Negative Integrals
- The area under a curve may appear fully or partially under the x-axis
- This occurs when the function
takes negative values within the boundaries of the area
- This occurs when the function
- The definite integrals used to find such areas
- will be negative if the area is fully under the
-axis
- possibly negative if the area is partially under the
-axis
- this occurs if the negative area(s) is/are greater than the positive area(s), their sum will be negative
- will be negative if the area is fully under the
- When using a GDC use the modulus (absolute value) function so that all definite integrals have a positive value
-
- This is given in the formula booklet
How do I find the area under a curve when the curve is fully under the x-axis?
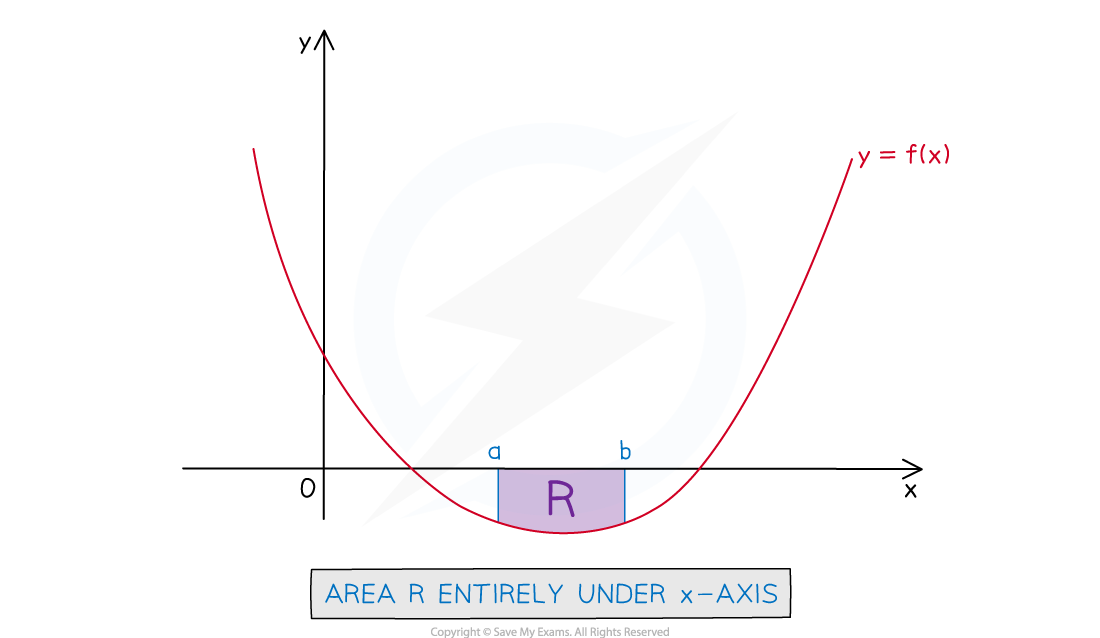
STEP 1
Write the expression for the definite integral to find the area as usual
This may involve finding the lower and upper limits from a graph sketch or GDC and f(x) may need to be rewritten in an integrable form
STEP 2
The answer to the definite integral will be negative
Area must always be positive so take the modulus (absolute value) of it
e.g. Ifformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%227.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EI%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math143f4d31b04031e49f5eb18baba%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2219.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math143f4d31b04031e49f5eb18baba%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x2212%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2254.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E36%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) then the area would be 36 (square units)
then the area would be 36 (square units)
How do I find the area under a curve when the curve is partially under the x-axis?
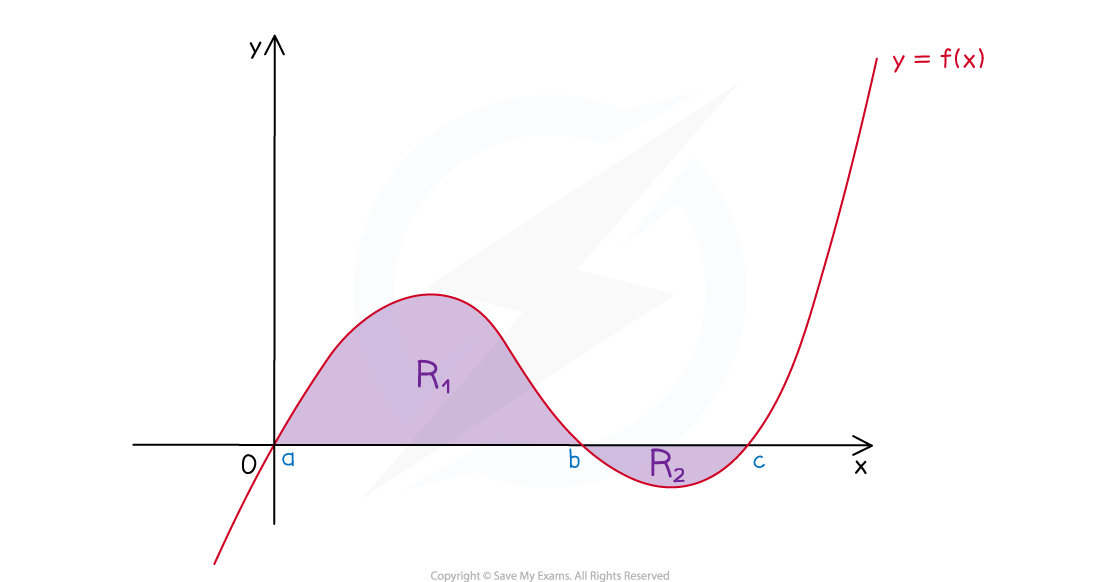
- For questions that allow the use of a GDC you can still use
- To find the area analytically (manually) use the following method
STEP 1
Split the area into parts - the area(s) that are above the x-axis and the area(s) that are below the x-axis
STEP 2
Write the expression for the definite integral for each part (give each part a name, I1, I2, etc)
This may involve finding the lower and upper limits of each part from a graph sketch or a GDC, finding the roots of the function (i.e. where%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmo%3E%3D%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmn%3E0%3C%2Fmn%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAsmhlYWQQC2qxAAACQAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAngAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKcAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACpAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAArAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALQAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEcAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABJAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAAD3%2F%2FwAAAD3%2F%2F%2F%2FEAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAsgABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%227.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ef%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2216.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2223.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2231.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E0%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) ) and rewriting
) and rewriting%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%227.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ef%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2216.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2223.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2231.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) in an integrable form
in an integrable form
STEP 3
Find the value of each definite integral separately
STEP 4
Find the area by summing the modulus (absolute values) of each integral
(Mathematically this would be writtenformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7PH4UAAADMAAAATmNtYXA3kjw6AAABHAAAADRjdnQgAQYDiAAAAVAAAAASZ2x5ZkyYQ7YAAAFkAAAAWWhlYWQLyR8fAAABwAAAADZoaGVhAq0XCAAAAfgAAAAkaG10eDEjA%2FUAAAIcAAAACGxvY2EAAEKZAAACJAAAAAxtYXhwBJsEcQAAAjAAAAAgbmFtZW7QvZAAAAJQAAAB5XBvc3QArQBVAAAEOAAAACBwcmVwu5WEAAAABFgAAAAHAAACDAGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg9AMD%2FP%2F8AAABVAABAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAA9AL%2F%2FwAA9AL%2F%2Fwv%2FAAEAAAAAAAABVABUAQAAKwCMAIAAqAAHAAAAAgAAAAAA1QEBAAMABwAAMTMRIxcjNTPV1auAgAEB1qsAAQBQAAAAoAFUAAMAHxgBsAMvsAA8sQIC9bABPACxAwA%2FsAI8fLEABvWwATwTMxEjUFBQAVT%2BrAAAAAABAAAAAQAAix6x7F8PPPUAAwQA%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7mT%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1a3uZP%2BA%2F%2F8B1gFYAAAACgACAAEAAAAAAAEAAAFU%2F%2F8AABdw%2F4D%2FgAHWAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACANUAAADwAFAAAAAAAAAAIQAAAFkAAQAAAAIACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABlAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABACYAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AJgAAAAAAAAADAEQANAAAAAAAAAAEACYAeAAAAAAAAAAFABYAngAAAAAAAAAGABMAtAAAAAAAAAAIABwAxwABAAAAAAABACYAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AJgABAAAAAAADAEQANAABAAAAAAAEACYAeAABAAAAAAAFABYAngABAAAAAAAGABMAtAABAAAAAAAIABwAxwADAAEECQABACYAAAADAAEECQACAA4AJgADAAEECQADAEQANAADAAEECQAEACYAeAADAAEECQAFABYAngADAAEECQAGABMAtAADAAEECQAIABwAxwBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAQgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAcwBtAGEAbABsACAAcwBpAHoAZQBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMEJyYWNrZXRzX3NtYWxsX3NpemUATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAAAqgBVAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAo2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EA%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2244.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EI%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2251.5%22%20y%3D%2224%22%3E1%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2269.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2279.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2279.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2279.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2279.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2299.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2299.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2299.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2299.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2287.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EI%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2294.5%22%20y%3D%2224%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22112.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22142.5%22%20y%3D%228%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22142.5%22%20y%3D%2214%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22142.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm47dfc8ff4929ef7202a7f1c%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22142.5%22%20y%3D%2226%22%3E%26%23xF402%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22130.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EI%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22137.5%22%20y%3D%2224%22%3E3%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22155.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22166.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E.%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22171.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E.%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b5dc6aeb84bcea29a76d1e9d00%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22176.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E.%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) )
)
Exam Tip
- If no diagram is provided, quickly sketch one so that you can see where the curve is above and below the x - axis and split up your integrals accordingly
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the graph of where
.

The region is bounded by the curve
, the
-axis and the
-axis.
The region is bounded by the curve
, the x-axis and the line
.
a)
Determine the coordinates of the point labelled .
.

b)
i)
Find a definite integral that would help find the area of the shaded region and briefly explain why this would not give the area of the region
and briefly explain why this would not give the area of the region .
.
ii)
Find the exact area of the shaded region .
.

c)
Find the exact total area of the shaded regions, and
and  .
.

Area Between a Curve and a Line
- Areas whose boundaries include a curve and a (non-vertical) straight line can be found using integration
- For an area under a curve a definite integral will be needed
- For an area under a line the shape formed will be a trapezium or triangle
- basic area formulae can be used rather than a definite integral
- (although a definite integral would still work)
- The area required could be the sum or difference of areas under the curve and line
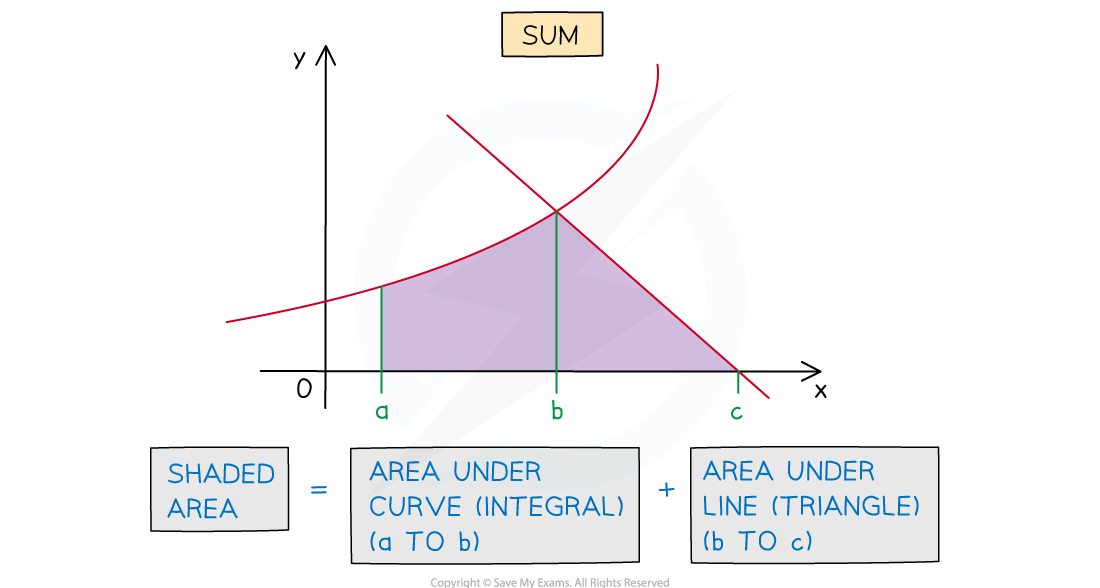
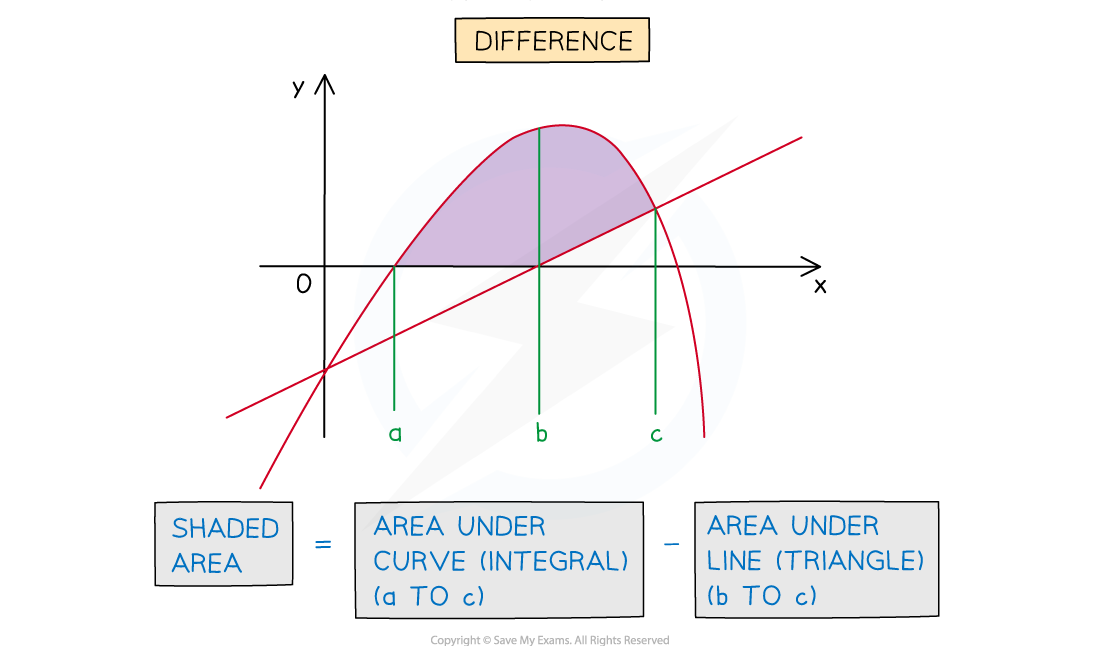
How do I find the area between a curve and a line?
STEP 1
If not given, sketch the graphs of the curve and line on the same diagram
Use a GDC to help with this step
STEP 2
Find the intersections of the curve and the line
If no diagram is given this will help identify the area(s) to be found
STEP 3
Determine whether the area required is the sum or difference of the area under the curve and the area under the line
Calculate the area under a curve using a integral of the form
Calculate the area under a curve using a integral of the form
Calculate the area under a line using eitherformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3EA%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2226.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2237.5%22%20x2%3D%2249.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E1%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3Eb%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2265.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3Eh%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) for a triangle or
for a triangle or%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADxjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVgAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGUAAABK2hlYWQQC2qxAAACwAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAvgAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAMcAAAADGxvY2EAHTwYAAADKAAAABBtYXhwBT0FPgAAAzgAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAANYAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAE%2BAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABRgAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACsAPf%2F%2FAAAAKwA9%2F%2F%2F%2F1v%2FFAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAywAgAEAAFYAKgJYAh4BDgEsAiwAWgGAAoAAoADUAIAAAAAAAAAAKwBVAIAAqwDVAQABKwAHAAAAAgBVAAADAAOrAAMABwAAMxEhESUhESFVAqv9qwIA%2FgADq%2FxVVQMAAAEAgABVAtUCqwALAEkBGLIMAQEUExCxAAP2sQEE9bAKPLEDBfWwCDyxBQT1sAY8sQ0D5gCxAAATELEBBuSxAQETELAFPLEDBOWxCwX1sAc8sQkE5TEwEyERMxEhFSERIxEhgAEAVQEA%2FwBV%2FwABqwEA%2FwBW%2FwABAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAQAAAAEAANV4zkFfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNz%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3MAAP8gBIADqwAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAD6P9qAAAXcAAA%2F7YEgAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwNSAFUDVgCAA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAoQAAASsAAQAAAAMAXgAFAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAADeAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABABIAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AEgAAAAAAAAADADAAIAAAAAAAAAAEABIAUAAAAAAAAAAFABYAYgAAAAAAAAAGAAkAeAAAAAAAAAAIABwAgQABAAAAAAABABIAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AEgABAAAAAAADADAAIAABAAAAAAAEABIAUAABAAAAAAAFABYAYgABAAAAAAAGAAkAeAABAAAAAAAIABwAgQADAAEECQABABIAAAADAAEECQACAA4AEgADAAEECQADADAAIAADAAEECQAEABIAUAADAAEECQAFABYAYgADAAEECQAGAAkAeAADAAEECQAIABwAgQBNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABSAGUAZwB1AGwAYQByAE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAgAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAxAC4AME1hdGhfRm9udABNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAAAMAAAAAAAAB9AD6AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5BxEAAI2FGACyAAAAFRQTsQABPw%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3EA%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2226.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2237.5%22%20x2%3D%2249.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E1%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3Eh%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2265.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2272.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3Ea%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2285.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2298.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3Eb%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22106.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) for a trapezium (y-coordinates will be needed)
for a trapezium (y-coordinates will be needed)
STEP 4
Evaluate the definite integrals and find their sum or difference as necessary to obtain the area required
Exam Tip
- Add information to any diagram provided
- Add axes intercepts, as well as intercepts between lines and curves
- Mark and shade the area you’re trying to find
- If no diagram is provided, sketch one!
Worked Example
The region is bounded by the curve with equation
and the line with equation
.
lies entirely in the first quadrant.
a)
Using your GDC, or otherwise, sketch the graphs of the curve and the line on the same diagram.
Identify and label the region on your sketch and use your GDC to find the
on your sketch and use your GDC to find the -coordinates of the points of intersection between the curve and the line.
-coordinates of the points of intersection between the curve and the line.

b)
i)
Write down an integral that would find the area of the region .
.
ii)
Find the area of the region .
.

Area Between 2 Curves
- Areas whose boundaries include two curves can be found by integration
- The area between two curves will be the difference of the areas under the two curves
- both areas will require a definite integral
- Finding points of intersection may involve a more awkward equation than solving for a curve and a line
- The area between two curves will be the difference of the areas under the two curves

How do I find the area between two curves?
STEP 1
If not given, sketch the graphs of both curves on the same diagram
Use a GDC to help with this step
STEP 2
Find the intersections of the two curves
If no diagram is given this will help identify the area(s) to be found
STEP 3
For each area (there may only be one) determine which curve is the ‘upper’ boundary
For each area, write a definite integral of the form
where is the function for the ‘upper’ boundary and
is the function for the ‘upper’ boundary and is the function for the ‘lower’ boundary
is the function for the ‘lower’ boundary
Be careful when there is more than one region – the ‘upper’ and ‘lower’ boundaries will swap
STEP 4
Evaluate the definite integrals and sum them up to find the total area
(Step 3 means no definite integral will have a negative value)
Exam Tip
- If no diagram is provided sketch one, even if the curves are not accurate
- Add information to any given diagram as you work through a question
- Maximise use of your GDC to save time and maintain accuracy:
- Use it to sketch the graphs and help you visualise the problem
- Use it to find definite integrals
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the curves with equations and
where
Find the area of the shaded region.


