 The picture reveals the source of almost all of our energy - the sun. This might be obvious for solar cells, but what's the link between the sun and other energy resources?
The picture reveals the source of almost all of our energy - the sun. This might be obvious for solar cells, but what's the link between the sun and other energy resources?
Key Concepts
 A fuel is any substance that contains chemical or nuclear energy that can be harnessed to produce heat energy:
A fuel is any substance that contains chemical or nuclear energy that can be harnessed to produce heat energy:
- Fossil fuels (oil, coal and gas) contain chemical energy. They can be combusted (burned in oxygen) to produce thermal energy.
- Nuclear fuels contain nuclear energy. Nuclear processes, such as radioactive decay, produce a net output of thermal energy.
The Sun is powered by nuclear fuels. Under the dense, high temperature conditions caused by immense gravitational forces, hydrogren nuclei overcome electrostatic repulson to fuse and form helium.
To convert heat into work requires some sort of engine, for example, a turbine.
Fuel is used to boil water in an enclosed vessel causing the pressure of the steam to increase. The high pressure steam is directed at the vanes of a turbine causing it to turn.
More info is included in Power stations.
How much of Energy sources have you understood?

 Plants on Earth absorb the energy from the Sun and use it to combine carbon dioxide and water to create carbohydrates. In terms of physics, charged particles are being pushed together, increasing their potential energy on a nano scale. Macroscopically, we call this chemical energy.
Plants on Earth absorb the energy from the Sun and use it to combine carbon dioxide and water to create carbohydrates. In terms of physics, charged particles are being pushed together, increasing their potential energy on a nano scale. Macroscopically, we call this chemical energy.
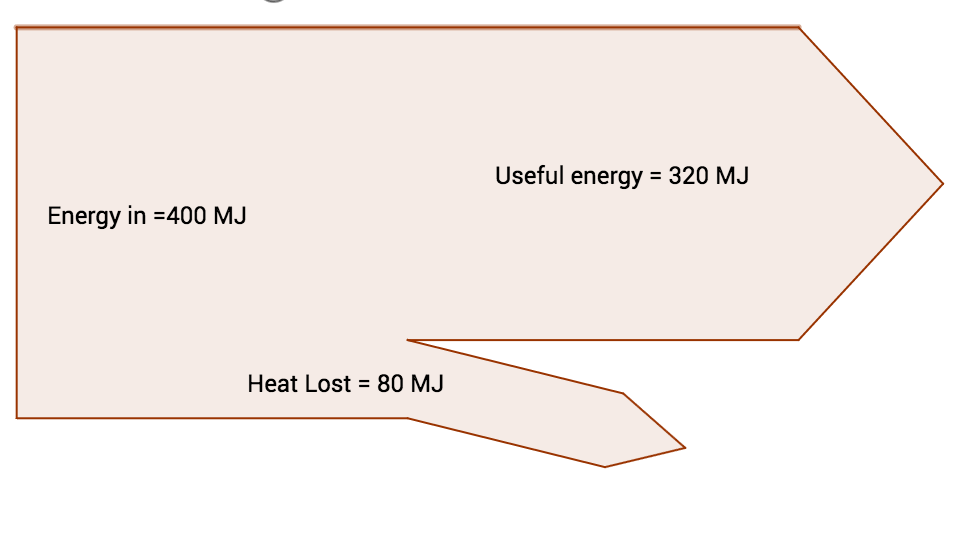 Sankey diagrams display the flow of enery through a system:
Sankey diagrams display the flow of enery through a system: In an exam, if squared paper is provided in the question paper, then your diargam must be perfectly to scale. If the answer space is blank, a sketch with approximate proportions is fine (but you should label all quantities).
In an exam, if squared paper is provided in the question paper, then your diargam must be perfectly to scale. If the answer space is blank, a sketch with approximate proportions is fine (but you should label all quantities). 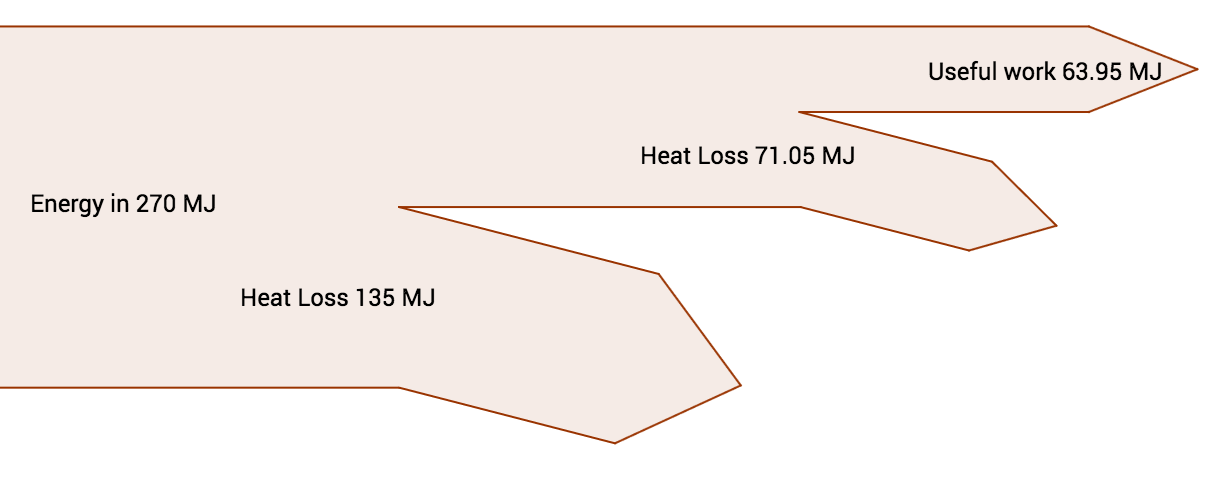 A power station produces electricity by burning fuel. The fuel could be coal, oil or gas but the principle is the same.
A power station produces electricity by burning fuel. The fuel could be coal, oil or gas but the principle is the same. Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn