including genes, chromosomes, meiosis, the theoretical genetics of inheritance, GMOs and biotechnology. Helpful for revision. Detailed...
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
A gene is a heritable factor. What is it made from?
A gene is a heritable factor.
It is made from DNA and controlls one specific characteristic.
Why are the chromosomes at the start of meiosis all double stranded?
DNA is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes at start of meiosis are 'double stranded' with two sister chromatids.
Gametes are said to be haploid. What does this term mean?
Haploid nuclei have one chromosome of each pair.
This chart is often used in the diagnosis of chromosome mutations.
What is the name given to this type of diagram and how is it traditionally made.
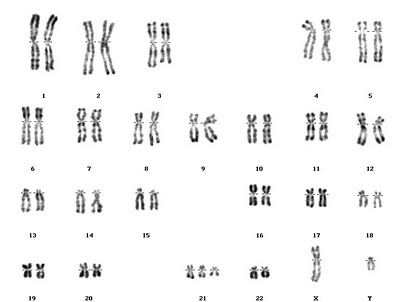
A karyogram (a chart) shows the chromosomes of an organism in homologous pairs of decreasing length.
(Karyotype is the number and type of chromosomes present in the nucleus)
This diagram shows the inheritance of a genetic disease in three generations of a family.
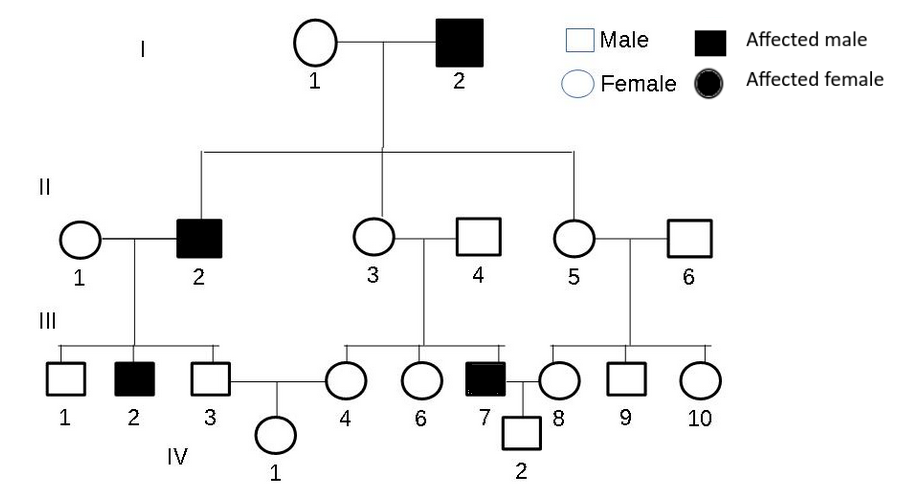
What type of inheritance is the most likely for this disease?
Only males in the familyinherit the disease so it is probably sex linked.
The disease can skip a generation suggesting that it is recessive.
It is likely that the grandmother in generation I and mother 3 in generation II are carriers of the disease.
This image shows the results of the gel electrophoresis of two samples of DNA.
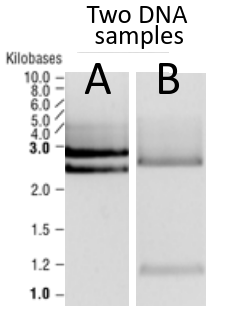
What has the process of gel electrophoresis done?
Gel electrophoresis is used for the separation of fragments of DNA (or proteins).
Different sizes of DNA more different distances, smaller fragments move more quickly than larger fragments.
What is the process called in which a small sample of DNA is amplified using PCR and then separated using gel elecrophoresis?
DNA profiling uses PCR and gel electrophoresis to compare samples of DNA (eg. in paternity disputes)
This experiment investigates the growth of roots in cuttings of plants.
Five lengths of the stem were tested, only two are shown in this photo.
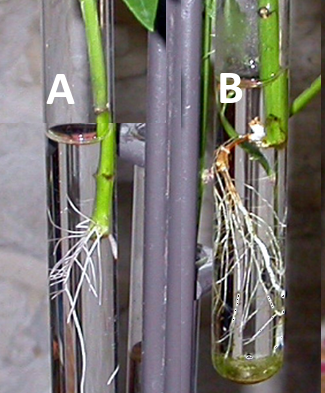
Which of the following variables would be a controlled variable for this experiment?
Design of an experiment to assess one factor affecting the rooting of stem-cuttings of a plant which easily produces roots in soil. Many plant species and some animal species have natural methods of cloning.
In this experiment the temperature of the water would be a controlled variable, as would the volume of water, brightness of light, species of plant.
In the image shown there is a small sample of DNA from two men and a child.
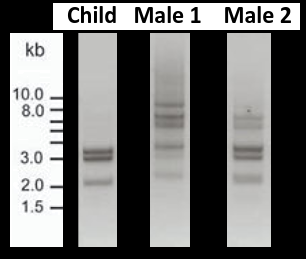
Which of the males is most likely to be the father and why?
Use images of DNA profiling to solve paternity disputes and other forensic examples.
The bands are very similar in male C, there is a small difference, but conditions in the gel may lead to some degree of uncertainty.
The human has approximately 23,000 genes, a small arthropod, the water flea Daphnia has about 31,000 genes. What can be concluded about the Daphnia, in comparison to the Human?
Genes are responsible for coding for proteins, it is reasonable to assume that the Daphnia can make more types of protein molecule, not all of which will be enzymes
Why is it difficult to assess exactly the effects of genetically modified (GM) crops on humans?
Studies that may harm health, done on humans, are unethical so animals are used to model the human response to consumption of the crops.
For this reason the data may not be applicable to humans in all cases.
The image shows a pride of lions. How are the genome and alleles of the members of the pride most accurately described?

The genome is the genetic information of a species (eg the human genome). These lions have the same genome (that of Panthera leo) but each has variation in their alleles of their genes giving individual characteristics.
The diagram shows chromosomes after chiasma during Prophase I of meiosis. What effect does crossing over have on alleles present in each of the chromosomes?
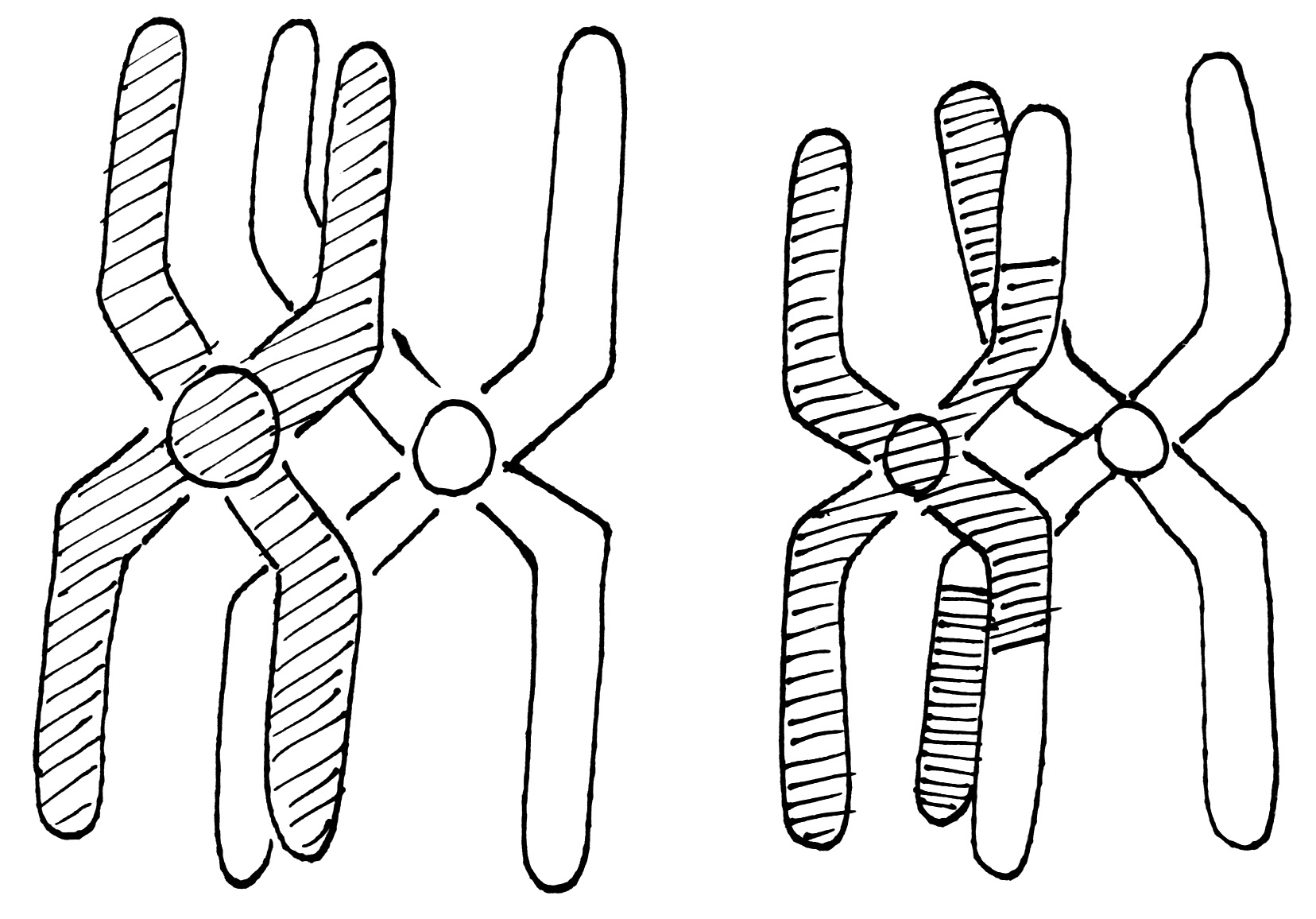
Chiasma (crossing over) is the exchange of alleles between homologous (matching) pairs of chromosomes.The genes on the chromosome remain the same but the allelic combinations are changed.
.The pedigree chart is of an inherited disease, where affected family members are shown as shaded. Deduce the pattern of inheritance of the inherited disease as shown in the pedigree chart.
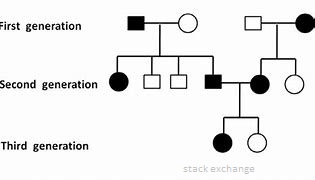
There is a female in the third generation not affected by the disease. Her parents are both affected and must be heterozygous, the gene causing the disease is autosomally recessive. It is not sex linked shown by the same inheritance pattern in males and females.
The photo shows a pink flowered Antirrhinum majus flower produced by crossing pure breeding red flowered with pure breeding white flowered plants. If these pink flowered plants were pollinated amongst themselves and the seeds planted to grow and produce flowers, what would be the expected ratio of flower colours in the next generation?

The red and white genes exhibit incomplete dominance as the F1 generation are all pink flowers, phenotypically intermediate. The F1 cross of pink flowered plants would be WRxWR, giving a predicted phenotypic ration of 2 pink: 1 white: 1 red flowers, where RR is red, WW is white and RW is pink (codominant).
Jane's maternal grandfather was a haemophiliac. Both her parents do not have haemophilia. Could Jane have a haemophiliac son?
If Jane's grandfather was a haemophiliac, her mother must be a carrier for the recessive haemophilia gene, genotype XXh. Jane has a 50% probability of being a carrier of the gene XX or XXh (carrier) and her son could inherit the gene if she is a carrier.
The image shows a genetic profiles from a crime scene and those of 3 suspects. What is the name of the process that produced the image?
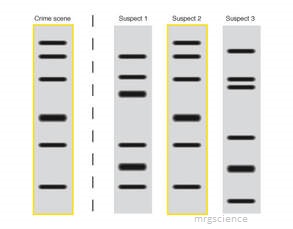
DNA samples are magnified by the PCR reaction and separated by gel electrophoresis.
Which of the suspects could have identified as having been at the crime scene according to the pattern achieved by the gel elctrophoresis?

All the bands of suspect 2 match those at the crime scene.
The sheep in the photograph are artificial clones. What is the source of the genetic material and the cell from which the embryos were formed that grew into these clones?

Adult nuclei from one sheep would be placed in two ovae from the same female with their own nuclei removed (enucleated). If an embryo splits and forms two embryos early in embryonic growth, this is a form of natural cloning.
The diagram below shows the change which differentiates the HbA allele from the HbS allele in sickle cell disease and in the amino acid sequence of the protein.

How does the DNA mutation change the polypeptide sequence of the protein?
The protein structure (1° structure) changes because one amino acid is now different.
In this case the 6th amino acid is changed from Glu (glutamic acid) to Val (valine)
This is caused by the mRNA transcribed from the DNA having a different codon.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 3 Genetics Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn