Topic 6.1
Paper 1 style questions are multiple choice. You are not permitted to use a calculator or the data book for these questions, but you should use a periodic table.
A periodic table pop-up is available on the left hand menu.
The diagram below represents a Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution of a gas at a temperature, T.
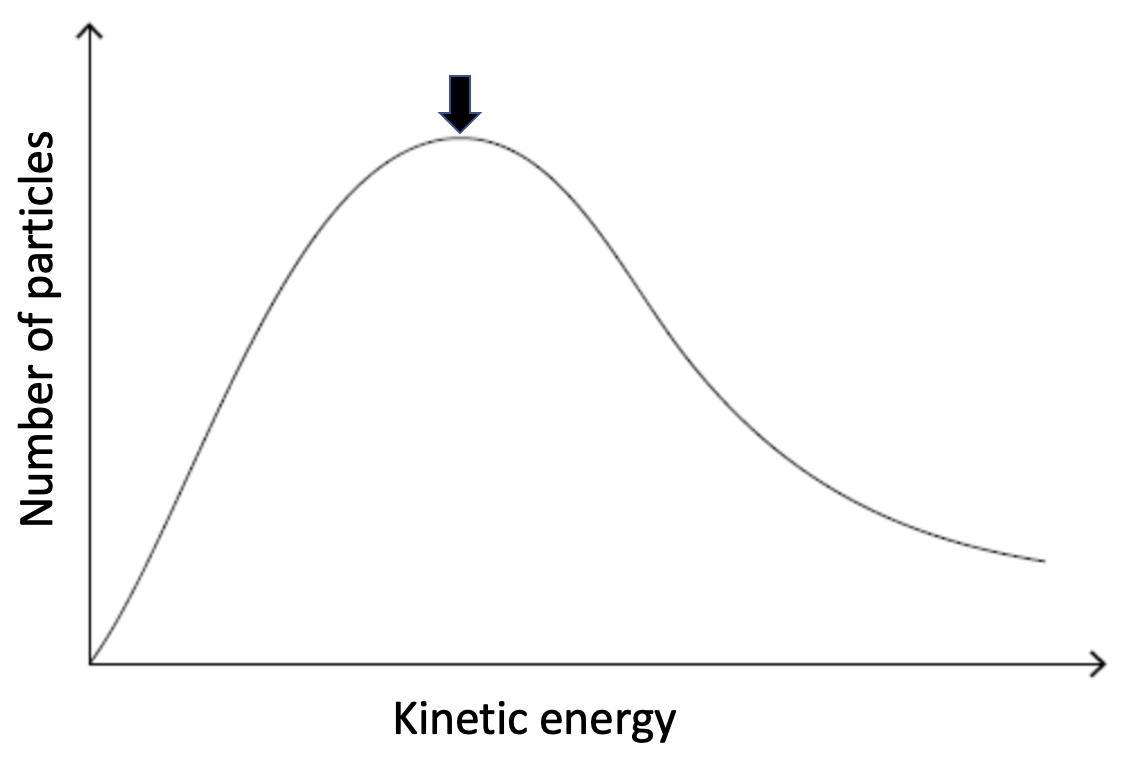
How will the curve change if the temperature is decreased, while other conditions remain constant?
If the temperature is decreased particles will gain kinetic energy, but the number of particles will remain the same. Thus, the distribution will pull together, the peak of the distribution will be higher and move to the left. See the example below.
The maximum is higher than and to the left of the arrow is therefore the correct answer.
Which properties may be monitored to determine the rate of reaction?
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
1: The change in total volume of solution
2: The change in colour of the solution
3: The change in temperature of the solution
Copper sulfate is blue. The colour will fade as the reaction proceeds, so colour of solution may be monitored.
The reaction is a replacement (displacement) reaction and so it is exothermic. Therefore the temperature change may be monitored.
The total volume of the solution will not change.
2 and 3 only is the correct answer.
The dotted line represents the volume of hydrogen gas evolved over time when excess magnesium ribbon is added to hydrochloric acid.
Which line represents the production of hydrogen gas when excess magnesium ribbon is added to the same volume of hydrochloric acid with half the concentration.
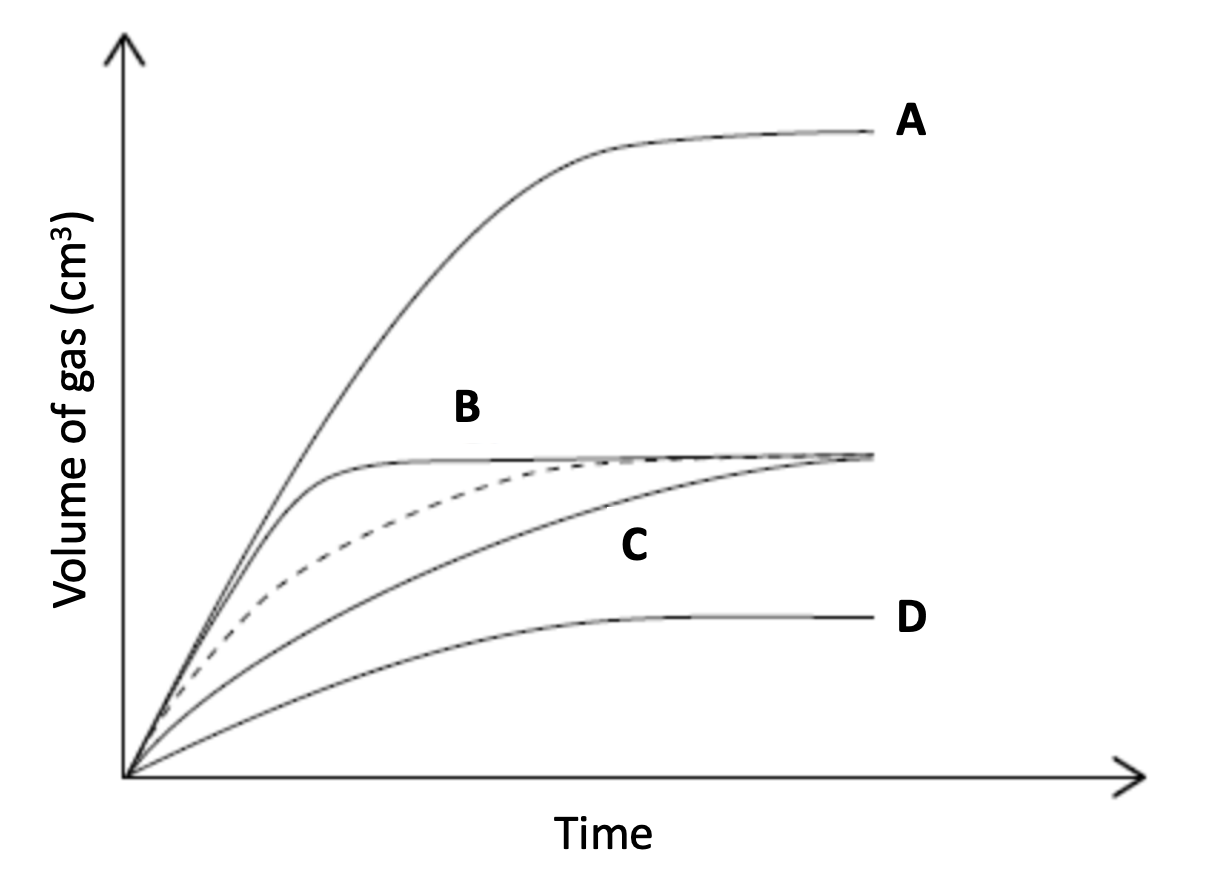
Magnesium and hydrochloric acid react to produce hydrogen gas:
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
The magnesium is in excess.
The change to the concentration of hydrochloric acid will decrease the frequency of the collisions, which will result in fewer successful collisions per unit time; the rate of reaction will decrease. Lines C and D have a shallower curve and therefore a slower rate.
However, there is also half the amount of hydrochloric acid (since the volume remains the same), so there will be half the amount of hydrogen produced at the end of the reaction.
Therefore Line D is the correct answer.
The dotted line represents the volume of oxygen gas (O2) evolved over time when a sample of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) decomposes.
Which line represents the production of oxygen gas when a catalyst is added to the same volume of hydrogen peroxide decomposing under the same conditions?

Hydrogen peroxide can decompose to produce oxygen gas:
H2O2 → ½O2 + H2O
The introduction of a catalyst will increase the rate of reaction by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction, of lower activation energy. So the line must be steeper than the dotted line.
However, there is the same amount of hydrogen peroxide so the same amount of oxygen will be produced at the end of the reaction.
Therefore Line B is the correct answer.
Which represents the activation energy for the reverse reaction?
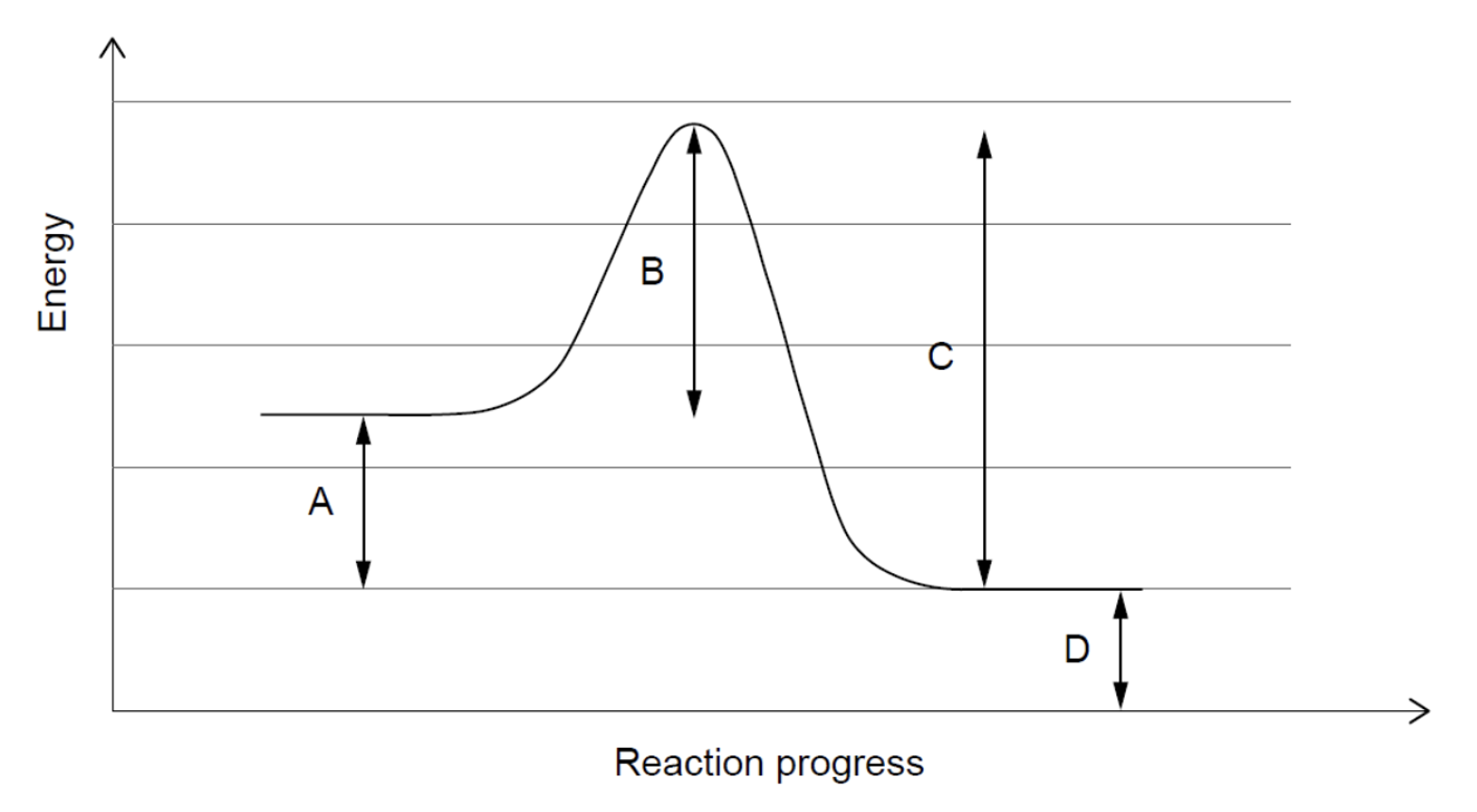
A is the difference in energy/enthalpy between reactants and products.
B is the activation energy for the forward reaction.
C is the activation energy of the reverse reaction.
D is a meaningless quantity.
Therefore Line C is the correct answer.
Several reactions of calcium carbonate chips with dilute hydrochloric acid are carried out at room temperature.
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
Which of the following has the greatest initial rate of reaction?
1: 100cm3 of 0.2 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with 3.0g of large CaCO3 (s) chips.
2: 100cm3 of 0.4 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with 3.0g of small CaCO3 (s) chips.
3: 100cm3 of 0.4 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with 3.0g of large CaCO3 (s) chips.
Using small calcium carbonate chips increases the surface area of the calcium carbonate. This will increase the frequency of the collisions, and the rate of reaction will be greater.
Using a higher concentration of HCl (0.4 rather than 0.2) also increases the frequency of the collisions, and the rate of reaction will be greater.
Therefore, 100cm3 of 0.4 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with 3.0g of small CaCO3 (s) chips will give the greatest initial rate.
Thus, 2 only is the correct answer.
Several reactions of excess solid sodium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid are carried out at room temperature.
Na2CO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
1: 100cm3 of 0.2 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with excess Na2CO3 (s).
2: 50cm3 of 0.4 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with excess Na2CO3 (s).
3: 100cm3 of 0.4 mol dm−3 HCl (aq) reacting with excess Na2CO3 (s).
Which statement is correct?
Reaction 1 uses the same moles of acid as reaction 2 (moles = concentration × volume), although the acid in reaction 2 is more concentrated, so reaction 2 will have a greater initial rate of reaction than reaction 1.
Reaction 3 uses twice the moles of reactions 1 and 2, although the concentration of the acid is the same as in reaction 2.
Therefore, Reactions 1 and 2 will produce the same total mass of CO2 is the only statement that is correct.
Which changes would increase the rate of reaction when zinc reacts with excess copper sulfate solution, assuming that all other conditions remain the same?
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
1: Increasing the temperature
2: Using larger pieces of Zinc (of the same mass)
3: Diluting the copper sulfate solution by adding water
Increasing the temperature of the reaction will increase the rate by increasing the frequency and energy of the collisions.
Using larger pieces of zinc will decrease the rate, since the zinc will have a smaller surface area, so will result in a decrease in the frequency of collisions.
Diluting the copper sulfate solution will decrease the rate, since the lower concentration of solution will result in a decrease in the frequency of collisions.
1 only is the correct answer.
Excess magnesium ribbon was added to hydrochloric acid, and the mass of the reaction vessel was monitored over time to give line X.
If the reaction was repeated, which change could give line Y, assuming all other conditions remained the same.
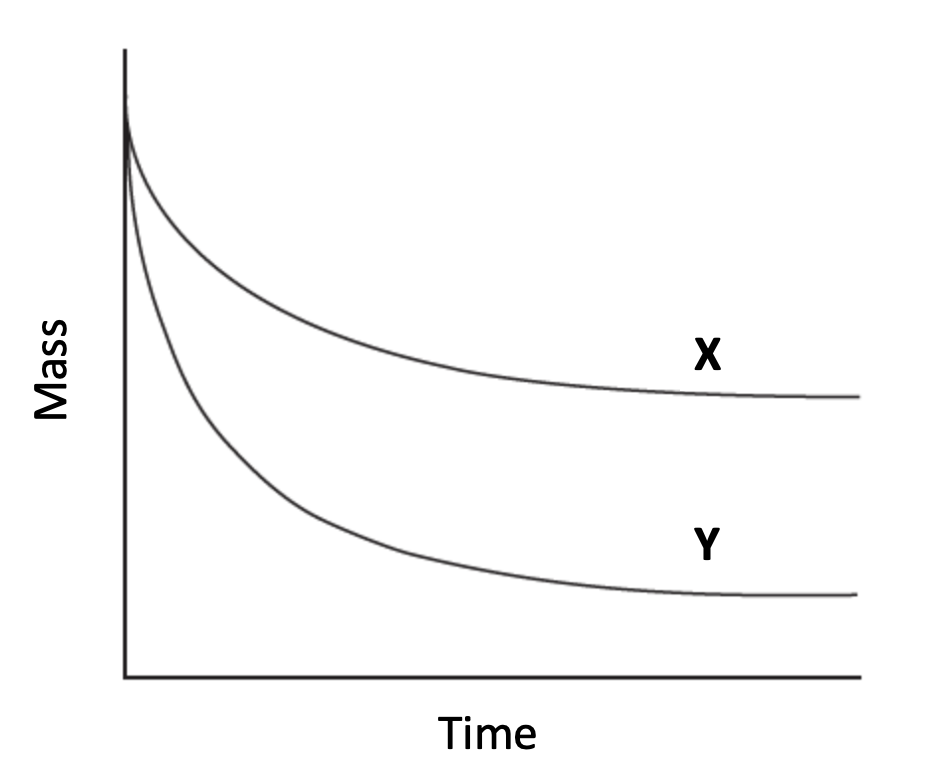
Magnesium and hydrochloric acid react to produce hydrogen gas:
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
The magnesium is in excess. Therefore, any change to the magnesium, or indeed a change in temperature, will not alter the total mass lost at the end of the experiment (even if the initial rate - the decline in the mass - is stepper).
Only using more concentrated hydrochloric acid will increase the total mass lost, so Using more concentrated hydrochloric acid is the correct answer.
Which of the following is/are true with respect to the action of a catalyst on increasing the rate of a chemical reaction?
1: The activation energy decreases
2: A greater proportion of particles have enough energy needed to react
3: There are a greater number of particle collisions
A catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by causing the reaction to follow a different reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Lowering the activation energy increases the number/proportion of the particles that have enough energy needed to react. The catalyst does not otherwise affect the energy of the particles (or the position of equilibrium) - it does not increase the collision energy or collision frequency.
Thus 1 and 2 only is the correct answer.
How much of Kinetics core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn