Topic 9.1 and 9.2
Paper 1 style questions are multiple choice. You are not permitted to use a calculator or the data book for these questions, but you should use a periodic table.
A periodic table pop-up is available on the left hand menu.
In which species does sulfur have the same oxidation state as in SOCl2?
In SOCl2, the oxygen atom has an oxidation state of −2, the chlorine atoms both have −1, therefore the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4.
The only other species in which the sulfur has a +4 oxidation state is SO32−. Three oxygen atoms gives (3 × −2) = −6, the overall charge is 2−, so the sulfur atom must be +4.
SO32− is therefore the correct answer.
In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, what happens to the sodium ion?
In an electrolytic cell the external potential difference pushes electrons out to one electrode making it negative and pulls electrons in from another electrode, making it positive. The ions in the electrolyte are then attracted to the oppositely charged electrode where they gain electrons (if positive ions) or lose electrons (if negative ions) to form atoms.
The sodium ion, being Na+ will go to the negative electrode and gain an electron to become Na, which is reduction; RIG.
It goes to the negative electrode where it is reduced is therefore the correct answer.
Where does reduction occur in a voltaic cell?
Red Cat; An Ox. Reduction at the Cathode; Oxidation at the Anode. This is true in both types of cell.

In a voltaic cell the redox reaction generates the charges on the electrodes and causes the current to flow. The most active metal loses electrons (oxidation; atoms to ions) causing the electrode to be negative, and the least active metal gains electrons (reduction; ions to atoms) causing the electrode to be positive.
So in a voltaic cell metal ions will gain electrons (reduction) at the positive electrode. Cations go to the cathode and (in a voltaic cell) they make it positive.
At the cathode, which is the positive electrode is therefore the correct answer.
Which chemical species is the oxidising agent in this reaction?
2KMnO4 + 3Na2SO3 + H2O → 2MnO2 + 3Na2SO4 + 2KOH
An oxidising agent oxidises another element and therefore is itself reduced (OILRIG: if it takes electrons away from another element, it has gained electrons).
Oxidation state changes are needed:
Manganese goes from +7 to +4 (KMnO4 to MnO2).
Sulfur goes from +4 to +6 (Na2SO3 to Na2SO4).
Thus sulfur is oxidised (OIL) and manganese is reduced (RIG). The KMnO4 is the oxidising agent.
Consider the following cell:
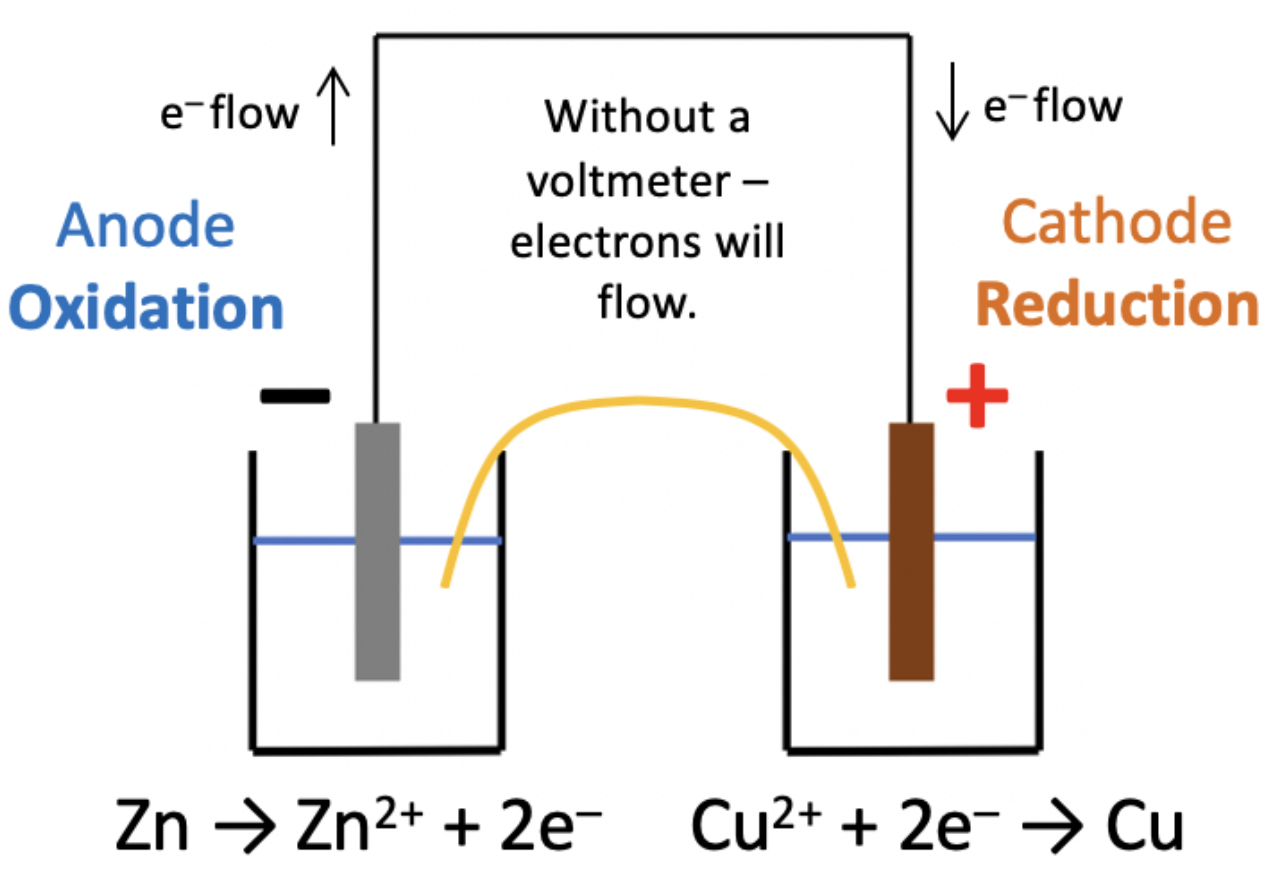
The salt bridge is made from filter paper soaked in saturated potassium nitrate (KNO3).
What happens to the ions in the salt bridge when the current flows?
In a voltaic cell the redox reaction generates the charges on the electrodes and causes the current to flow. The most active metal loses electrons (zinc) causing the electrode to be negative, and the least active metal (copper) gains electrons causing the electrode to be positive.
As electrons are flowing from zinc to copper, the charge will be equalised by negative ions flowing across the salt bridge to the zinc half-cell and positive ions flowing across to the copper half cell.
Thus K+ ions flow to copper half cell and NO3− ions flow to the zinc half cell is the correct answer.
The following reaction occurs in a voltaic cell:
Mg(s) + Zn2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Zn(s)
Which reaction takes place at each electrode?
In a voltaic cell the redox reaction generates the charges on the electrodes and causes the current to flow. The most active metal loses electrons (magnesium) causing the electrode to be negative, and the least active metal (zinc) gains electrons causing the electrode to be positive.
Negative electrode: Mg(s) → Mg2+(aq) + 2e− Positive electrode: Zn2+(aq) + 2e− → Zn(s) is therefore the correct answer.
Which of these reactions is not a redox reaction?
The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide is not a redox reaction as it involves some ion exchange without a change in oxidation state.
Oxidation states change in the three other reactions:
4Cl2 + CH4 → CCl4 + 4HCl (chlorine 0 to −1 and carbon −4 to +4)
CH3CH2OH + [O] → CH3CHO + H2O (carbon −2 to −1 and oxygen 0 to −2)
CO2 + C → 2CO (carbon from both +4 and 0 to +2)
Therefore Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2 + 2KNO3 is the correct answer.
This question refers to voltaic cells, but the only information needed is that zinc is more active than silver.
The strongest reducing agent (reduction is gain of electrons) is the species most likely to lose electrons and give them to something else, thereby reducing it. Zinc atoms have the greatest tendency to lose electrons as they are the most active (silver is less likely to lose electrons, and zinc and silver ions, having already lost electrons are unlikely to lose any more).
Thus the correct answer is Zn
Balance the following redox equation to give the lowest whole number ratio:
MnO4− + SO32− + H2O → MnO2 + SO42− + OH−
How many moles of SO42− ions are produced?
Always balance the electrons first by calculating changes in oxidation states:
Oxygen remains as −2 throughout.
Hydrogen remains as +1 throughout.
Sulfur (S) changes from +4 to +6 (loss of 2 electrons).
Manganese (Mn) changes from +7 to +4 (gain of 3 electrons).
To balance electrons lost and gained (6 electrons), three sulfur atoms and two manganese atoms are needed.
2MnO4− + 3SO32− + H2O → 2MnO2 + 3SO42− + OH−
Now atoms of other elements can be balanced:
2MnO4− + 3SO32− + H2O → 2MnO2 + 3SO42− + 2OH−
So the correct answer is 3.
What is the order of decreasing reactivity of the metals (most reactive first)?
Zn + CrSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cr
Ba + Zn(NO3)2 → Ba(NO3)2 + Zn
CrSO4 + Sb → no reaction
These reactions are replacement/displacement reactions.
Zn displaces Cr so in reactivity Zn > Cr
Ba displaces Zn so in reactivity Ba > Zn
Sb cannot displace Cr so in reactivity Cr > Sb
Ba > Zn > Cr > Sb is therefore the correct answer.
Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell?
1: A spontaneous redox reaction produces electrical energy.
2: Oxidation occurs at the anode (negative electrode).
3: The electrons flow from the cathode (positive electrode) to the anode (negative electrode).
Voltaic cells use spontaneous redox reactions to generate electrical energy. (Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous redox reactions.)
Thus statement 1 is correct.
In both types of electrolytic cell oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction occurs at the cathode. In a voltaic cell the anode is negative, and the cathode is positive. (In an electrolytic cell the anode is positive, and the cathode is negative.)
Thus statement 2 is correct.
In a voltaic cell the redox reaction causes the electrodes to become charged and this generates electron flow from negative electrode (anode) to positive electrode (cathode).
Thus statement 3 is incorrect.
Therefore 1 and 2 only is the correct answer.
Which statement is correct for the redox equation?
Sn2+(aq) + Ni (s) → Sn (s) + Ni2+ (aq)
In the reaction, tin (Sn) gains electrons. This means that it has been reduced (reduction is gain of electrons). Therefore, the nickel is the reducing agent, since it reduces the tin.
Each nickel atom loses two electrons to form a nickel ion. This means that it has been oxidised (oxidation is loss of electrons). Therefore, the tin (Sn) is the oxidising agent, since it oxidises the nickel.
Therefore Sn2+ is reduced and Ni is the reducing agent is the correct answer.
How much of Redox core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn