Topic 9: Plant biology HL 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about HL Plant biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Plant biology HL revision resources
This is an introduction to the HL Plant biology topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 9 including structure and function of xylem and phloem, meristems, growth and reproduction. Helpful for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Which of the following statements explains the importance of adhesion to the transpiration stream?
Adhesion is an attraction between water molecules and the inner wall of xylem ducts and the cells of the leaf.
Then water column cannot be pulled away from the wall of xylem ducts due to strong adhesion of water. This helps to create tension, or transpiration pull.
The diagram below shows a phloem sieve tube and its companion cell.
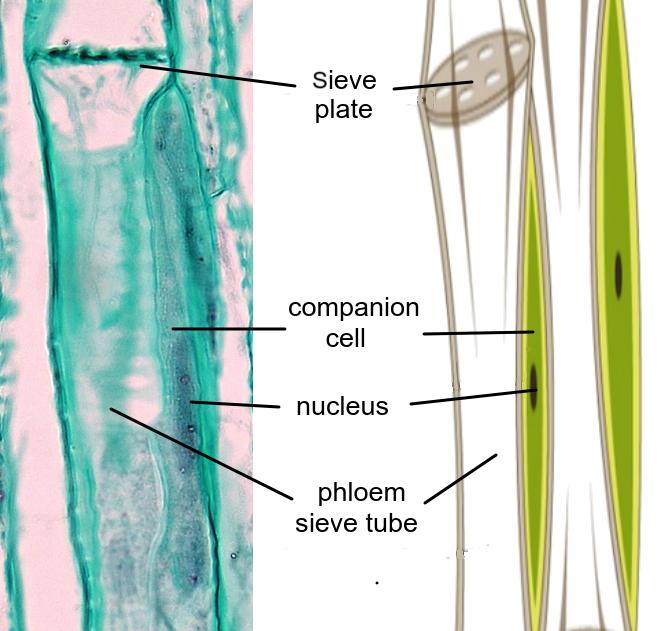
Distinguish between companion cells and sieve tube cells?
Phloem sieve tube elements have perforated cell walls, no nucleus and pale cytoplasm because there is a flow of sap through them.
The companion cells have very metabolically active dense cytoplasm, with lots of mitochondria because they perform many of the metabolic functions for the sieve tube cells.
The diagram below shows xylem and phloem tissue.
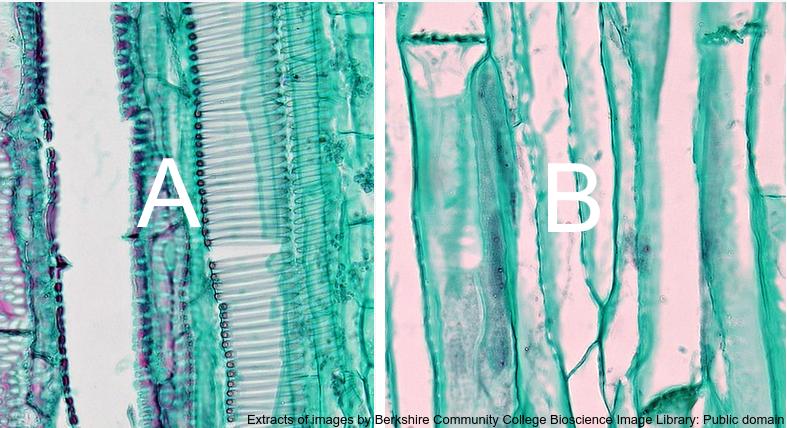
Which is the correct label for each cell type?
Xylem cells have no cytoplasm and spiral thickening in A, not found in phloem. Companion cells and sieve plates of phloem tissue can be seen in the phloem cells in B.
The image below shows results of an experiment in translocation in a photosynthesising plant.

What can be determined from the results?
Sucrose is translocated from photosynthesising leaves (sucrose sources) to rapidly growing leaves (sucrose sinks).
It is interesting to note that only the rapidly growing leaves on the same side as the leaf given radioactive carbon dioxide have received sucrose from this mature leaf.
A student has carried out a germination experiment.

The radical can be seen in 19 of the seeds, but not in 3 of them.
What is the % germination?
19out of 22 seeds is 19/22*100% = 86%
In an investigation of the factors which influence germination of seeds, groups of seeds were planted in different conditions of pH, ranging from pH 5 to 8.
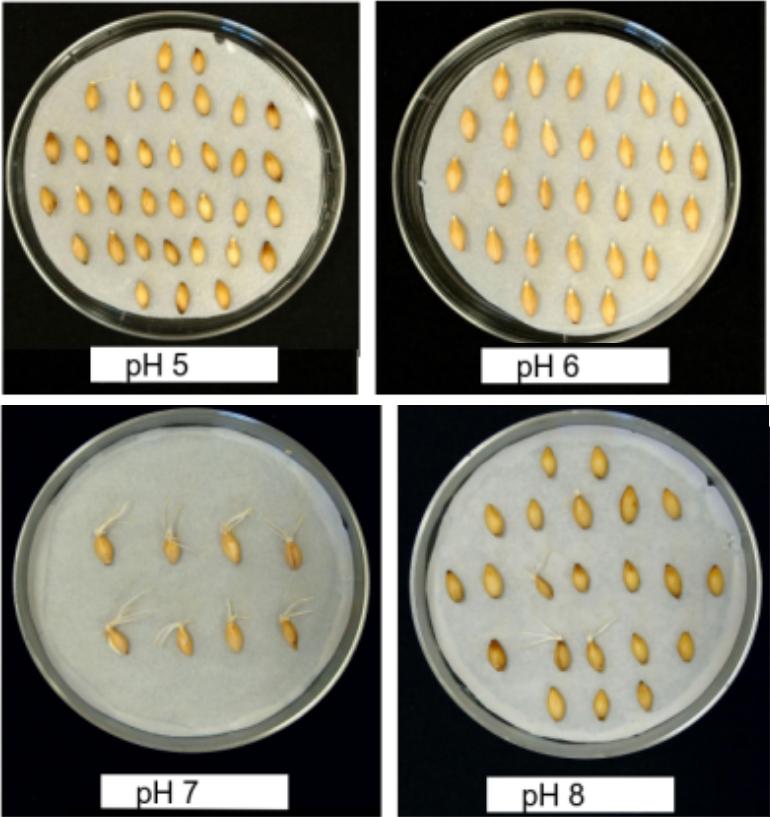
Which of the following statements is a conclusion which could be made from the data?
100% of seeds in pH 7 and pH 8 have germinated, but some seeds germinated in pH6 and 8 too.
The seeds in pH7 have the longest roots, suggesting they have germinated more quickly.
A short day plants flower when the nights are long.
Phytochrome pigments regulate this response.
What happens to Pfr when it is placed in darkness and how does this affect short day plants?
Exposure to light causes Pr to be converted to Pfr but in the darkness, the Pfr is converted to Pr. Pfr inhibits short day plants from flowering.
Which of the following processes are involved in water uptake by root hair cells?
I Tension
II Osmosis
III Active transport
IV Adhesion
Active transport is used by plants to take up nitrates and other ions from the soil. This active uptake of minerals increases the concentration of dissolved ions in root cells and increases the uptake of water by osmosis.
Which of the following are involved in transport of substances in phloem vessels?
I Hydrostatic pressure
II Incompressibility of water
III Active transport
IV Osmosis
The companion cell uses active transport to transport materials to phloem sieve tubes. Water follows by osmosis. This increases hydrostatic pressure, as the volume of water increases, and water is incompressible.
During a whole year's growth of an onion plant, which of the following parts could be regarded as both a source and a sink?
The bulb both stores and releases sugars and other organic molecules, as does the seed when growing and germinating.
The leaves gain nutrients from the bulb in their early growth and then photosynthesise, becoming a source of sucrose.
What creates the increased hydrostatic pressure at the source area of phloem vessels?
As sucrose is actively transported into the phloem vessels, water enters by osmosis into the phloem vessels and increases the hydrostatic pressure.
What creates the decreased hydrostatic pressure at the sink area of phloem vessels?
As sucrose is actively transported out of the phloem vessels, water exits by osmosis from the phloem vessels lowering the hydrostatic pressure.
Why were aphids were used to study the movement of substances within phloem vessels?
Aphid stylets penetrate single phloem vessels. If the insect is separated from its stylet then the contents of the phloem vessel can be tested.
In which type of medium are apical meristem cells placed for micropropagation?
The cells are planted in gel with inorganic nutrients and auxins to increase growth rates.
Which is the main environmental factor that causes most plants to flower in a certain season?

In short and long day plants, the length of the day (and of the night) stimulates flowering in the correct season.
What is meant by indeterminate growth in plants?

Indetrminate growth is continuous production of new organs if there are resources and suitable conditions. It is common in plants. Most animals have determinate growth, they grow and mature to a certain size.
Short day plants, such as the chrysanthemum, grow vegetatively (leaves and stems) when the dark period (night) is more than 12 hours and switch to producing flowers when the dark period is less than 12 hours. What is the name for the effect that day length has on flowering?

Plant growth responses to day length is known as photoperiodism.
Which of the following processes are involved in water movement from root xylem to leaves?
I Tension
II Osmosis
III Active transport
IV Cohesion
The loss of water from the leaf by transpiration causes a pressure gradient that puts the column of water in a xylem vessel under tension and draws water up the stem.
This is aided by cohesion of water to molecules to maintain the water column.
The image shows the response of a plant shoot towards lateral light.

What is the best description of this response?
Only one answer is accurate - read the alternatives carefully.
The other answers are distractors, close to correct.
Which of the following relationships are considered mutualistic?
In mutualism, both organisms benefit, the pollinator gaining food and the Angiosprm flower being pollinated is an example.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 9 Plant biology HL Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn