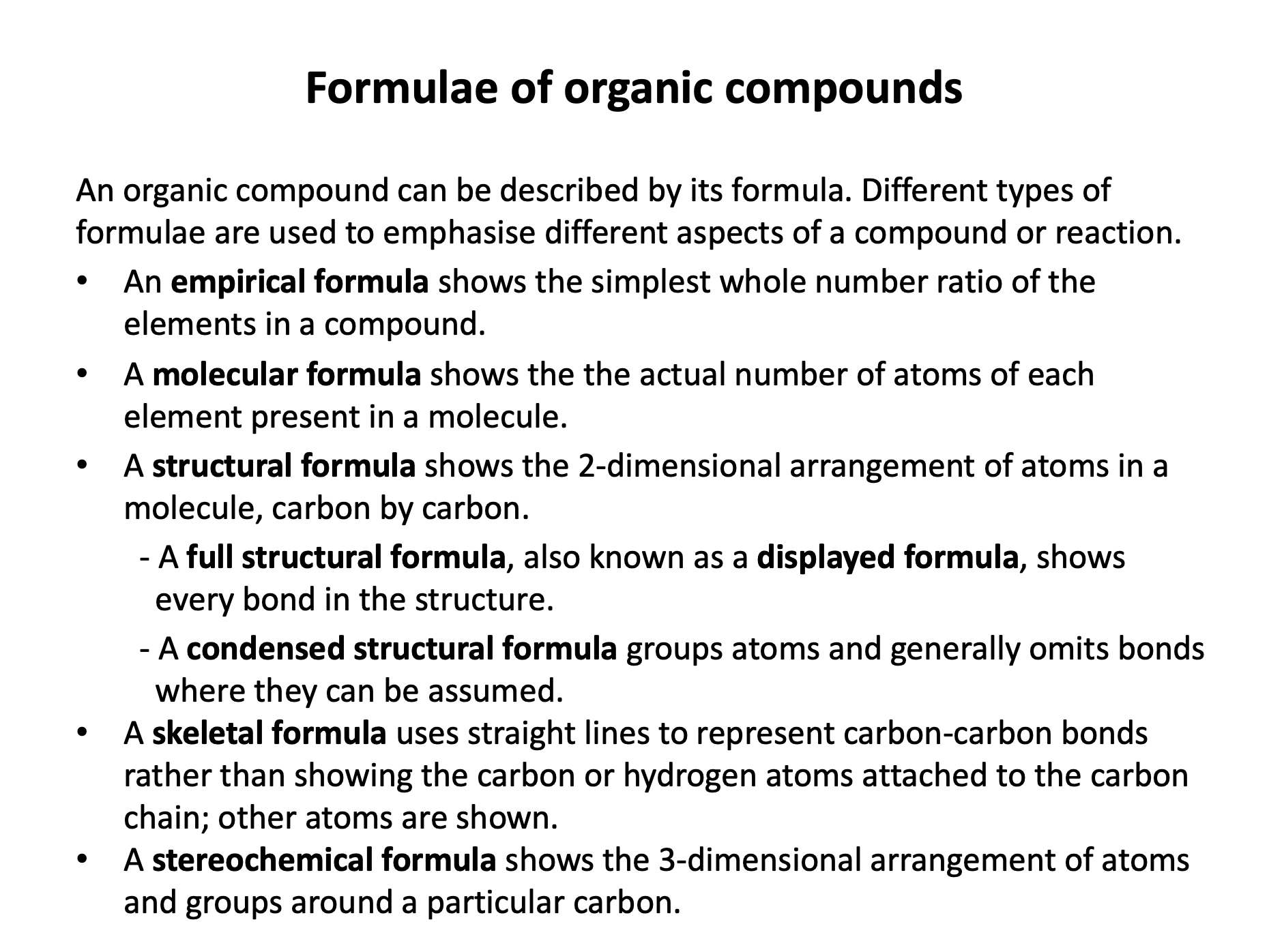
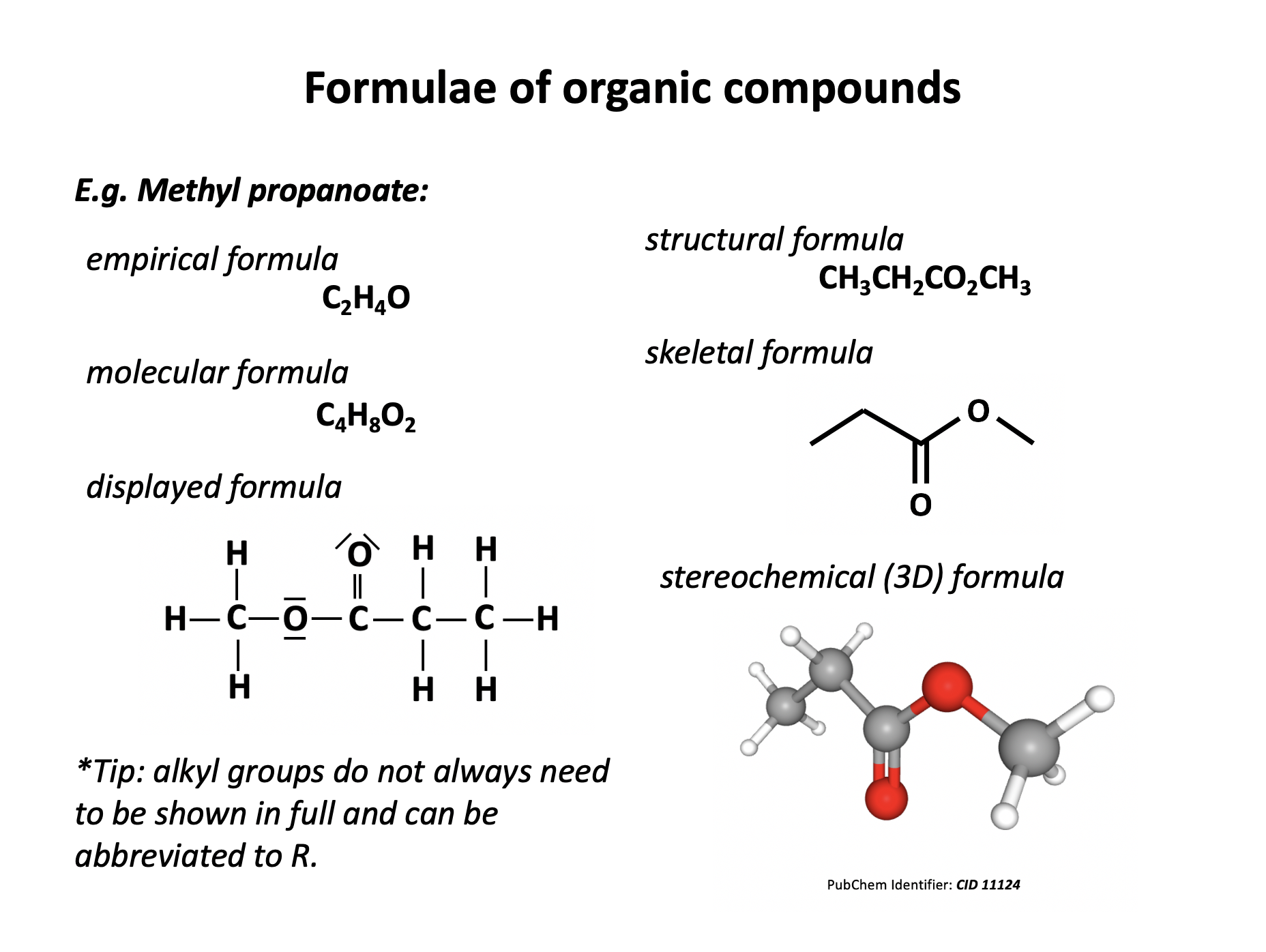
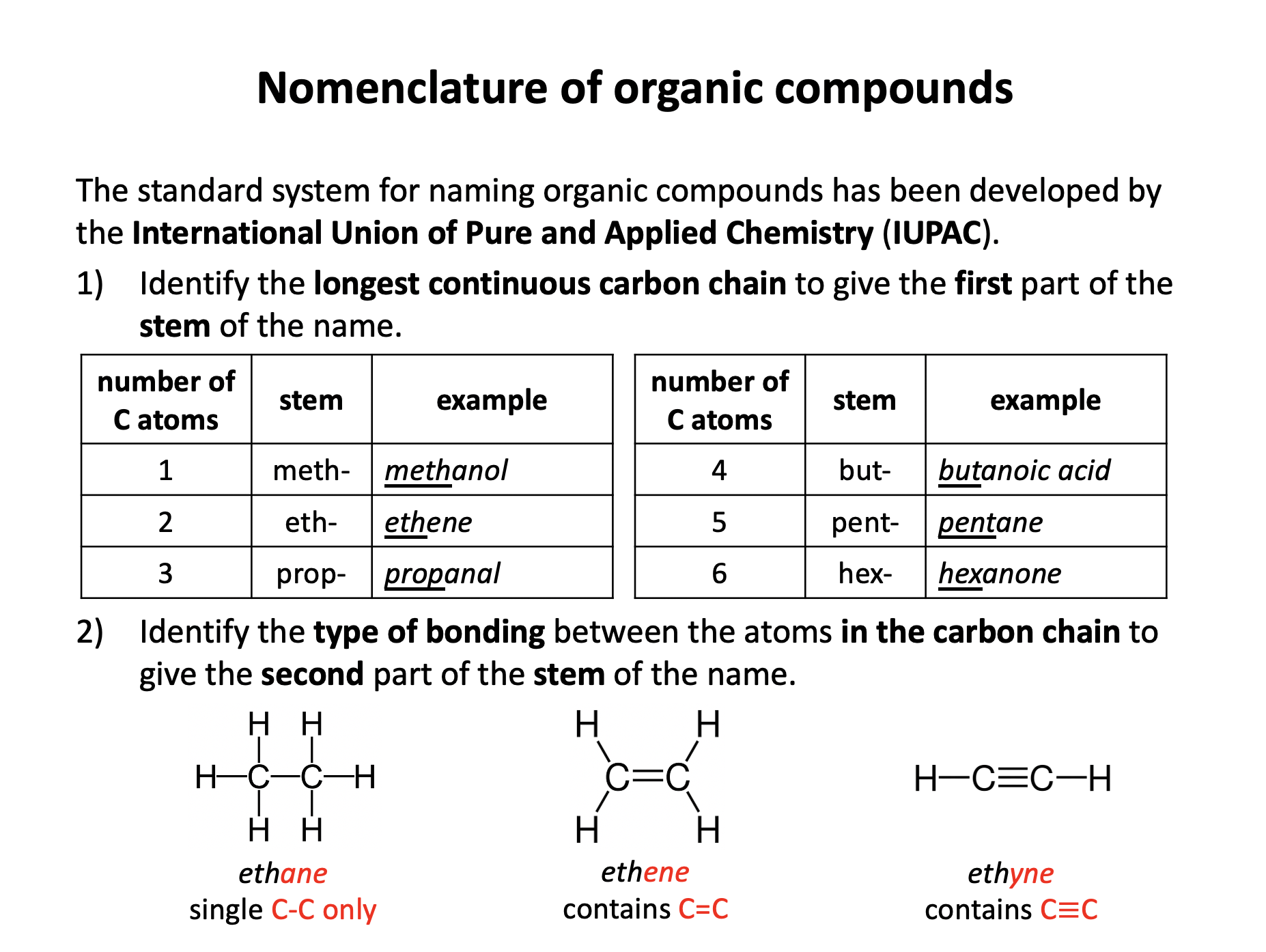
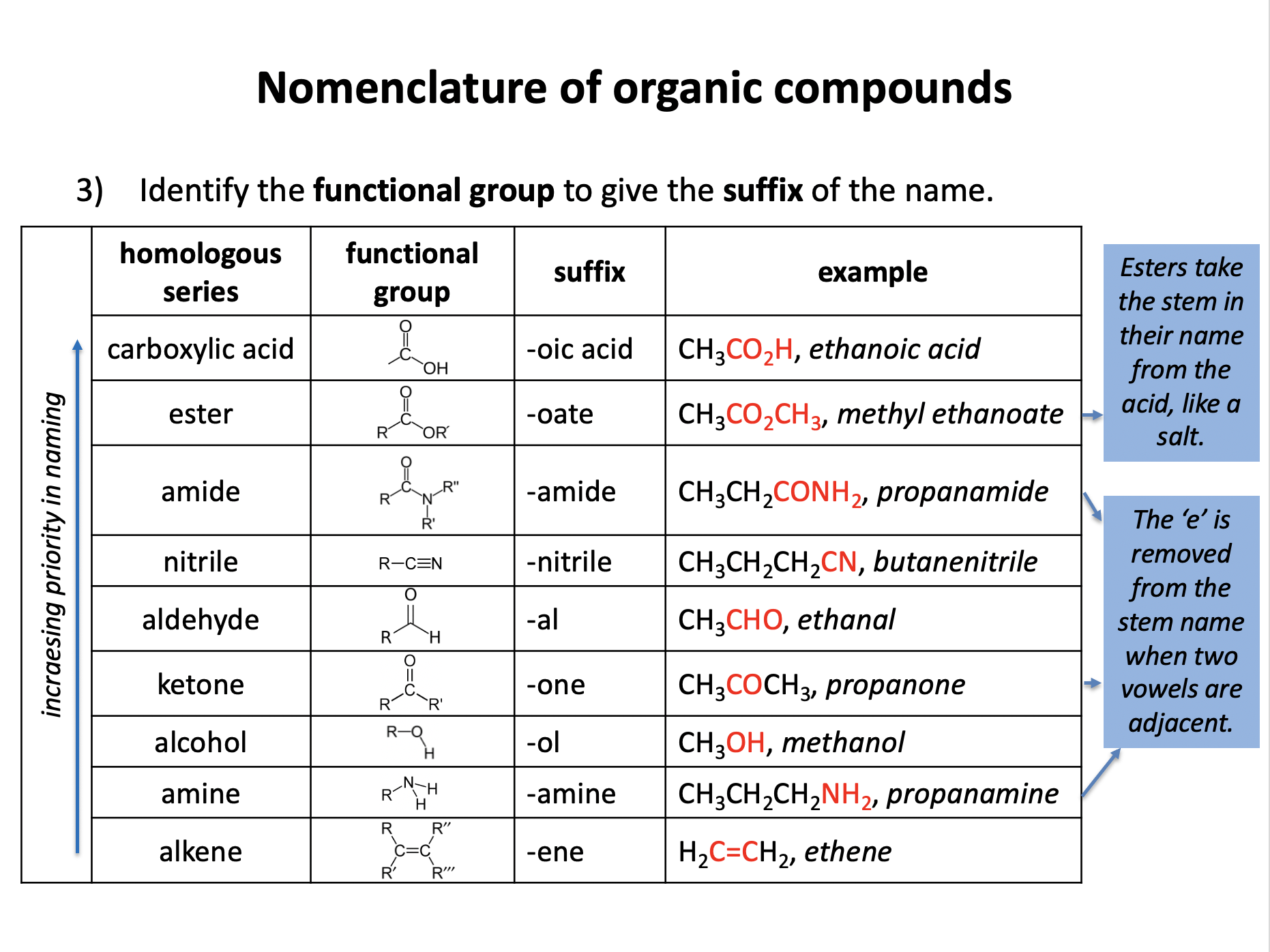
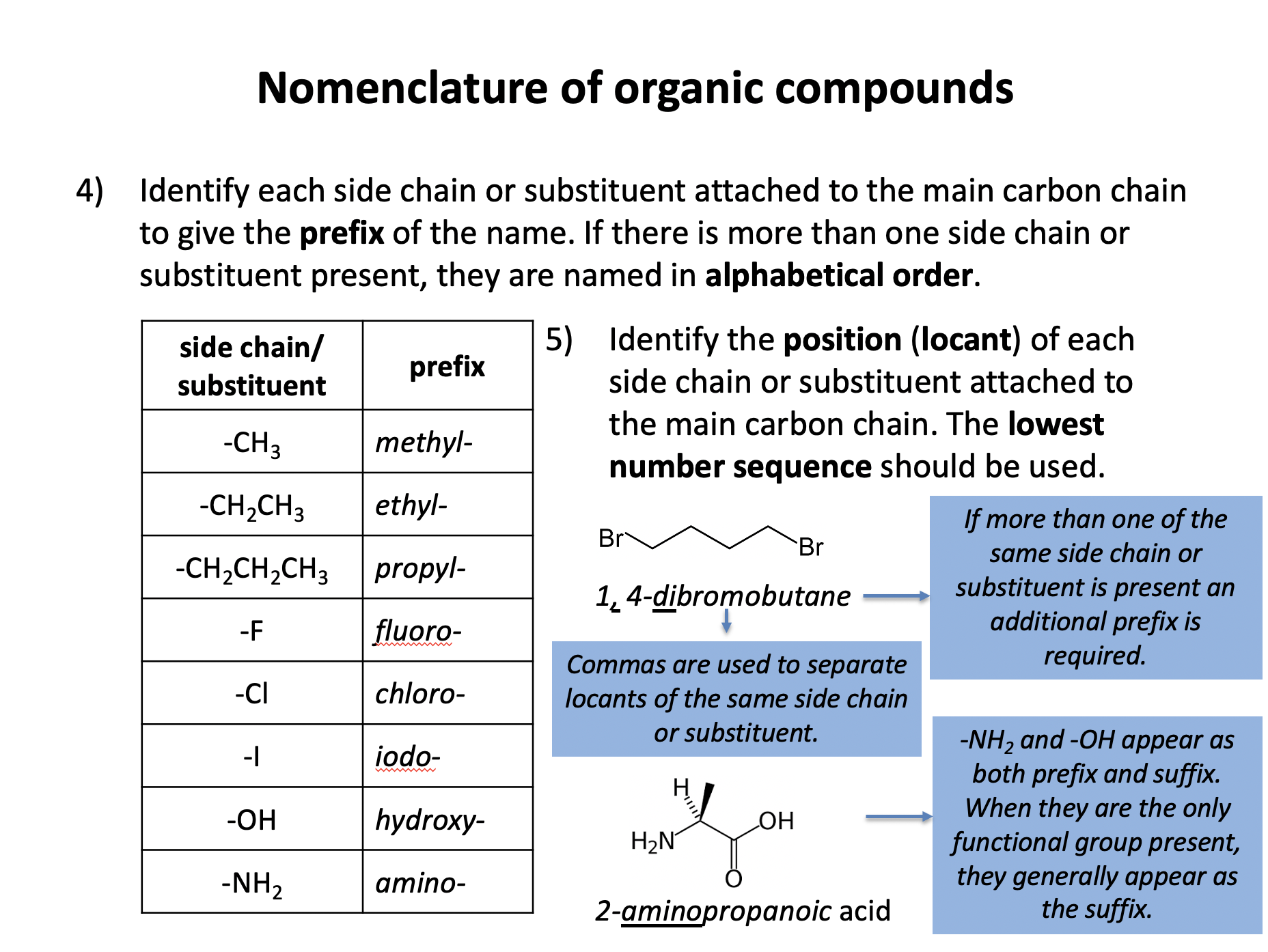
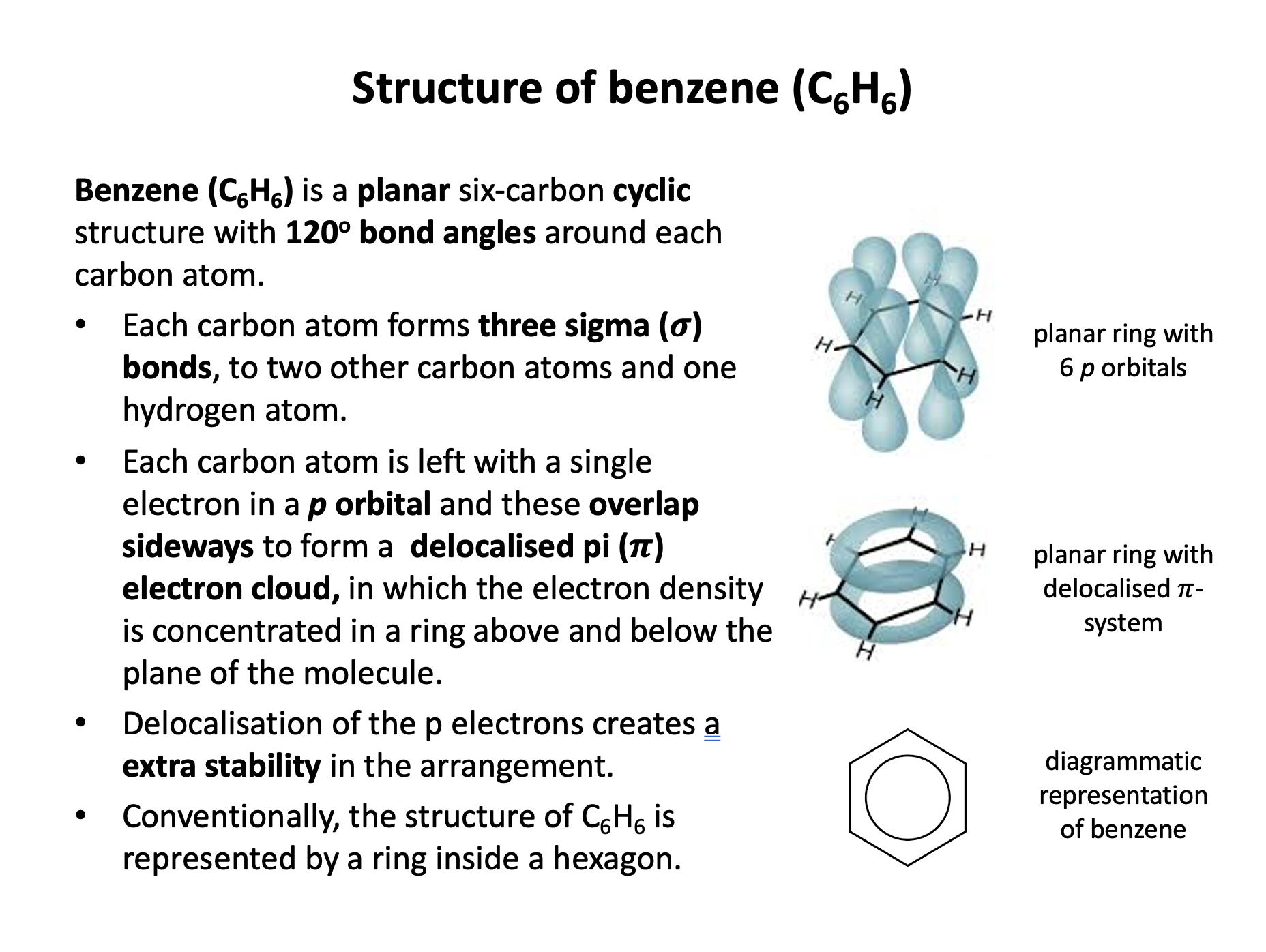
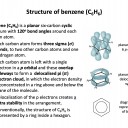
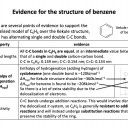
 Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry dedicated to the study of carbon-based compounds. This section looks at their nomenclature and how they are classified. Naming and writing formulae of organic compounds are fundamental skills that require attention to detail. Use the revision cards to familiarise yourself with the IUPAC rules of organic nomenclature and then use the practice questions to apply them. Benzene is an an aromatic unsaturated compound but it does not behave like other unsaturated molecules due to the presence of a delocalised pi-electron cloud. Use revision card 10 to ensure that you understand how this model of benzene is supported by evidence.
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry dedicated to the study of carbon-based compounds. This section looks at their nomenclature and how they are classified. Naming and writing formulae of organic compounds are fundamental skills that require attention to detail. Use the revision cards to familiarise yourself with the IUPAC rules of organic nomenclature and then use the practice questions to apply them. Benzene is an an aromatic unsaturated compound but it does not behave like other unsaturated molecules due to the presence of a delocalised pi-electron cloud. Use revision card 10 to ensure that you understand how this model of benzene is supported by evidence.
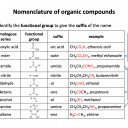
Ensure you are confident using the terms below and learn the asterisked* definitions
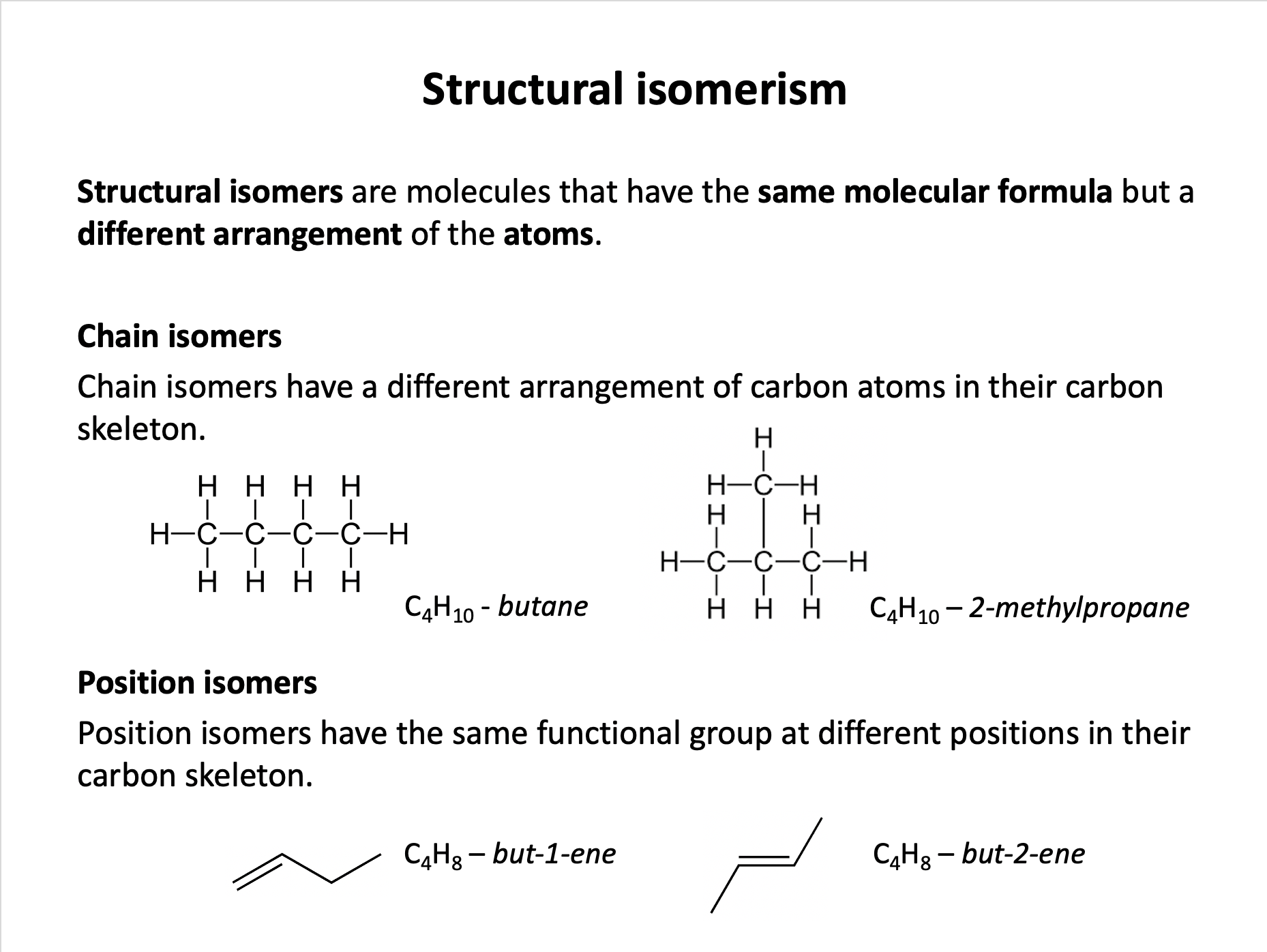
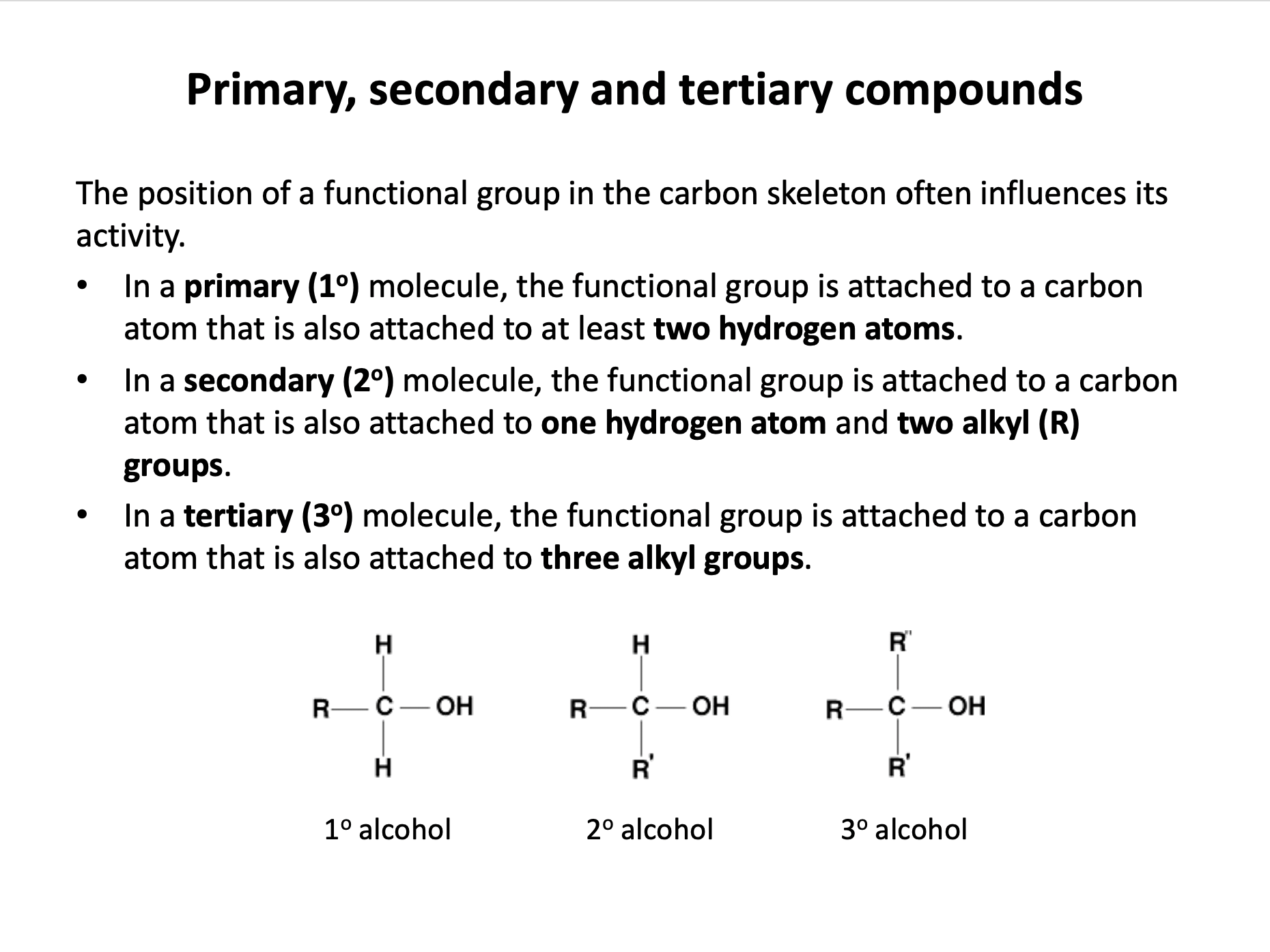
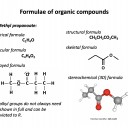
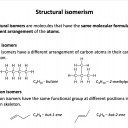
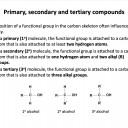
homologous series*, full structural (displayed) formula, structural formula, skeletal formula, stereochemical formula, structural isomers*, chain isomers, position isomers, 1o molecule, 2o molecule, 3o molecule
Which of the following correctly describes the properties of the compounds of a homologous series?
1: They differ in formula in successive series by CH2
2: They have the same chemical properties
3: They have the same functional group
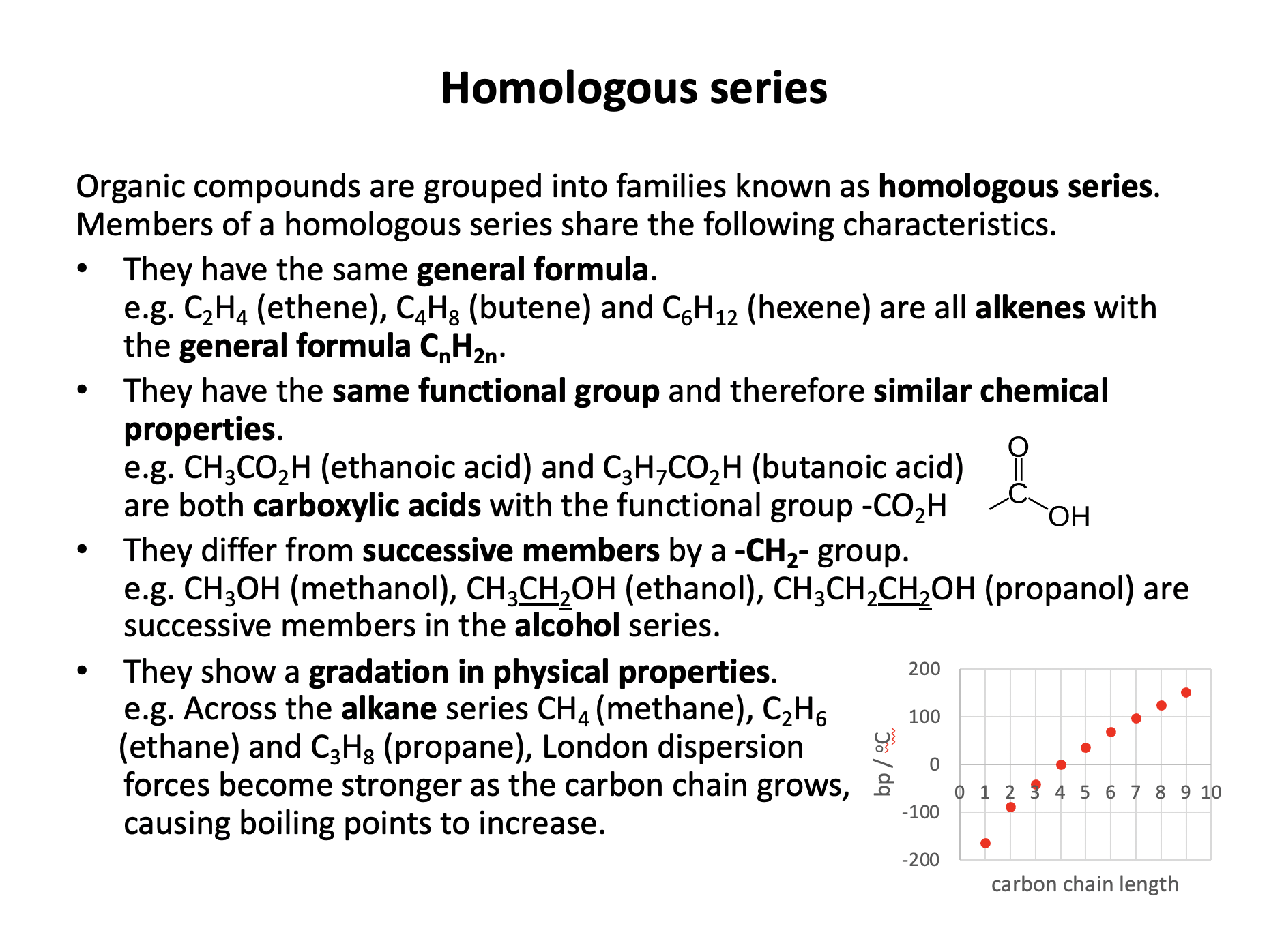
Homologous series of compounds have the same general formula. Their formulae differ in successive sequence by CH2. They have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. They show a gradation in physical properties.
Therefore statements 1 and 3 only are correct, but statement 2 is not correct, as homologous series do not have the same chemical properties, but similar chemical properties; an important distinction.
Which of the following compounds are members of the same homologous series?
1: CH3CH2CHO
2: CH3COCH3
3: CH3COC2H5
Homologous series of compounds have the same general formula. Their formulae differ in successive sequence by CH2. They have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. They show a gradation in physical properties.
Compound 1 is an aldehyde. Compounds 2 and 3 are both ketones are differ in formula by CH2 so are neighbouring members of the same homologoues series.
Therefore 2 and 3 only is the correct answer.
Which of the following formulae represent a molecule of ethyl ethanoate?
In formulae 3, the red atoms are oxygen, grey are carbon and white are hydrogen.
1: CH3CH2CO2CH3
2: 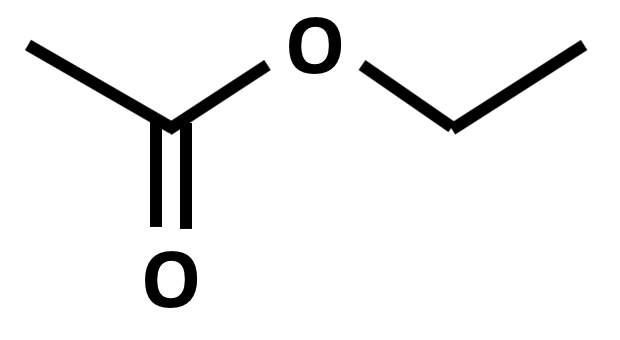
3: 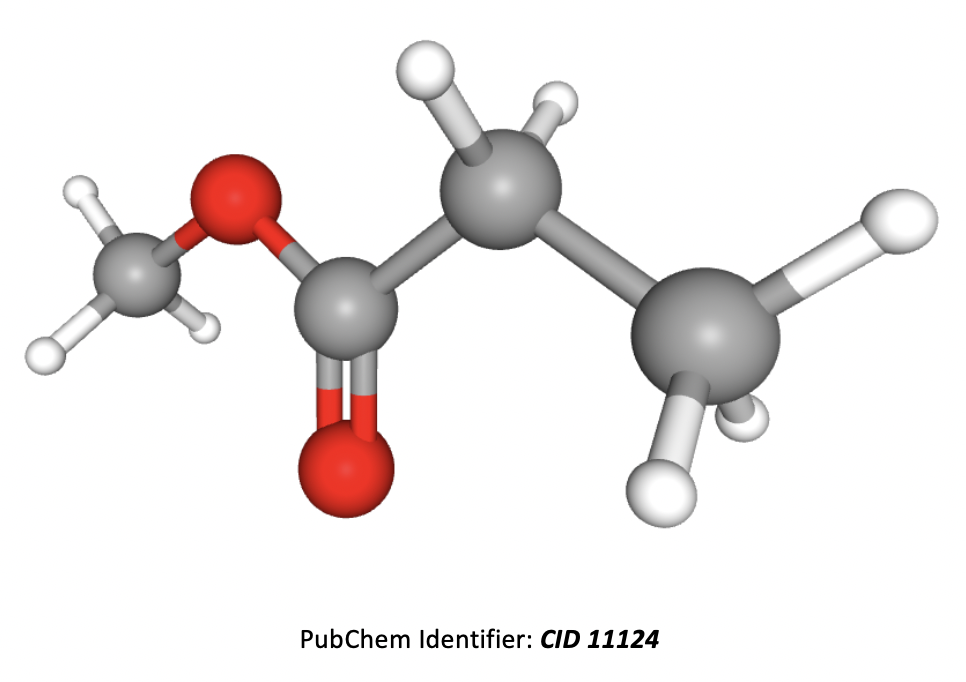
Esters are named by the 'alcohol bit' first then the 'acid bit', that is firstly the carbon chain section that is directly attached to the oxygen atom by a single bond, then the carbon chain section that includes the C=O.
Formulae 1 represents methyl propanoate. Formulae 2 represents ethyl ethanoate. Formulae 3 also represents methyl propanote.
Therefore 2 only is the correct answer.
Which of the following compounds is an amide?
It is important to thoroughly learn all of the functional groups and the classes of compounds by heart.
The amide group is 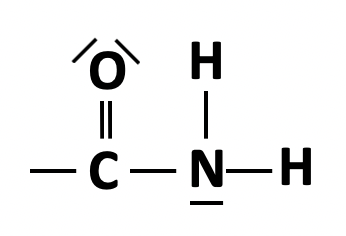 represented in structural formula by CONH2.
represented in structural formula by CONH2.
Therefore CH3CH2CONH2 is the correct answer.
Which of the following compounds is an alkene?
It is important to thoroughly learn all of the functional groups and the classes of compounds by heart,a nd to be confident in drawing out displayed formulae from structural formula.
CH3CCH is propyne (CH3C≡CH), CH3CH2CH3 is propane, CH3CH(CH3)CH3 is methyl propane, and CH3CH2CHCH2 is but-1-ene.
Therefore CH3CH2CHCH2 is the correct answer.
What is the correct IUPAC name for the compound below?
Grey atoms are carbon, white are hydrogen, and green are chlorine.
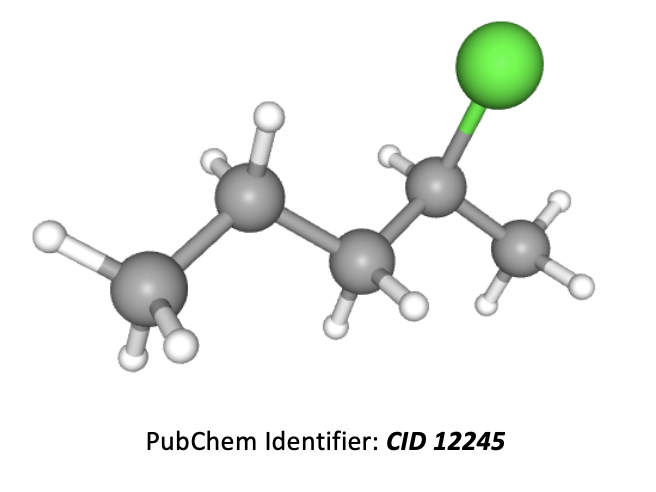
The longest carbon chain is 5 atoms, so the root of the name is pentane. A chlorine atom in an organic molecule is named with the prefix 'chloro' and the number (before it) is used to indicate the numbered carbon in the chain that it is found on. Numbers should be kept as low as possible.
Thus the correct answer is 2-chloropentane.
What is the correct IUPAC name for the compound below?
Grey atoms are carbon, white are hydrogen, and red are oxygen.
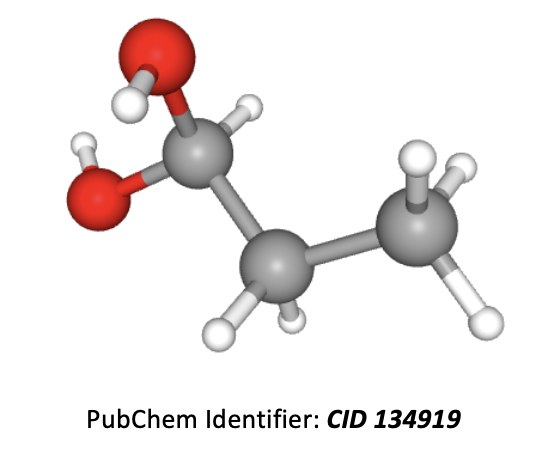
The longest carbon chain is 3 atoms, so the root of the name is propane. An OH group in an organic molecule is named with the prefix 'hydroxy' or a suffix (preferred) of 'ol' and the number (before it) is used to indicate the numbered carbon in the chain that it is found on. Numbers should be kept as low as possible. Two groups the same (as here) also require the prefix 'di'.
Thus the correct answer is Propan-1,1-diol.
Which of the following molecules represent pentane or structural isomers of pentane?
1: CH3CH2CH2CH3
2: CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH3
3: CH3CH2CHCHCH3
Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12 and is a straight chain hydrocarbon. Isomers of pentane have the same molecular formula but different structures.
Molecule 1 is butane with formula C4H10. Molecule 2 is methylbutane (C5H12). Molecule 3 is pent-2-ene (C5H10). Only methylbutane is an isomer of pentane.
Therefore 2 only is the correct answer.
Which of the following molecules are secondary alcohols?
1: propan-1-ol
2: propan-2-ol
3: CH3CH2CHOHCH3
A secondary alcohol has a hydroxyl group (−OH) that is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to two other carbon atoms.
This is the case for molecule 2: propan-2-ol (CH3CHOHCH3) and for molecule 3: CH3CH2CHOHCH3 (butan-2-ol).
Therefore 2 and 3 only is the correct answer.
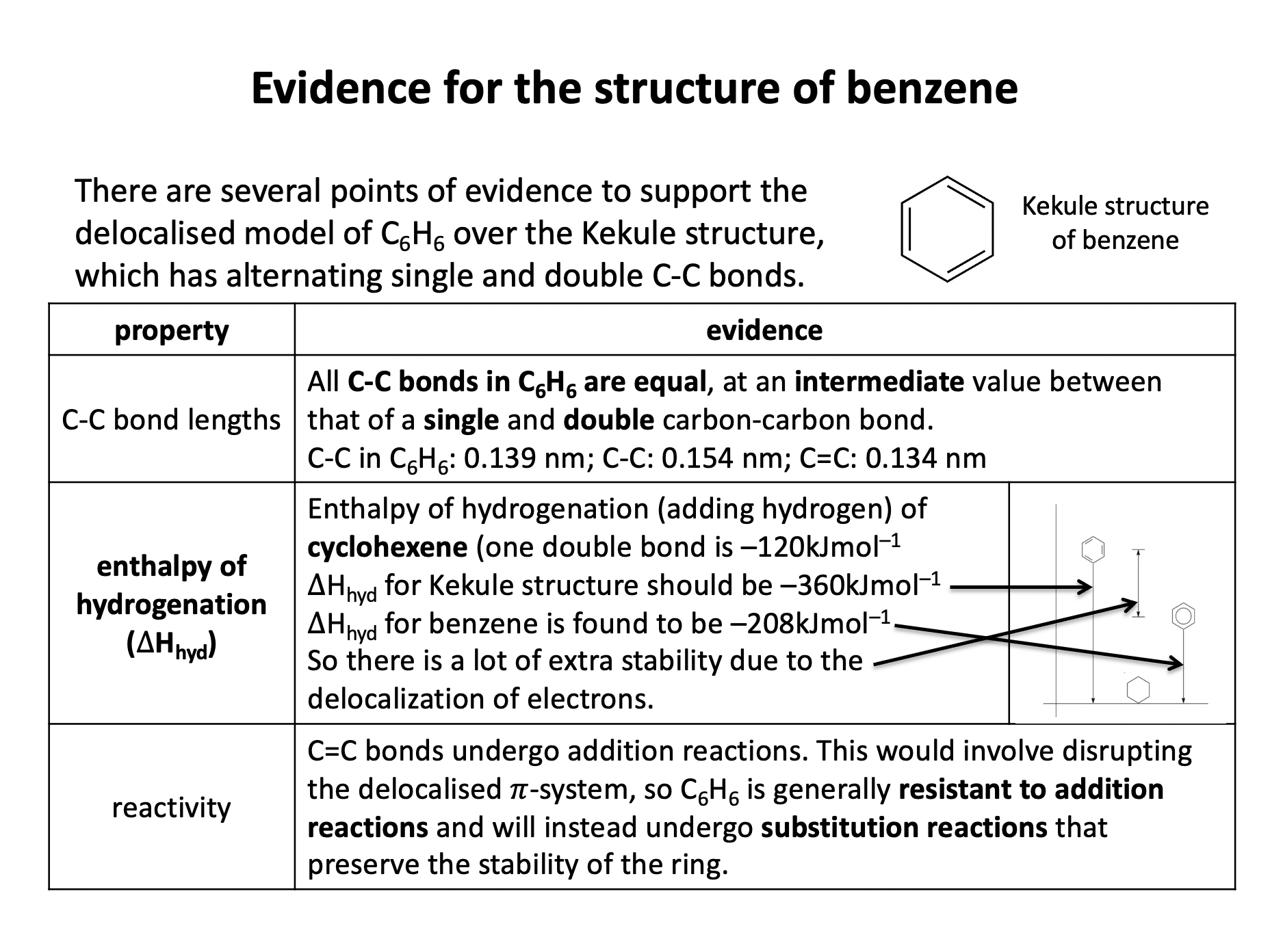
Which of the following statements about benzene (C6H6) are true?
1: Benzene has a planar structure
2: Benzene has three double carbon-carbon bonds
3: Benzene will not react with bromine in an addition reaction
Benzene is a planar molecule, with the six carbon atoms forming the shape of a regular hexagon. The carbon-carbon bonds are all the same length, but that is an intermediate length between a double and single bond. Although we sometimes draw it with three double (C=C) and three single (C−C) bonds, it does not possess double bonds because benzene is a delocalised structure. The delocalised structure gives benzene extra stability.
Therefore statement 1 and 3 only are correct, but statement 2 is not correct; the bonds are delocalised and all of an intermediate length.
Paper 1
Core (SL&HL): Organic chemistry core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions
AHL (HL only): Organic chemistry AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions
Paper 2
Core (SL&HL): Organic chemistry core (SL & HL) paper 2 questions
AHL (HL only): Organic chemistry AHL (HL only) paper 2 questions
How much of Fundamentals of organic chemistry have you understood?







 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn