 This is a short introduction to acids and bases. Much of which you may have encountered pre-IB. A few keys things to remember here include recognising acid-base conjugate pairs and remembering how to write and balance acid reactions.
This is a short introduction to acids and bases. Much of which you may have encountered pre-IB. A few keys things to remember here include recognising acid-base conjugate pairs and remembering how to write and balance acid reactions.
Ensure you are confident using the terms below and learn the asterisked* definitions
Brønsted-Lowry acid*, Brønsted-Lowry base*, Hydroxonium (hydronium) ion, Conjugate acid base pairs, Amphiprotic, Amphoteric, A salt
Which is the best definition of a Brønsted-Lowry base?
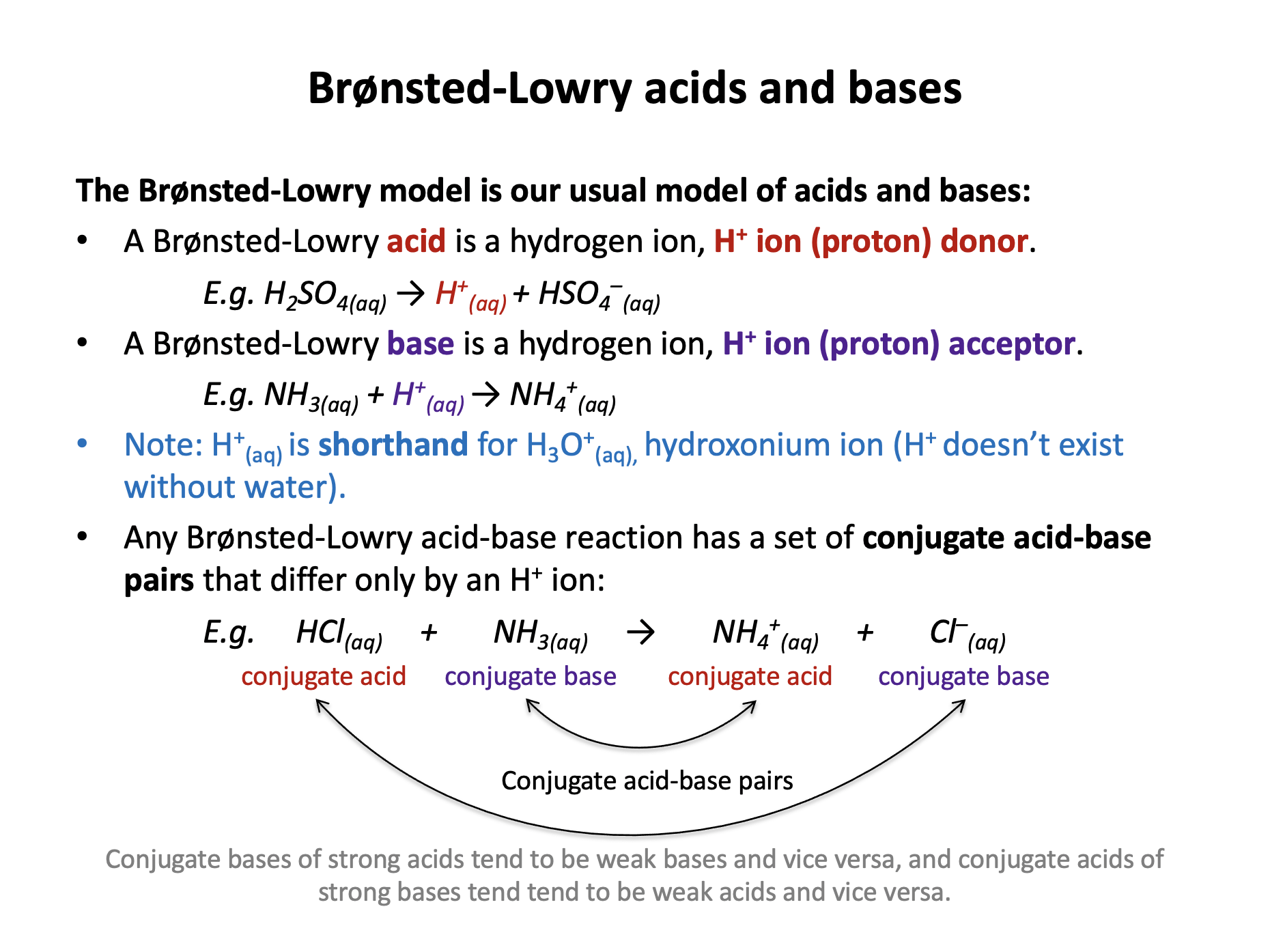
The Brønsted-Lowry model is our usual model for defining acids and bases.
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton/hydrogen ion/H+ donor and a Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton/hydrogen ion/H+ acceptor. These definitions need to be learned.
Thus A hydrogen ion (H+) acceptor is the correct answer.
Which is the best definition of a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
The Brønsted-Lowry model is our usual model for defining acids and bases.
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton/hydrogen ion/H+ donor and a Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton/hydrogen ion/H+ acceptor. These definitions need to be learned.
Thus A hydrogen ion (H+) donor is the correct answer.
What is the conjugate base of H2PO4−?
Every base has a conjugate acid. Likewise, every acid has a conjugate base.
To find the conjugate base of a Bronsted-Lowry acid, simply remove an H+ ion from the acid (and vice versa).
Therefore HPO42− is the correct answer.
What is the conjugate acid of HSO4−?
Every base has a conjugate acid. Likewise, every acid has a conjugate base.
To find the conjugate acid of a Bronsted-Lowry acid, simply add an H+ ion to the base (and vice versa).
Therefore H2SO4 is the correct answer.
Which are a correct set of acid-base conjugate pairs from the reaction below (in aqueous solution)?
HNO3 + NH3 → NO3− + NH4+
Conjugate acid-base pairs differ in formula by a single H+ ion. The conjugate acid should have an extra H+ when compared to the conjugate base.
Therefore the correct answer is: Conjugate acid: HNO3 Conjugate base: NO3−
Note that; Conjugate acid: NH3 Conjugate base: NH4+ is also an acid-base pair, but the labels are incorrect as the base has the extra H+ ion.
Which of the following are formed when magnesium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid?
1: A salt
2: Hydrogen gas
3: Water
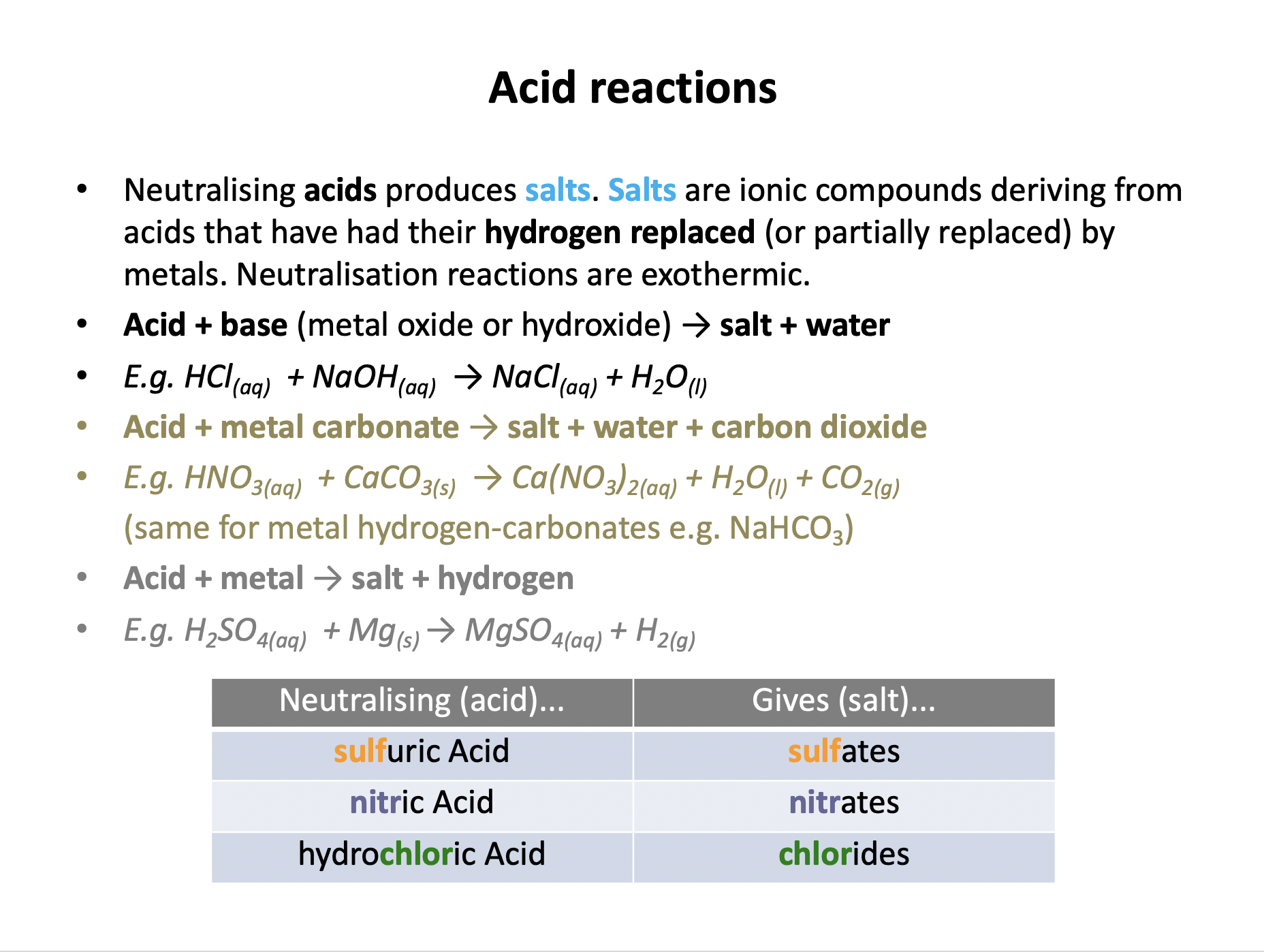
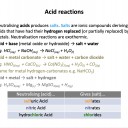
Acid reactions need to be learned:
Acid + Base (metal oxide/hydroxide) → Salt + Water
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Magnesium hydroxide is a base, so 1 and 3 only is the correct answer.
Which of the following are formed when sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid?
1: Sodium chloride
2: Carbon dioxide gas
3: Water
Acid reactions need to be learned:
Acid + Base (metal oxide/hydroxide) → Salt + Water
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
And neutralising: hydrochloric acid produced chlorides; sulfuric acid produces sulfates; nitric acid produces nitrates.
Sodium carbonate is a metal carbonate, and the salt produced will be sodium chloride, so 1, 2 and 3 is the correct answer.
Which of the following are formed when magnesium reacts with sulfuric acid?
1: Magnesium chloride
2: Hydrogen gas
3: Carbon dioxide gas
Acid reactions need to be learned:
Acid + Base (metal oxide/hydroxide) → Salt + Water
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
And neutralising: hydrochloric acid produced chlorides; sulfuric acid produces sulfates; nitric acid produces nitrates.
Magnesium is a metal, and the salt produced will be magnesium sulfate (not magnesium chloride), so 2 only is the correct answer.
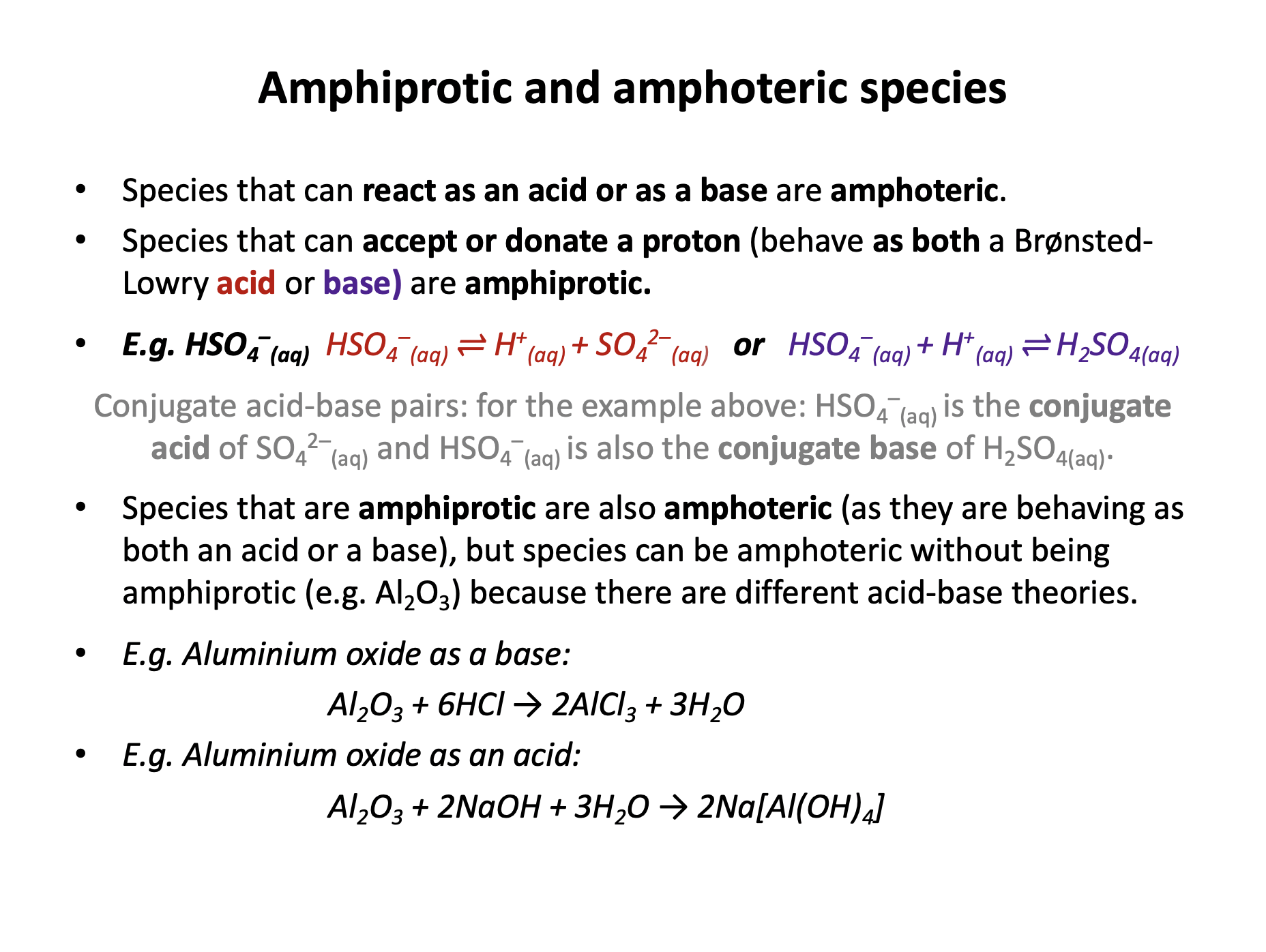
Which of the following could act as either a Brønsted-Lowry acid or base in aqueous solution?
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is an H+ ion (proton) donor and a base is an H+ ion (proton) acceptor. So in order to behave as both, a species must be able to both donate and accept an H+ ion.
H2PO4− can accept a proton to form H3PO4, or can donate a proton to form HPO42−. We should recognise that both these species (produced) are stable. Therefore H2PO4− is the correct answer.
The other species can accept or donate protons, but cannot do both.
H2PO3− takes part in the following reactions:
H2PO3−(aq) + OH−(aq) → HPO32−(aq) + H2O(l)
H2PO3−(aq) + H+(aq) → H3PO3(aq)
Which of the following apply to H2PO3− in any/all of these reactions?
1 It is a Bronsted-Lowry base
2 It is a Bronsted-Lowry acid
3 It is Amphiprotic
In the first reaction, H2PO3− donates a proton, acting as a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
In the second reaction, H2PO3− accepts a proton, acting as a Bronsted-Lowry base.
If a substance is both a Bronsted-Lowry acid and a Bronsted-Lowry base, then it is amphiprotic (can both accept and donate a proton (H+ ion)).
Paper 1
Core (SL&HL): Acids and Bases core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions
AHL (HL only): Acids and Bases AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions
Paper 2
Core (SL&HL): Acids and Bases core (SL & HL) paper 2 questions
AHL (HL only): Acids and Bases AHL (HL only) paper 2 questions
How much of Theories and properties of acids and bases have you understood?





 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn