 Concept wise, this is not the most challenging section of the course, but there is so much detail that it can seem very daunting. The more you commit to memory the more confident you will feel with the organic section of the course. An organic compound is classified according to the specific functional groups that are present. Note that a distinction is made between class (type of compound - e.g. alcohol) and functional group (reactive site in compound - e.g. hydroxyl). Use the flash cards to learn the vocabulary and conventions used in organic chemistry thoroughly. Each class of organic compounds is associated with characteristic reactions and you should use the revision cards and practice questions to drill yourself in recognising these. Pay particular attention to what is happening to the formulae and functional groups as reactions take place.
Concept wise, this is not the most challenging section of the course, but there is so much detail that it can seem very daunting. The more you commit to memory the more confident you will feel with the organic section of the course. An organic compound is classified according to the specific functional groups that are present. Note that a distinction is made between class (type of compound - e.g. alcohol) and functional group (reactive site in compound - e.g. hydroxyl). Use the flash cards to learn the vocabulary and conventions used in organic chemistry thoroughly. Each class of organic compounds is associated with characteristic reactions and you should use the revision cards and practice questions to drill yourself in recognising these. Pay particular attention to what is happening to the formulae and functional groups as reactions take place.
Ensure you are confident using the terms below and learn the asterisked* definitions
Hydrocarbon*, Saturated, Unsaturated, Free radical*, Nucleophile*, Electrophile*, Homolytic bond fission*, Heterolytic bond fission*
Which of the following is a saturated hydrocarbon?
A hydrocarbon is a compound of carbon and hydrogen only. Saturated compounds contain only single carbon-carbon bonds (no double bonds).
CH3CH2CHCH2 is but-1-ene and is unsaturated (but is a hydrocarbon). CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2OH both contain oxygen and therefore are not hydrocarbons.
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH3 is methylbutane, a saturated hydrocarbon and is the correct answer.
Which of the following statements explain why alkanes are relatively unreactive?
1: They have strong C−H and C−C bonds
2: The bonds are non-polar
3: They have delocalised electrons
Alkanes are relatively unreactive because they have strong carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds that require a lot of energy to break. In addition, the bonds are all non-polar, which means they are not vulnerable to attack by most chemical reagents.
Alkanes do not have delocalised electrons.
Therefore 1 and 2 only is the correct answer.
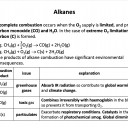
What is the sum of all coefficients when the following equation (the complete combustion of pentane) is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers?
___C5H12 + ___O2 → ___CO2 + ___H2O
C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O is the balanced equation, so the total sum is 20 - don't forget that C5H12 does have a '1' in front of it, although by convention we don't actually write that into the equation.
(When balancing combustion reactions of hydrocarbons, first balance out carbon and hydrogen atoms by adding coefficients (numbers) in front of CO2 and H2O, after that balance the oxygen atoms and the hydrocarbon as required.)
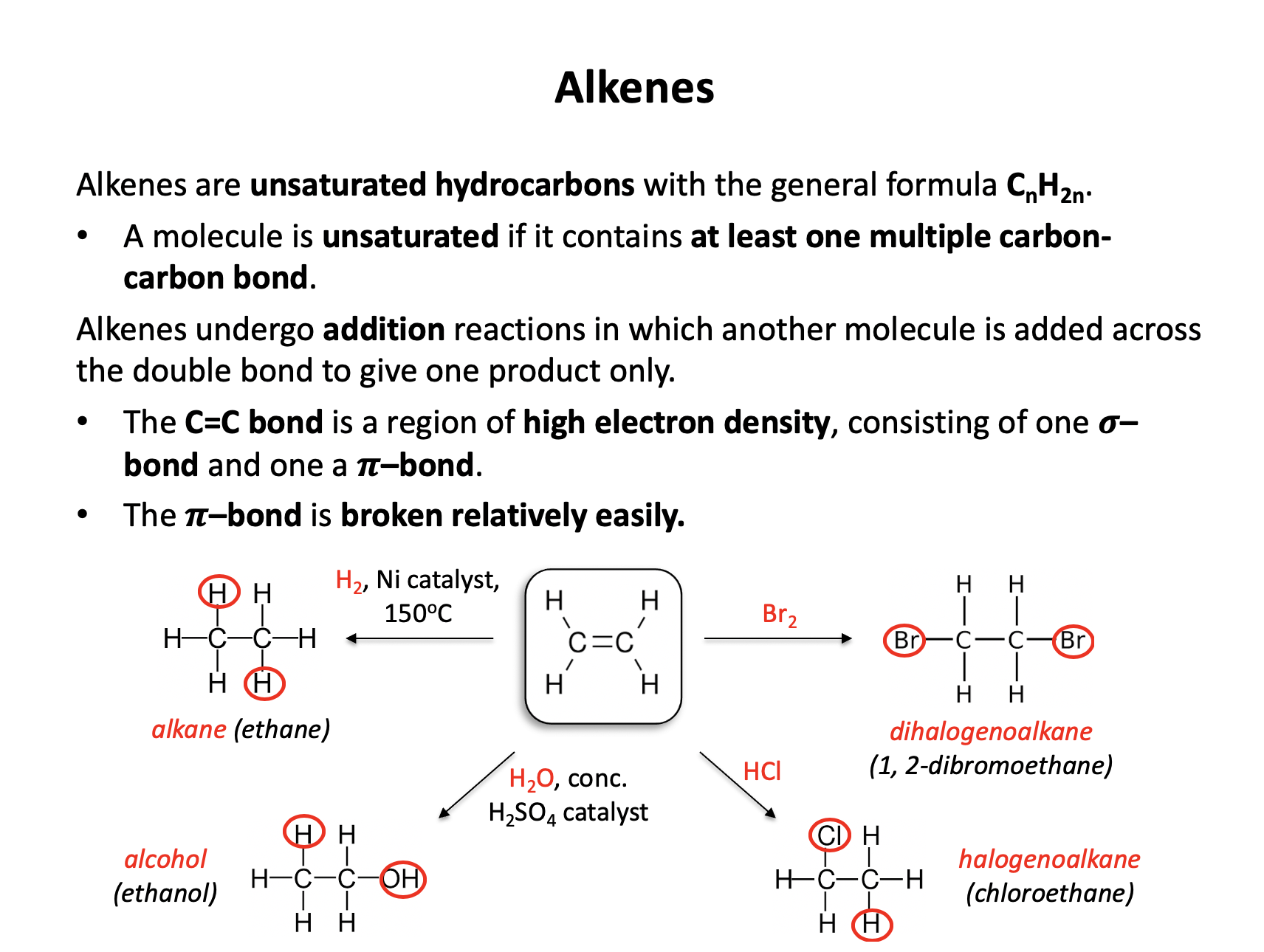
What is the product of the reaction between propene (CH3CHCH2) and bromine?
Propene contains a double carbon-carbon bond (C=C) that will readily undergo an addition reaction with bromine. The bromine molecule adds across the double bond, with one atom attaching to each carbon atom of the double bond.
Thus CH3CHBrCH2Br is the correct answer.
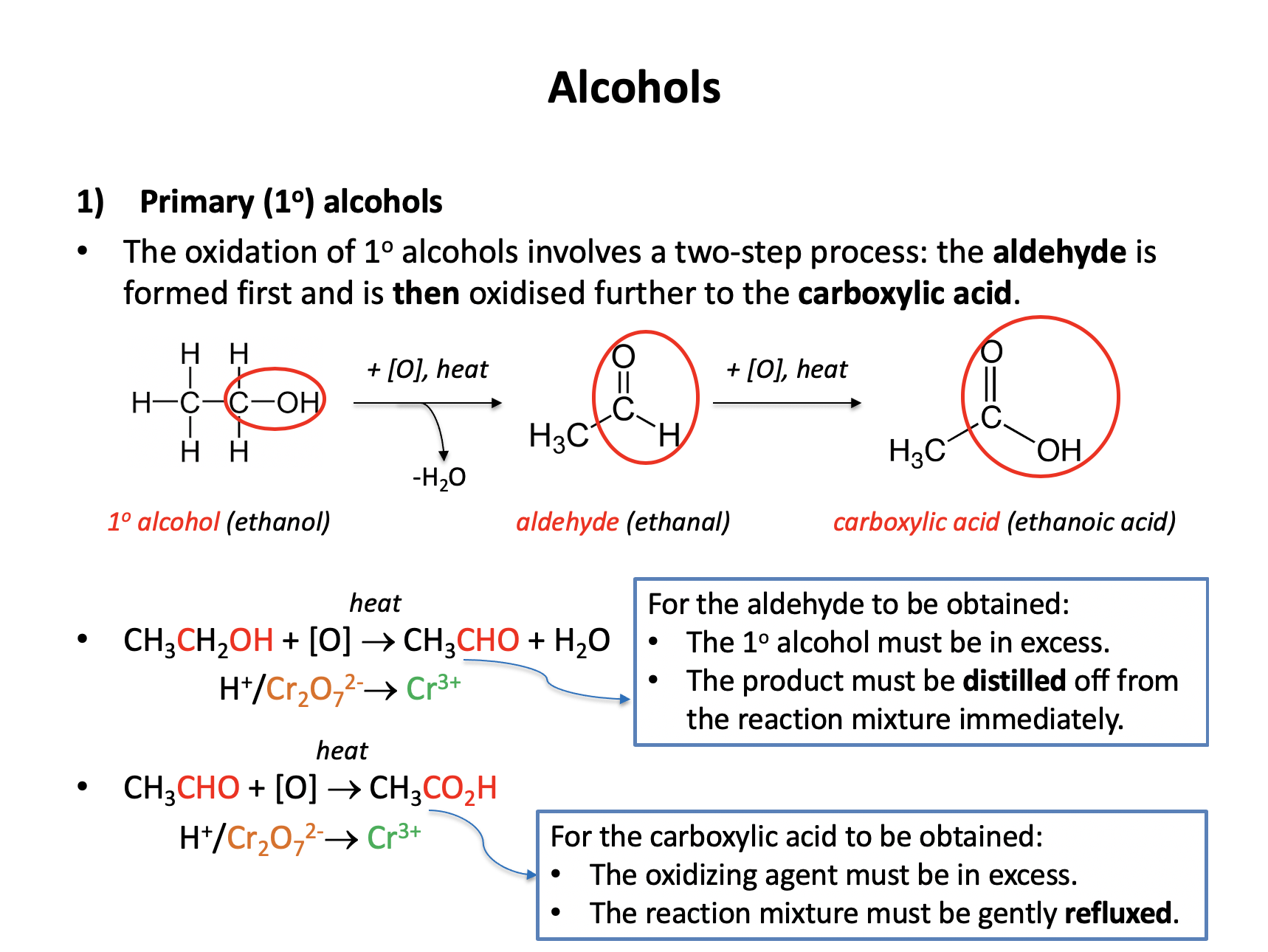
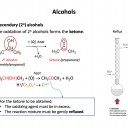
What is the major organic product at the end of the reaction when ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is refluxed with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) (H+/K2Cr2O7)?
Ethanol is a primary alcohol. When oxidised primary alcohols produce an aldehyde initially (must be distilled off immediately as formed) that then readily reacts further to form a carboxylic acid (under reflux).
Ethanol will therefore form ethanoic acid (CH3CO2H).
CH3CHO is an aldehyde (ethanal), CH3CH2CO2H is propanoic acid (too many carbons), CH3COOCH3 is methyl ethanoate, an ester.
CH3CO2H is the correct answer.
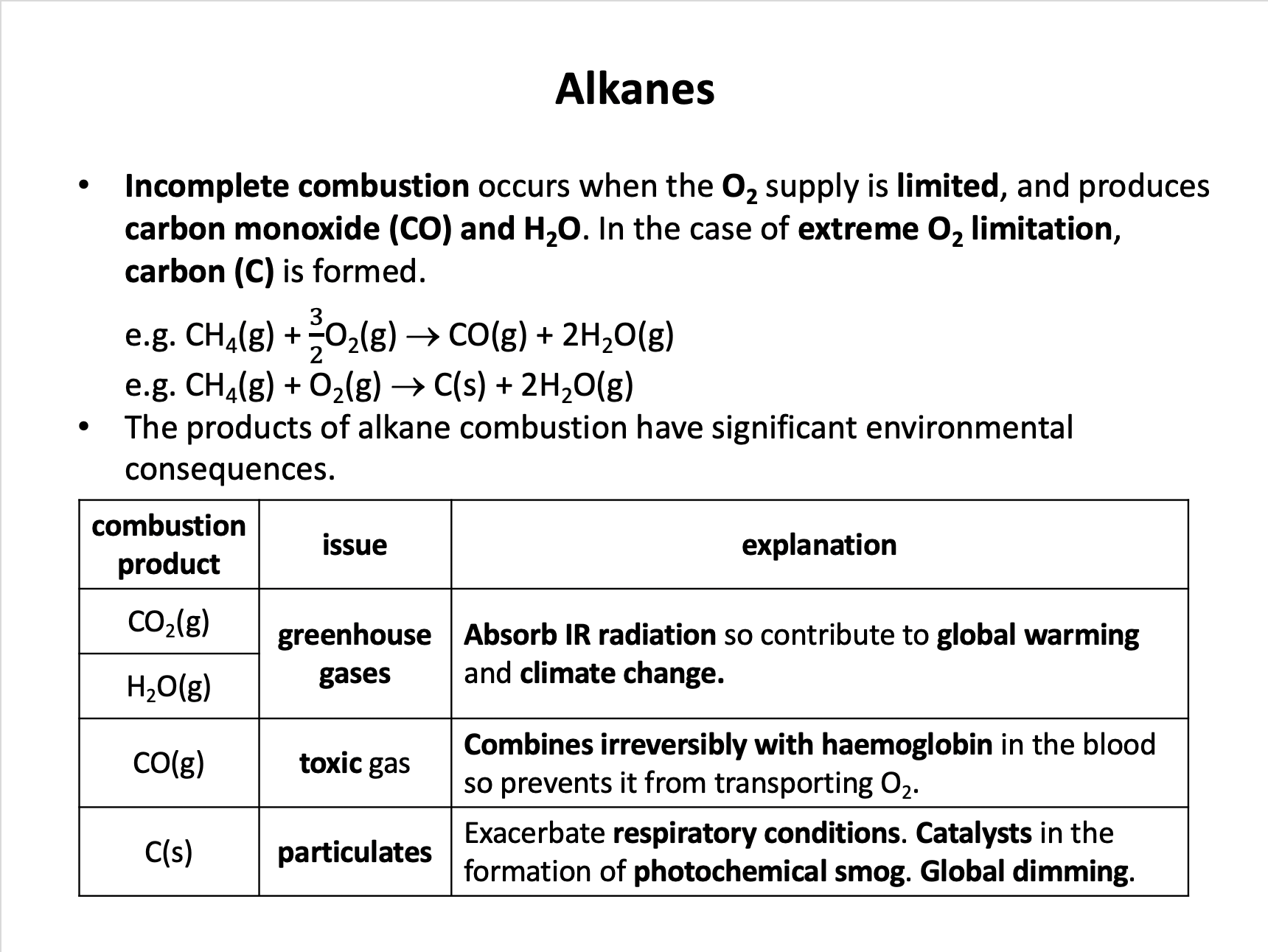
Which of the following could be formed during the incomplete combustion of octane fuel (C8H18)?
1: Carbon monoxide
2: Hydrogen
3: Carbon
Alkanes will completely combust in excess oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water. If there is insufficient oxygen then carbon monoxide and carbon (soot) may be formed. Hydrogen gas will never be formed (it is too reactive especially at high temperature).
Therefore 1 and 3 only is the correct answer.
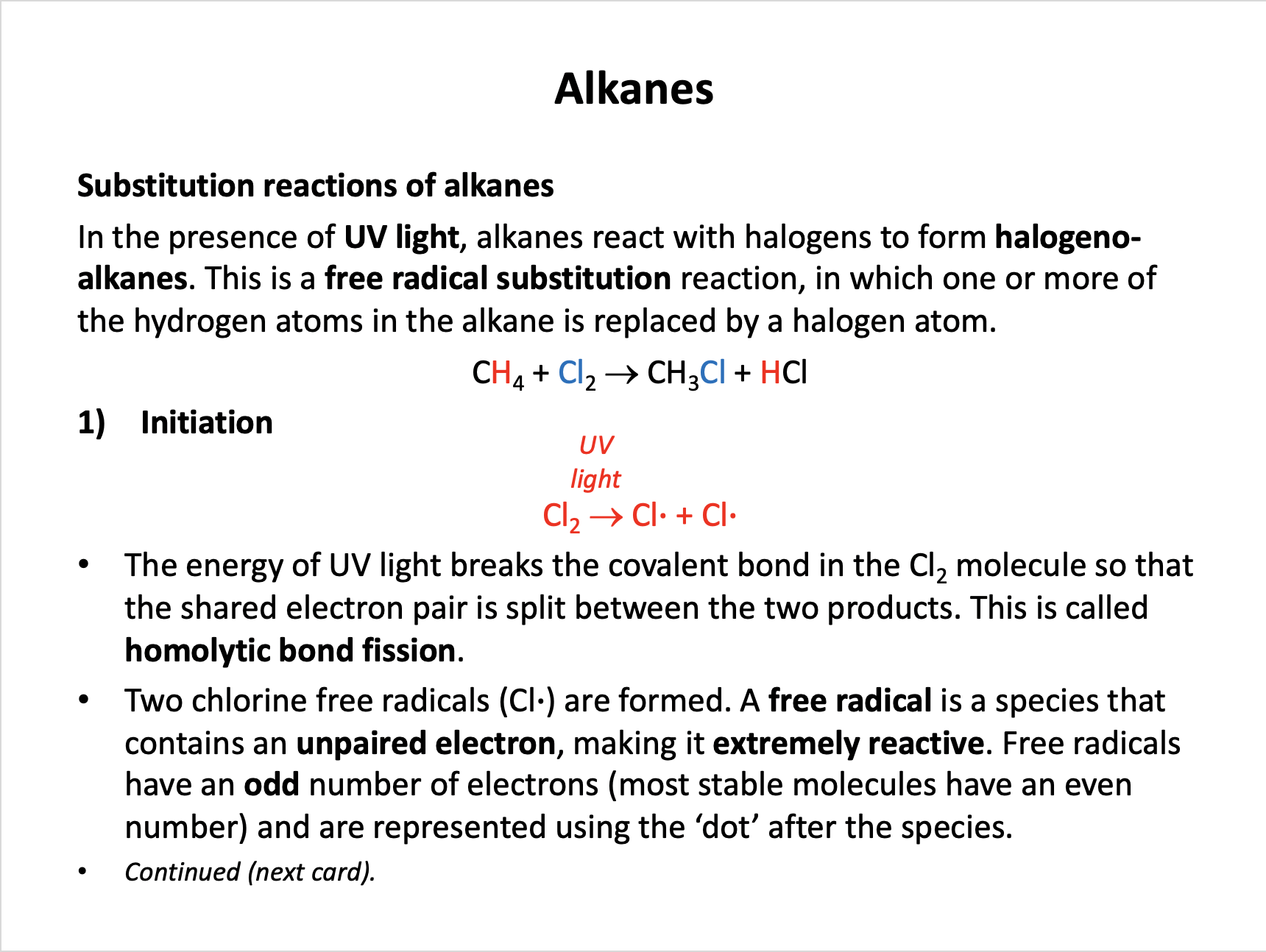
Which of the following statements about the free radical substitution reaction of methane and chlorine are true?
1: Chlorine undergoes homolytic fission
2: Ultraviolet light is required to produce the free radicals
3: Two free radicals are produced in the termination step
Typically in free radical substitution an alkane reacts with a halogen and hydrogen atoms are readily substituted with halogen atoms.
Initiation involves UV light breaking the halogen bond (homolytic fission) and producing two halogen free radicals (species with an unpaired electron - an odd number of electrons).
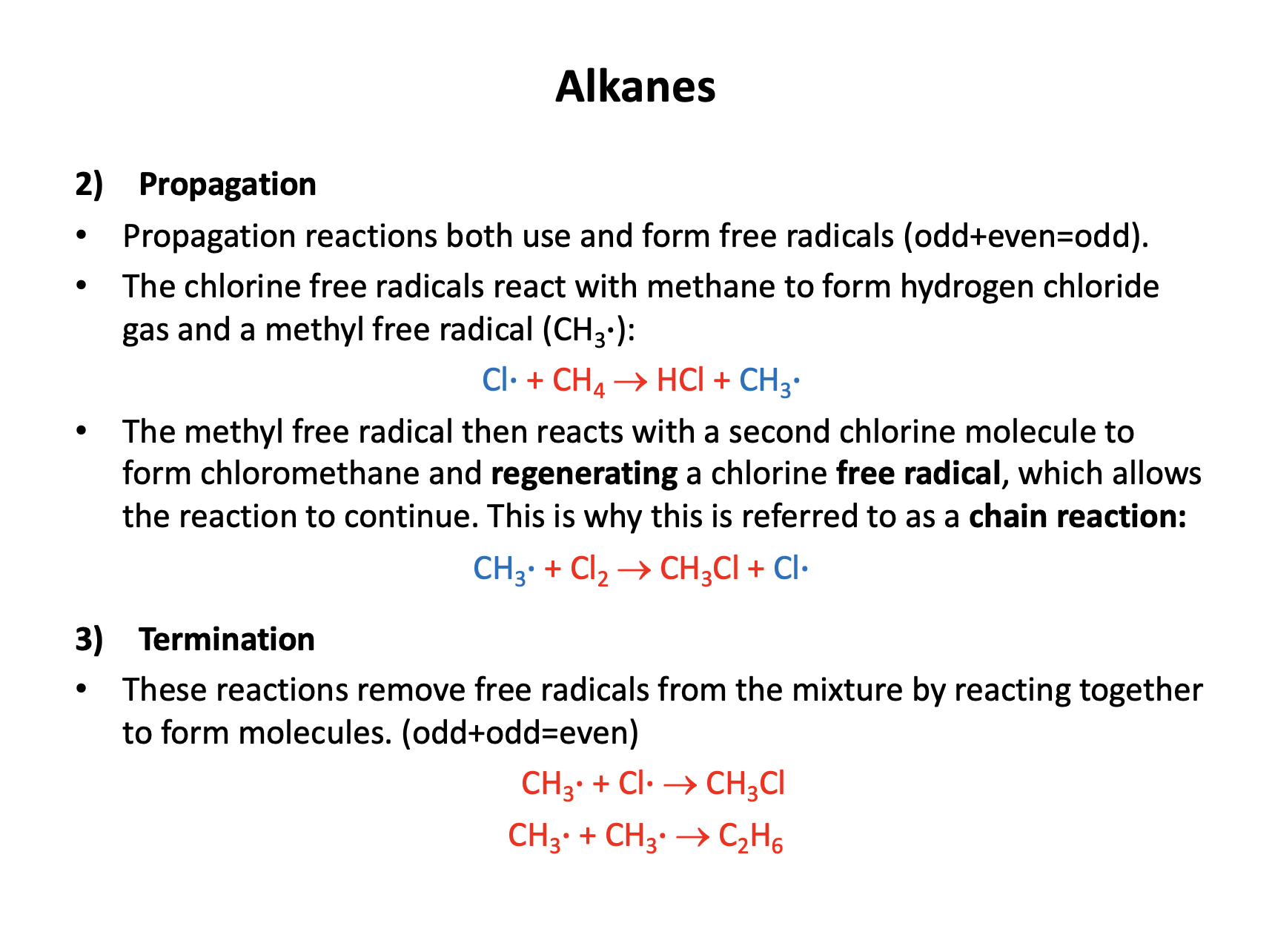
Propogation involves radicals (odd) reacting with non-radical species (even) to produce a radical (odd) and a non-radical (even).
Termination involves two free radicals (odd) coming together to produce a non-radical (even).
Therefore 1 and 2 only is the correct answer.
Ethene can react to form 1-chloroethane. Which reagent is best used to react with ethene to produce this product?
Ethene (CH2CH2) is an alkene with a double C=C bond that readily reacts through addition reactions.
1-chloroethane has formula CH3CH2Cl. HCl has been added to ethene, therefore HCl is the correct answer.
Addition of chlorine would produce 1,2-dichloroethane (CH2ClCH2Cl). Sodium chloride will not react with ethene (under any normal conditions) and exposure to UV light without a source of chlorine will not lead to a suitable product - even with chlorine this reaction would not be best used as the products would be very variable.
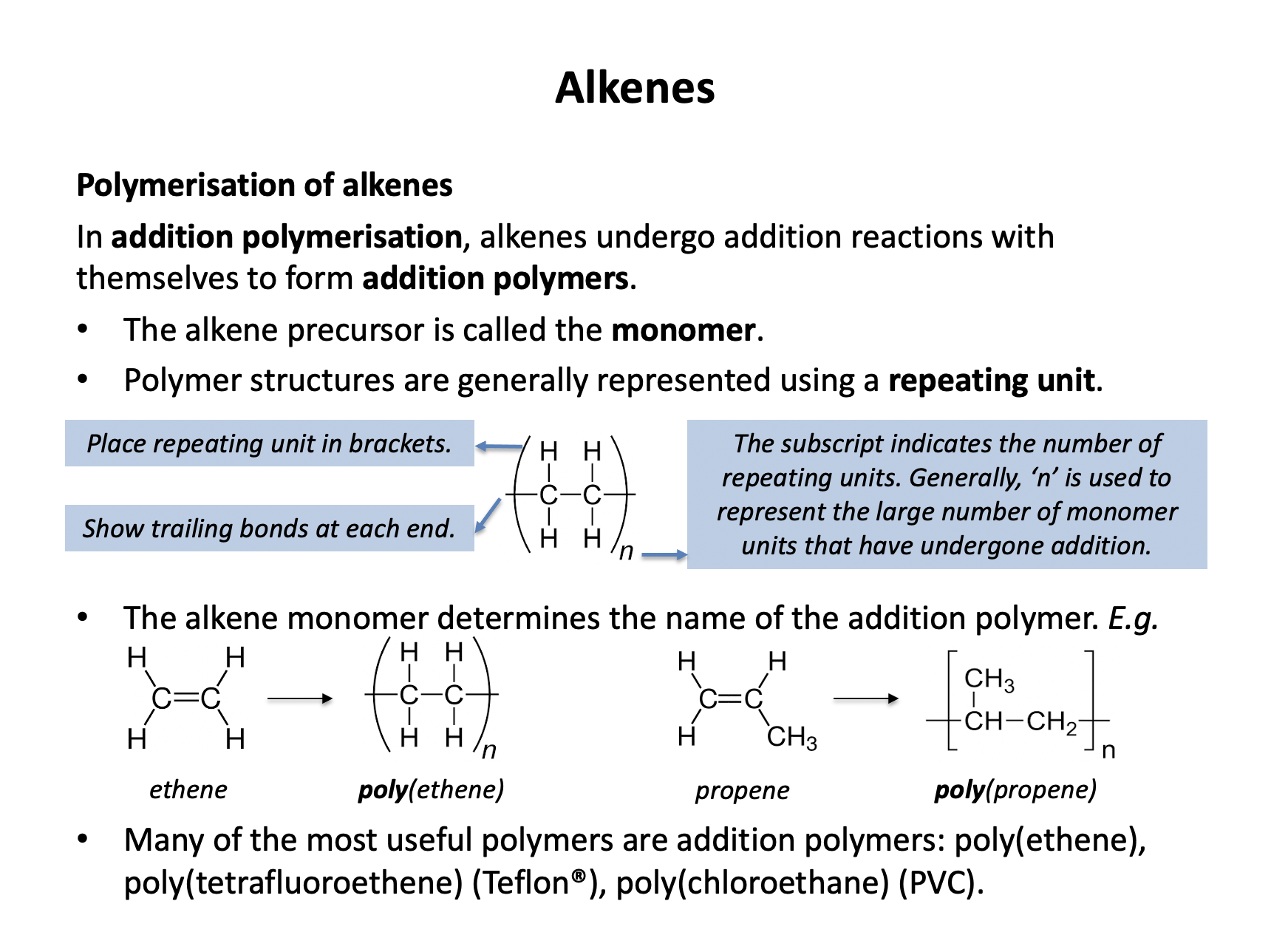
Which monomer would be used to produce poly(chloroethene) using addition polymerisation?
To produce poly(chloroethene) the monomer needs to be chloroethene. The formula of chloroethene is CHClCH2, which is therefore the correct answer. This molecule has a double C=C bond and one chlorine atom.
The other options either have no double C=C bond (CH2ClCH3) or two chlorine atoms (CHClCHCl) or both (CH2ClCH2Cl).
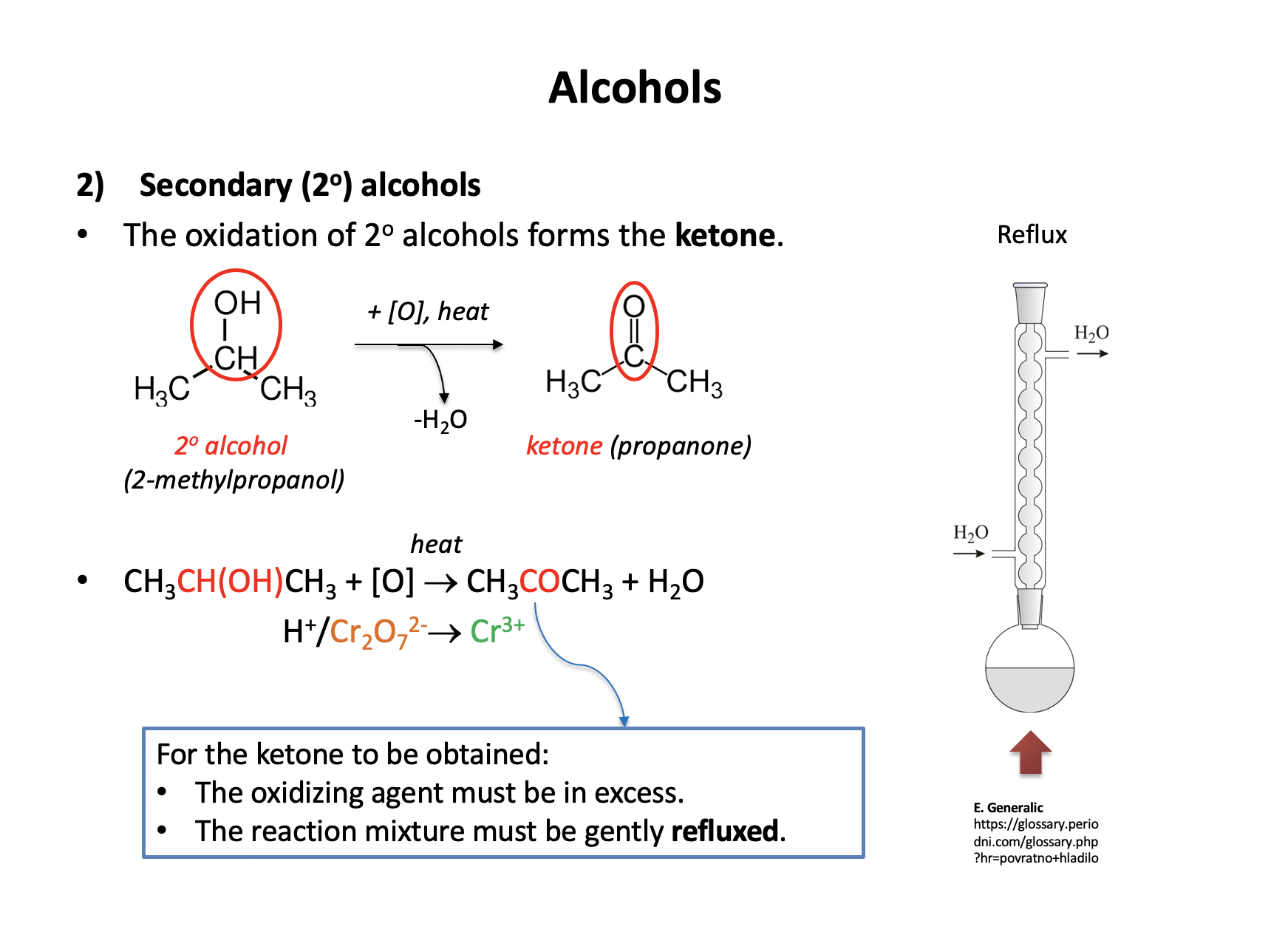
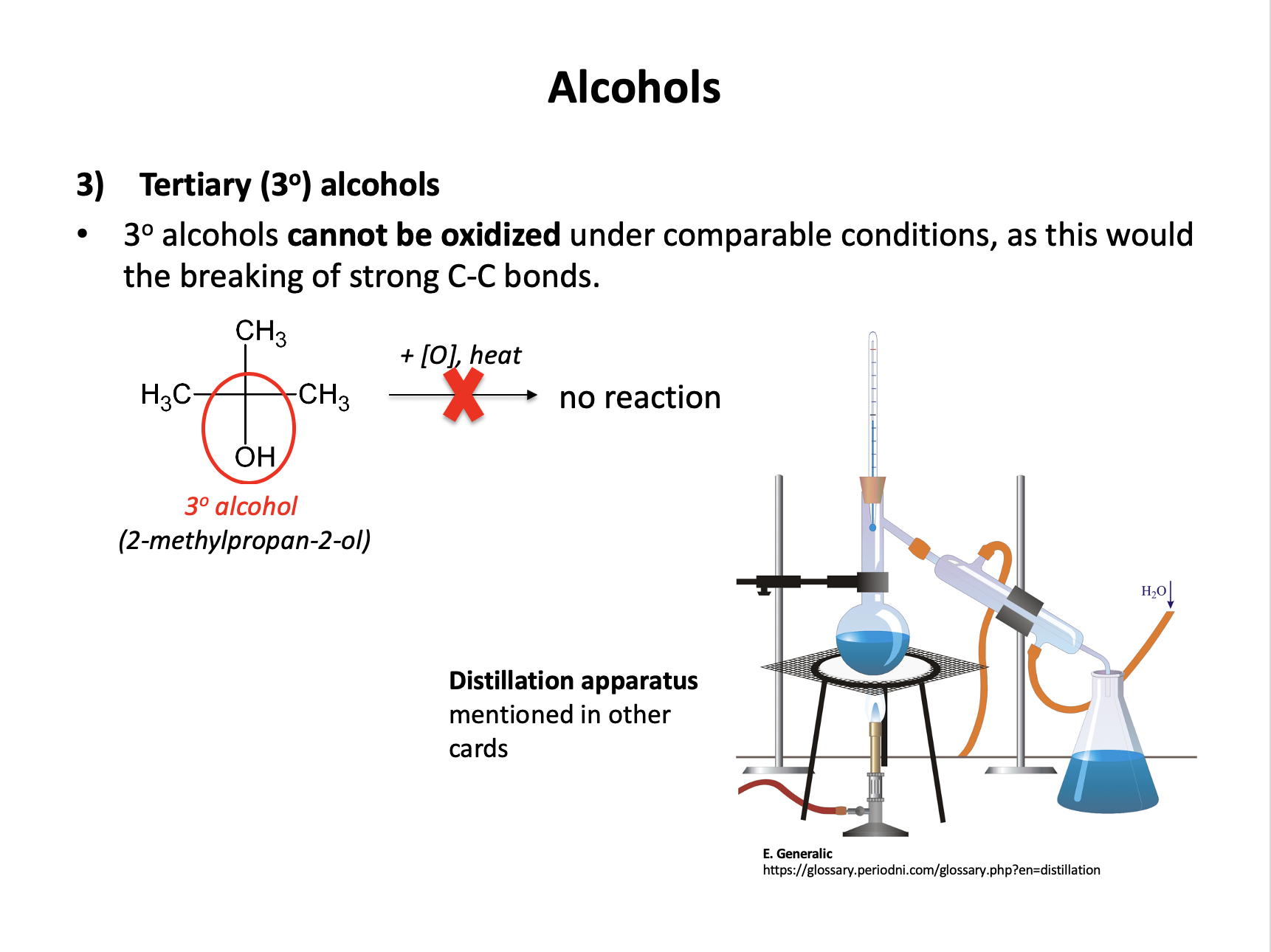
What colour change is seen when a tertiary alcohol is oxidised (under reflux) with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) (H+/K2Cr2O7)
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) so no reaction will take place, and there will be no colour change (the reaction mixture will remain orange).
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidised (to aldehydes or carboxylic acids and to ketones respectively) and teh colour change would be orange to green.
Therefore No change is the correct answer.
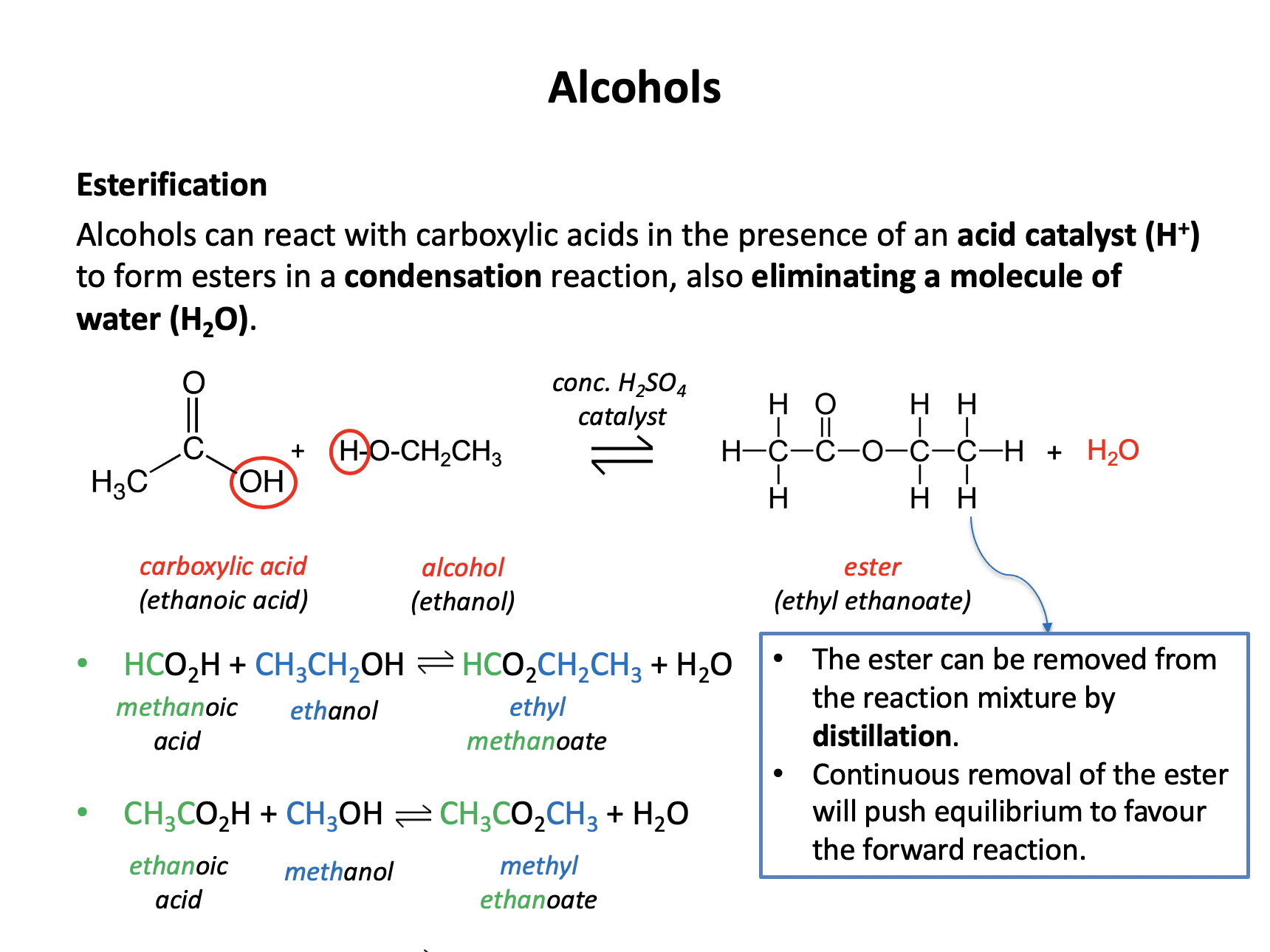
What is the correct formula for the organic product of the reaction between propanoic acid and ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst?
This is an esterification reaction. Esters are named by the 'alcohol bit' first then the 'acid bit', that is firstly the carbon chain section that is directly attached to the oxygen atom by a single bond, then the carbon chain section that includes the C=O.
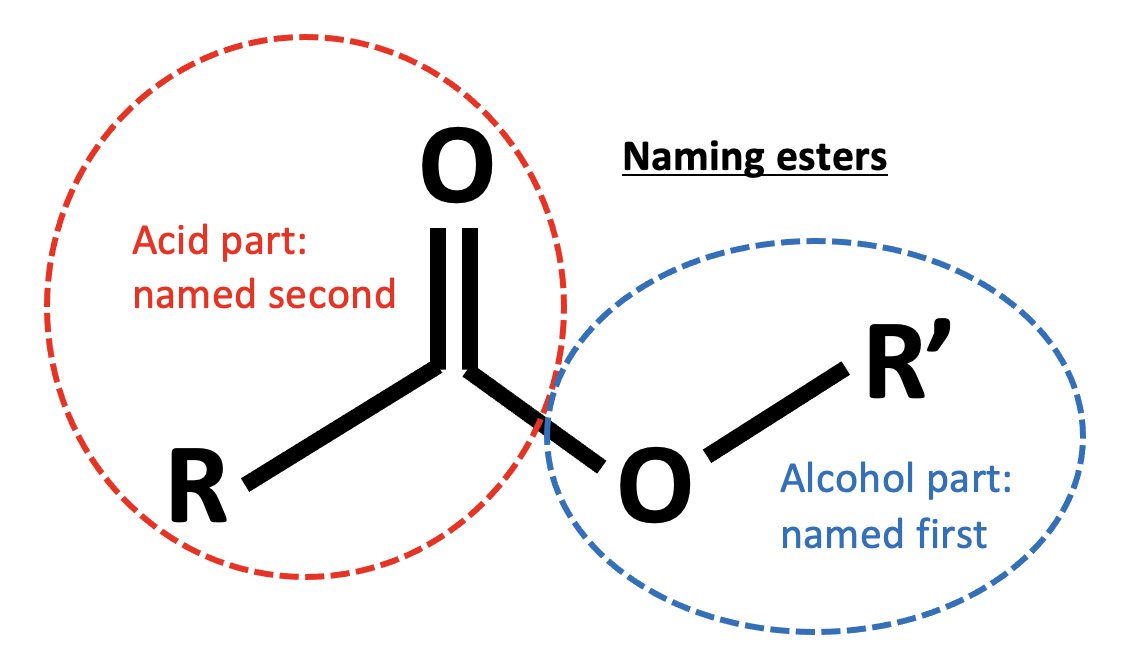
Propanoic acid and ethanol will form the ester ethyl propanoate, the formula of which is CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3. The other compounds are all esters, but propyl ethanoate (CH3CO2CH2CH2CH3), methyl propanoate (CH3CH2CO2CH3) and ethyl ethanoate (CH3CO2CH2CH3).
Therefore the answer is CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3.
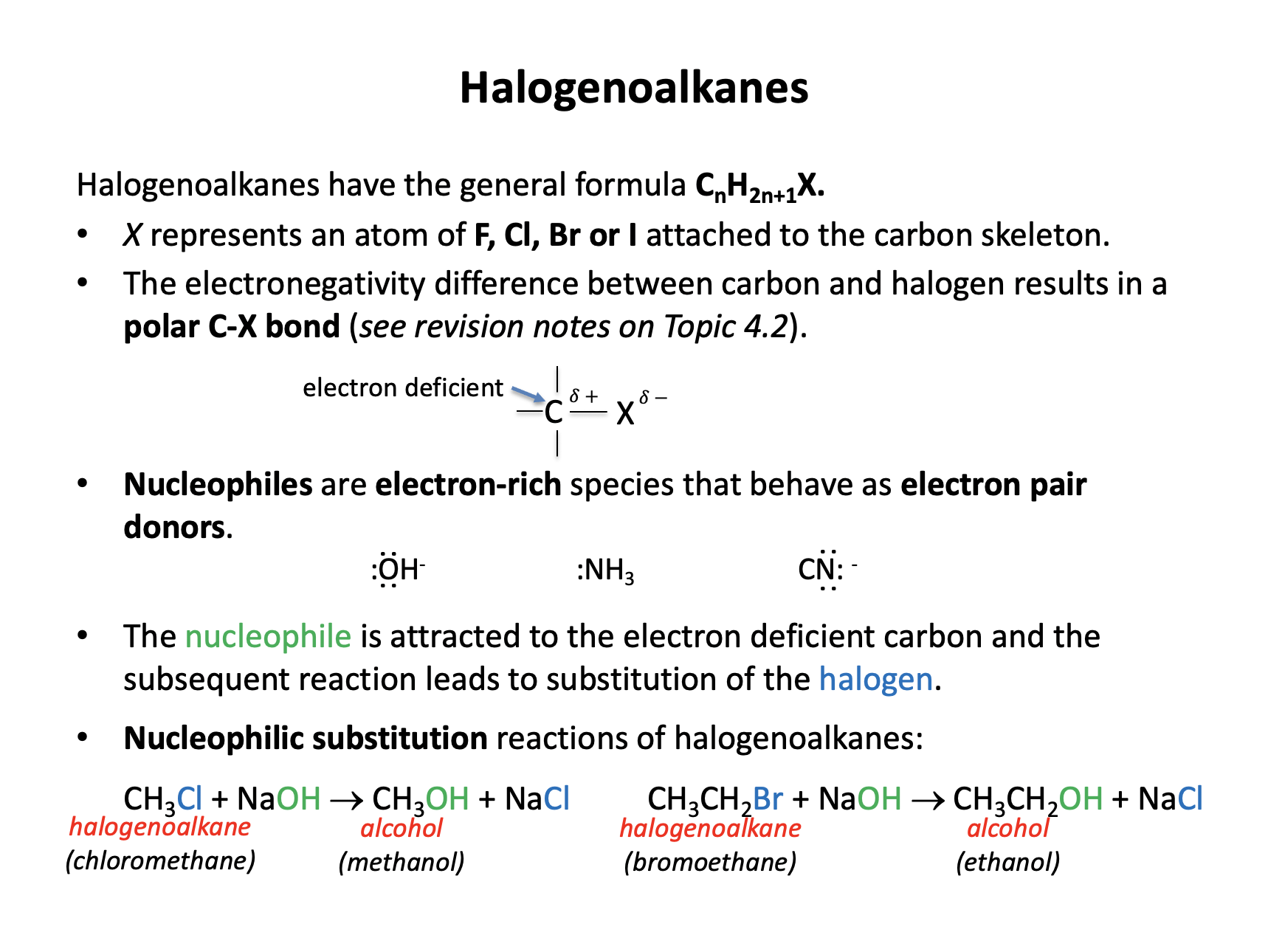
Which of the following are nucleophiles?
1: OH−
2: NH3
3: CH4
Nucleophiles are electron pair donors. In order for a species to be a nucleophile it must have a lone (non-bonding) pair of electrons. The hydroxide ion (OH−) has three lone pairs on the oxygen atom, ammonia (NH3) has one lone pair on the nitrogen atom. Both OH− and NH3 can therefore behave as nucleophiles.
Methane (CH4) has no lone (non-bonding) pairs and therefore cannot behave as a nucelophile.
Therefore 1 and 2 only is the correct answer.
Chloroethane (CH3CH2Cl) reacts to produce ethanol (CH3CH2OH). What reagent is needed for this reaction and what is the type of reaction taking place?
Halogenoalkanes will undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions will sodium hydroxide in water, to produce the corresponding alcohol. Thus chloroethane reacts with NaOH(aq) in a nucleophilic substitution reaction to produce ethanol.
Halogenoalkanes have no double bonds and cannot undergo addition reactions. The reagent conc. sulfuric acid (H2SO4(aq)) is a common reagent (and catalyst) but will not react to produce the alcohol in this reaction.
Therefore the correct answer is NaOH(aq) / nucleophilic substitution.
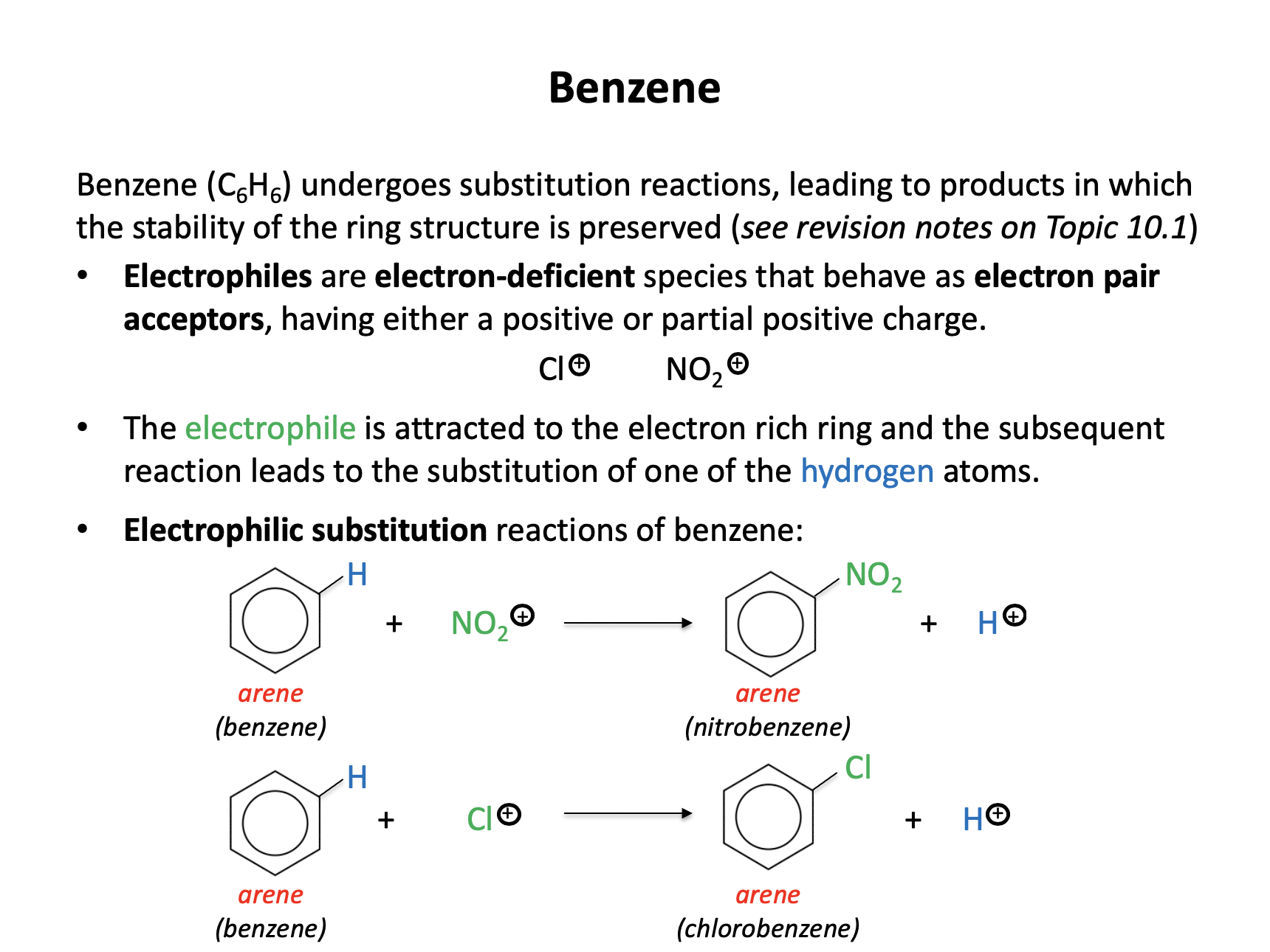
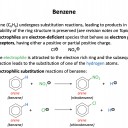
Benzene can react through an electrophilic substitution reaction to produce nitrobenzene.
Which of the following statements are correct with respect to this reaction?
1: The electrophile is NO2+
2: A hydrogen atom on the benzene ring is lost in the process
3: Nitrobenzene has the formula C6H5NO2
An electrophile is an electron pair acceptor. Electrophiles are electron deficient (often with a positive charge). Benzene will react, via an electrophilic substitution reaction with an electrophile which will replace a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring.
The nitration of benzene reaction: C6H6 + NO2+ → C6H5NO2 + H+
Therefore 1, 2 and 3 is the correct answer.
Paper 1
Core (SL&HL): Organic chemistry core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions
AHL (HL only): Organic chemistry AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions
Paper 2
Core (SL&HL): Organic chemistry core (SL & HL) paper 2 questions
AHL (HL only): Organic chemistry AHL (HL only) paper 2 questions
How much of Functional group chemistry have you understood?
















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn