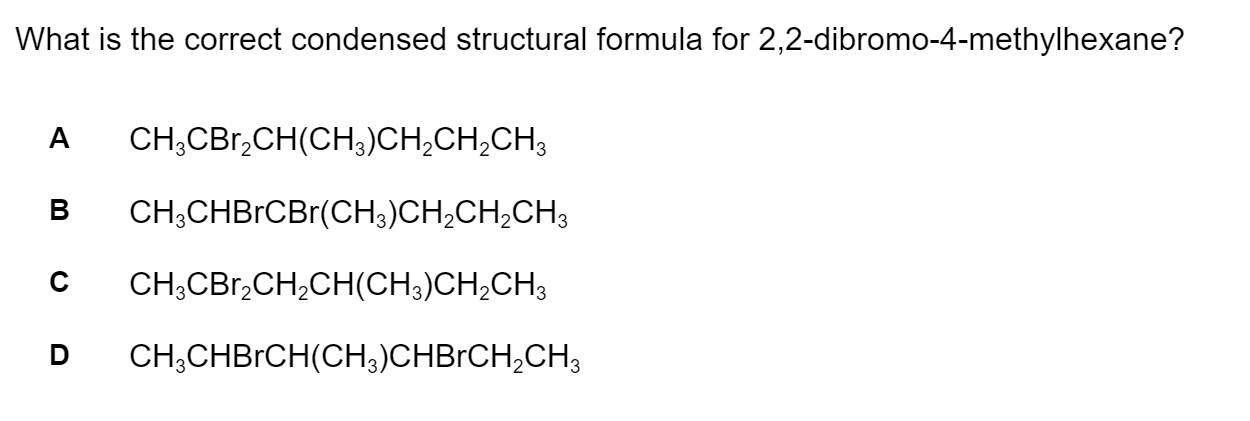
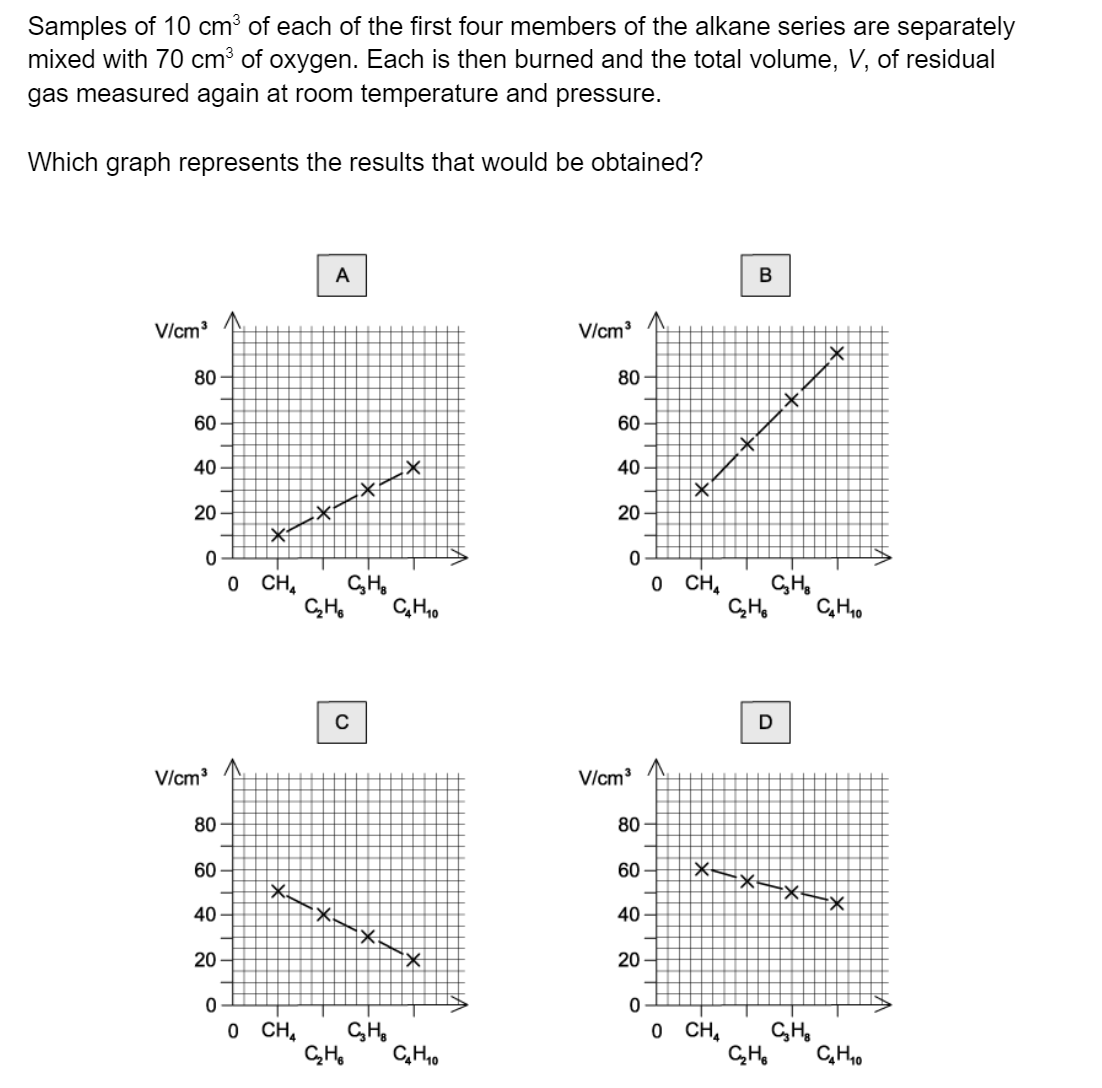
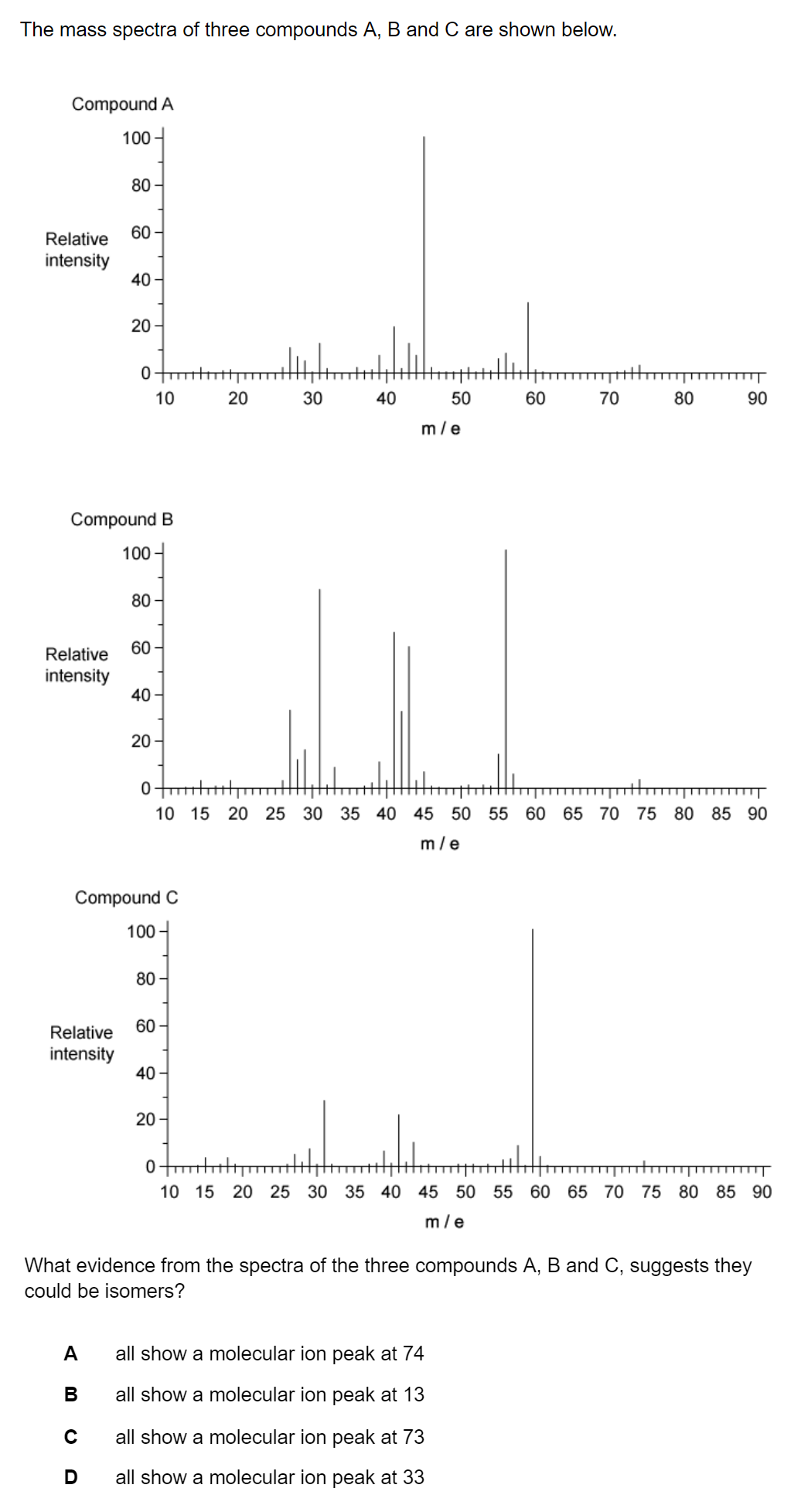
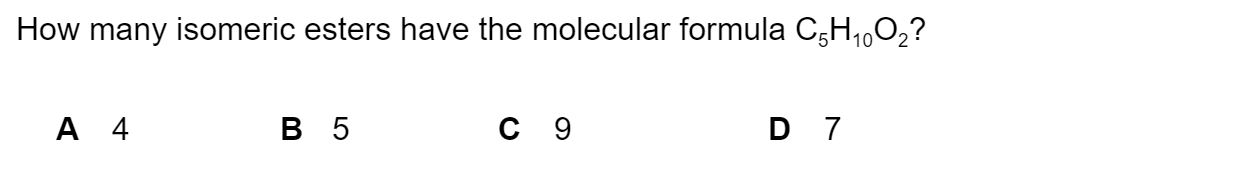Question 1


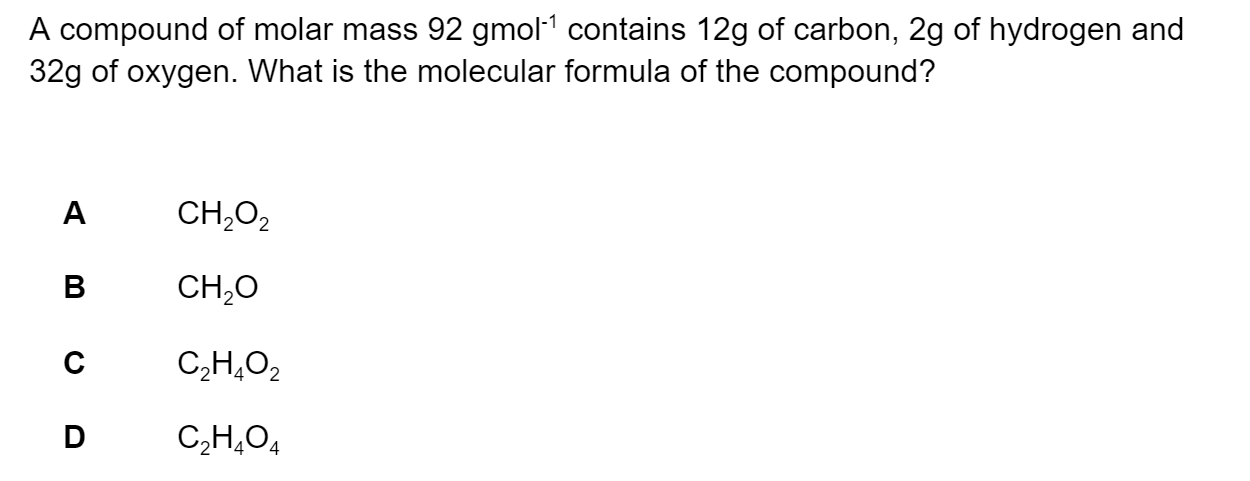




| ionic radius | atomic radius | |
| A | sodium < sulfur | sodium < sulfur |
| B | sodium < sulfur | sodium > sulfur |
| C | sodium > sulfur | sodium > sulfur |
| D | sodium > sulfur | sodium < sulfur |
Which statement correctly describes the trend in metallic radius in group I elements
Na to Rb?
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
Phosphine, PH3, can react with a hydrogen ion, H+, to form the phosphonium ion.
Which type of bond is formed in this reaction?
dipole-dipole forces
dative covalent bond
ionic bond
hydrogen bond
Which of the following statements about graphite are correct?
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
The properties of alloys can be explained in terms of metals having
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
A student mixed 30.0 cm3 of 0.0250 mol dm-3 potassium hydroxide solution with 30.0 cm3 of 0.0250 mol dm-3 nitric acid. The temperature rose by 0.50 oC. Assume no heat was lost to the surroundings.
The mixture had a specific heat capacity of 4.18 J g -1 K-1.
What is the molar enthalpy change for the reaction?
The reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide produced an overall temperature increase of 24.4 K.
Given the following data, how much thermal energy was evolved during this reaction?
Initial temperature of 25.0 cm3 hydrochloric acid = 17.6 oC
Initial temperature of 25.0 cm3 sodium hydroxide = 18.5 oC
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1.
(25.0 x 4.18 x 6.8) + (25.0 x 4.18 x 5.9)
50.0 x 4.18 x
(50.0 x 4.18 x 6.8) + (50.0 x 4.18 x 5.9)
The first stage in the industrial production of nitric acid from ammonia can be represented by the following equation.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ⇌ 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Using the following standard enthalpy change of formation data, what is the value of the standard enthalpy change for this reaction?
|
Compound |
|
|
NH3 (g) |
-46.1 |
|
NO (g) |
+90.3 |
|
H2O (g) |
-241.8 |
Which equation correctly shows how the bond energy for the covalent bond Y–Z can be calculated by dividing ΔH by n?
nYZ(g) → nY(g) + Z2(g)
Z(g) + YZn-1(g) → YZn(g)
2YZn (g) → 2YZn-1(g) + Y2(g)
YZn(g) → Y(g) + nZ(g)
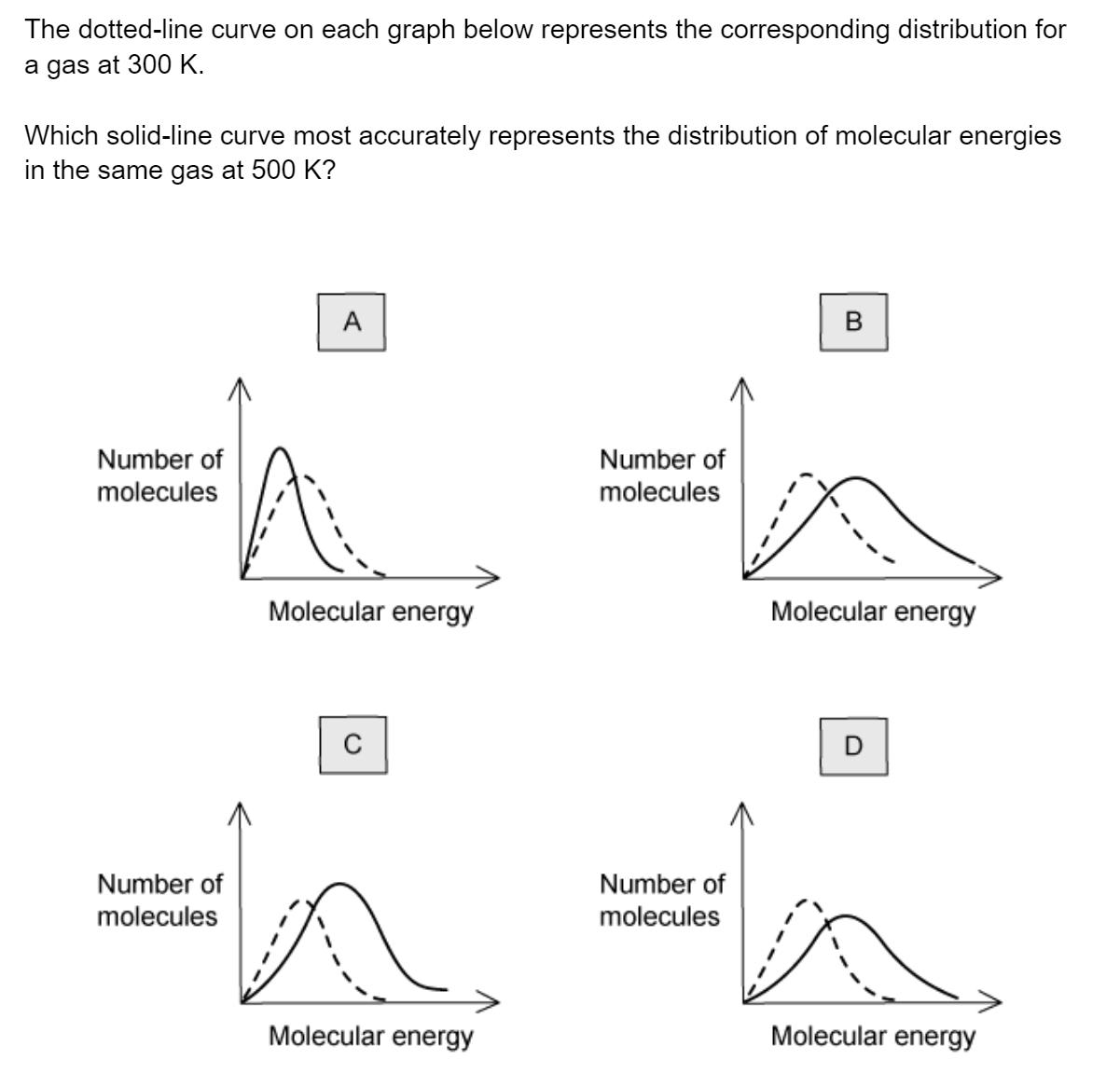
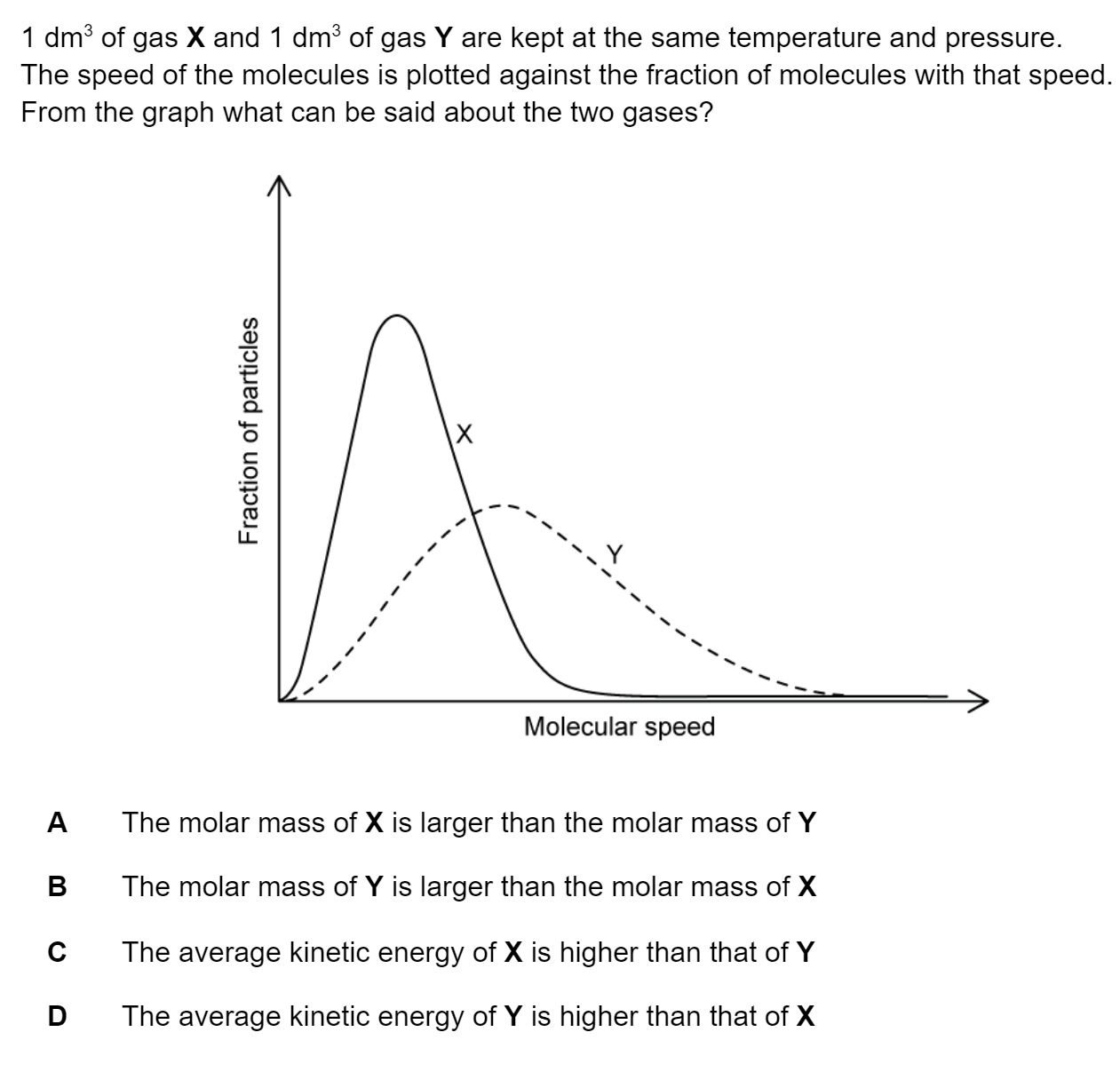

The following reaction occurs between concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids.
H2SO4 + HNO3 ⇋ H2NO3+ + HSO4-
Identify the two species which are acting as Brønsted–Lowry bases.
H2NO3+ and HSO4-
HNO3 and H2NO3+
H2SO4 and HSO4-
HNO3 and HSO4-
Calculate the pH of a solution of NaOH of concentration 0.001 mol dm-3
1
3
11
13
Acid rain can be up to 50 times more acidic than normal rain, which has a pH around 5.5. What is the approximate concentration of H+ in acid rain?
2.50 10-3 mol dm-3
2.50 10-4 mol dm-3
2.50 10-5 mol dm-3
50.0 10-4 mol dm-3