Topics 20.1 to 20.3
Paper 1 style questions are multiple choice. You are not permitted to use a calculator or the data book for these questions, but you should use a periodic table.
A periodic table pop-up is available on the left hand menu.
Which compound will react the most rapidly when the halogen is substituted by aqueous hydroxide ions?
Secondary haloalkanes (CH3CHClCH3) react slower than primary haloalkanes (CH3CH2Br; CH3CH2Cl), as secondary tend to react via both the SN1 and SN2 mechanisms rather slowly. Primary haloalkanes react faster than secondary; they react via SN2. Tertiary haloalkanes ((CH3)3CCl) react the fastest; they react via SN1.
(Within a primary/secondary/tertiary series, iodoalkanes react faster than bromoalkanes, that react faster than chloroalkanes because the bonds are longer and weaker. Bond length: C−I > C−Br > C−Cl bond.)
Therefore (CH3)3Cl is the correct answer.
Which reagent/s will react with butanone to produce a new organic product?
1: K2Cr2O7 / H+
2: NaBH4(aq) followed by reaction with H+
Ketones (CH3CH2COCH3 is butanone) cannot be oxidised using K2Cr2O7 / H+.
However, they can be reduced to secondary alcohols (in this case butan-2-ol) using NaBH4(aq) followed by reaction with H+.
Therefore 2 only is the correct answer.
Which is the major product of the electrophilic addition reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide?
This is a Markovnikov electrophilic addition reaction mechanism.
The hydrogen bromide (H−Br) will add across the double bond. CH3CHBrCH2Br has two bromine atoms added, and CH3CH=CHBr still has a double bond, so these are both incorrect answers.
The mechanism will go preferentially via the secondary carbocation (positive inductive effect makes the secondary more stable) and produce 2-bromopropane (CH3CHBrCH3) rather than 1-bromopropane (CH3CH2CH2Br) which is formed via the primary carbocation.
Therefore CH3CHBrCH3 is the correct answer.
Which solvent is aprotic?
Polar protic solvents can form H-bonds, e.g. water and ethanol, and they favour SN1, as they are effective at stabilising the carbocation and negative nucleophile. Polar aprotic solvents cannot form H-bonds, e.g. propanone and ethoxyethane, and they favour SN2.
All the solvent molecules shown here can form H-bonds apart from CH3COCH3, propanone.
CH3COCH3 is therefore the correct answer.
Which of the following statements about benzene are true?
1: Benzene has a planar structure.
2: Benzene will react with NO2+ in an electrophilic substitution reaction.
3: Benzene will react with Br2 in an electrophilic addition reaction.
Benzene is a planar molecule, with the six carbon atoms forming the shape of a regular hexagon. The carbon-carbon bonds are all the same length, but that is an intermediate length between a double and single bond ('bond order' 1.5). Although we sometimes draw it with three double (C=C) and three single (C−C) bonds, it does not possess double bonds because benzene is a delocalised structure. The delocalised structure gives benzene extra stability.
The extra stability means that benzene will not react with Br2 in an electrophilic addition reaction, since that would disrupt the delocalisation. Benzene will however react with NO2+ in an electrophilic substitution reaction, since the delocalisation is maintained in the product.
Therefore statement 1 and 2 only are correct.
Which compound shows cis-trans isomerism?
Cis-trans isomerism is shown by compounds when the two substituents attached to both of the carbon atoms of the C=C double bond are different, or when two substituents are on different carbon atoms in a cyclic carbon compound.
1,2-dimethylcyclobutane is shown below:
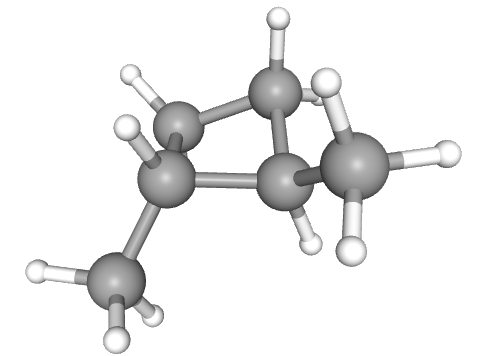
1,2-dimethylcyclobutane will show cis-trans isomerism, since there is no free rotation around the bonds in the ring, so the two methyl groups can be oriented 'up' from the plane of the ring, or 'down' from the plane of the ring. This diagram shows trans (one 'up' and one 'down').
The other compounds all have two substituents that are the same attached to one of the carbon atoms of the double bond, or have no substituents attached to the ring in the case of cyclobutane.
Therefore 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane is the correct answer.
Which statement/s about the reaction of an organic compound with aqueous hydroxide ions is/are correct?
1: 1-bromopropane predominantly follows an SN1 mechanism.
2: 2-bromo-2-methylpropane predominantly follows an SN2 mechanism.
3: Reaction with 1-bromopropane occurs at a faster rate than with 1-chloropropane.
Primary haloalkanes (1-bromopropane) react via an SN2 mechanism. Tertiary haloalkanes (2-bromo-2-methylpropane) react via an SN1 mechanism. So neither statement 1 nor 2 are correct.
Within a primary/secondary/tertiary series, iodoalkanes react faster than bromoalkanes, that react faster than chloroalkanes because the bonds are longer and weaker. Bond length: C−I > C−Br > C−Cl bond. So statement 3 is correct.
Therefore 3 only is the correct answer.
How many chiral carbon atoms are present in one molecule of CH3CBr(CH3)CH2CHBrCH3?
A chiral carbon atom, is a carbon atom with four different substituents attached.
CH3CBr(CH3)CH2CHBrCH3 is 2,4-dibromo-2-methyl-pentane and is shown below:
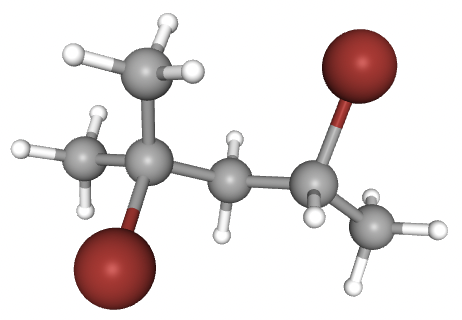
The fourth carbon atom in the chain has four different substituents attached and so is chiral. The other carbons are not chiral (any carbon with 2 or more hydrogen atoms attached cannot be chiral and the second carbon has two CH3 groups attached).
Therefore 1 is the correct answer.
What is the name of this compound (applying IUPAC rules)?
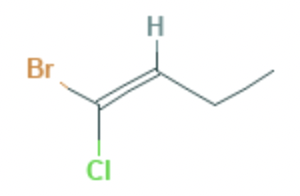
In E/Z isomerism each substituent is given a priority according to the atomic number (Z) of the atom attached to the carbon. Moving to the next atom in the event of a ‘draw’. The highest substituents on each carbon atom are then compared to see if they are E (entgegen) or Z (zusammen) relative to one-another.
In this molecule, across the double bond, the bromine atom (Z=35) has higher priority than chlorine (Z=17) on carbon 1 and the carbon atom (Z=6) has higher priority than hydrogen (Z=1) on carbon 2.
In this molecule, the highest priorities are therefore on the opposite side of the carbon chain and therefore the E, 'entgegen', isomer.
The molecule has four carbons in the longest chain, so the full name is: (E)-1-bromo-1-chlorobut-1-ene which is therefore the correct answer.
Which reagents and catalysts are needed to convert benzene to phenylamine in three steps?
C6H6 → C6H5NO2 → C6H5NH2
Organic reaction types, reagents, catalysts and conditions need to be learned.
Nitration of benzene (C6H6) is carried out using concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid in a 'nitrating mixture'. (The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, as it is re-produced at the end of the reaction.)
Conversion of nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2) to phenylamine (C6H5NH2) is carried out in a two step process: using tin (Sn) and concentrated hydrochloric acid first, and then in a second step, using sodium hydroxide.
Therefore Step 1 conc. HNO3 and conc. H2SO4; Step 2 Sn and conc. HCl; Step 3 dilute NaOH (aq) is the correct answer.
Which substitution mechanism do these reactions undergo?
Reaction 1: C6H6 → C6H5Cl
Reaction 2: C6H5CH3 → C6H5CH2Cl
Organic reaction types, reagents, catalysts and conditions need to be learned.
The substitution of hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring can only be carried out by electrophilic substitution. The nitration of benzene is the example we usually see, but other atoms/groups can be substituted in by the same mechanism.
The substitution of hydrogen atoms on an alkyl group (or alkane) by halogens is carried out by free radical substitution. (Note that the substitution in reaction 2 is on the alkyl chain and not on the benzene ring.)
Therefore Reaction 1: Electrophilic Reaction 2: Free radical is the correct answer.
Which is the final major organic product (Compound Z) when propene (CH3CHCH2) undergoes this reaction sequence?
Reaction 1: CH3CHCH2 + HCl → Organic compound X
Reaction 2: Organic compound X + NaOH (aq) → Organic compound Y
Reaction 3: (Carried out with Cr2O72−/H+) Organic compound Y + [O] → Organic compound Z
Organic reaction types, reagents, catalysts and conditions need to be learned.
Reaction 1 is a Markovnikov electrophilic addition reaction. The hydrogen chloride (H−Cl) will add across the double bond. The mechanism will go preferentially via the secondary carbocation (positive inductive effect makes the secondary more stable) and produce 2-chloropropane (CH3CHClCH3).
Reaction 2 is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the chlorine atom will be substituted by the hydroxyl group, forming propan-2-ol (CH3CHOHCH3).
Reaction 3 is an oxidation reaction. The secondary alcohol, propan-2-ol, will form a ketone when oxidsed with acidified dichromate ions, that is propanone (CH3COCH3).
Therefore CH3COCH3 is the correct answer.
How much of Organic chemistry AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn