Fundamental Forces
The Strong Nuclear Force
- In the nucleus, there are electrostatic forces between the protons due to their electric charge and gravitational forces due to their mass
- Comparatively, gravity is a very weak force and the electrostatic repulsion between protons is therefore much stronger than their gravitational attraction
- If these were the only forces, the nucleus wouldn’t hold together
- Therefore, the force that does hold the nucleus together is called the strong nuclear force
- The strong nuclear force keeps the nucleus stable since it holds quarks together
- Since protons and neutrons are made up of quarks, the strong force keeps them bound within a nucleus
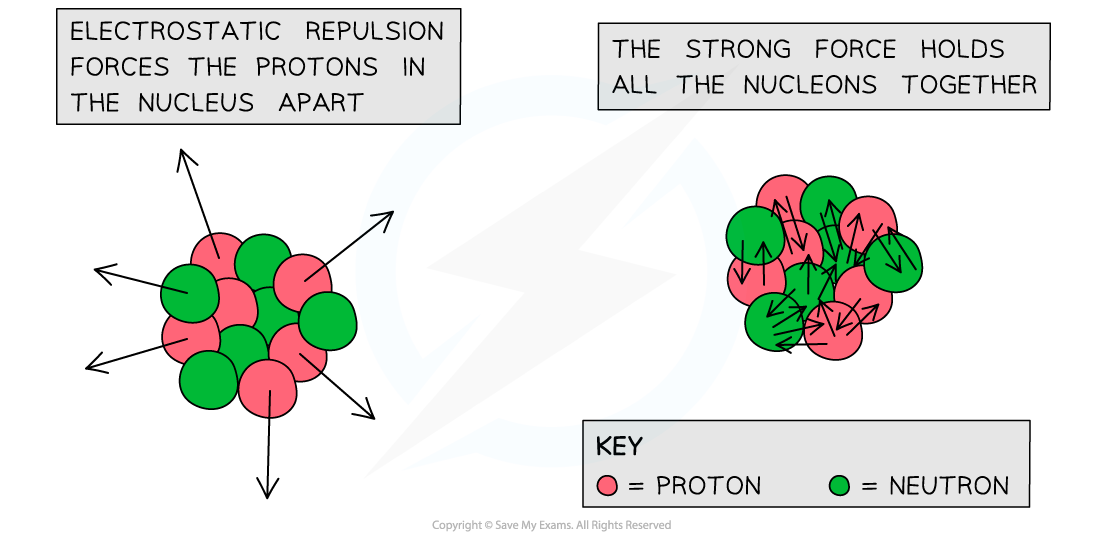
Whilst the electrostatic force is a repulsive force in the nucleus, the strong nuclear force holds the nucleus together
Range of the Strong Nuclear Force
- The strength of the strong nuclear force between two nucleons varies with the separation between them
- This can be plotted on a graph which shows how the force changes with separation
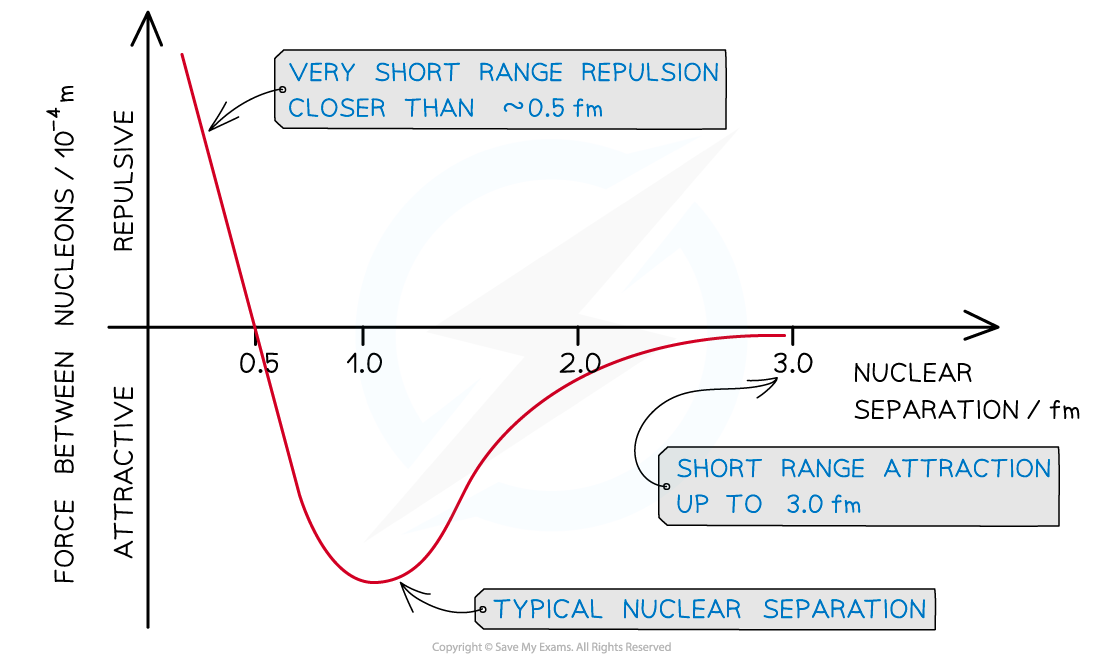
The strong nuclear force is repulsive before a separation of ~ 0.5 fm and attractive up till ~ 3.0 fm
- The key features of this graph are that the strong nuclear force is:
- Repulsive closer than around 0.5 fm
- Attractive up to around 3.0 fm
- Reaches a maximum attractive value at around 1.0 fm (the typical nuclear separation)
- Becomes zero after 3.0 fm
- In comparison to other fundamental forces, the strong force therefore has a very small range (only up to 3.0 fm)
Hadrons & The Strong Nuclear Force
- Hadrons are particles that are made up of quarks
- Hence they are subject to the strong interaction
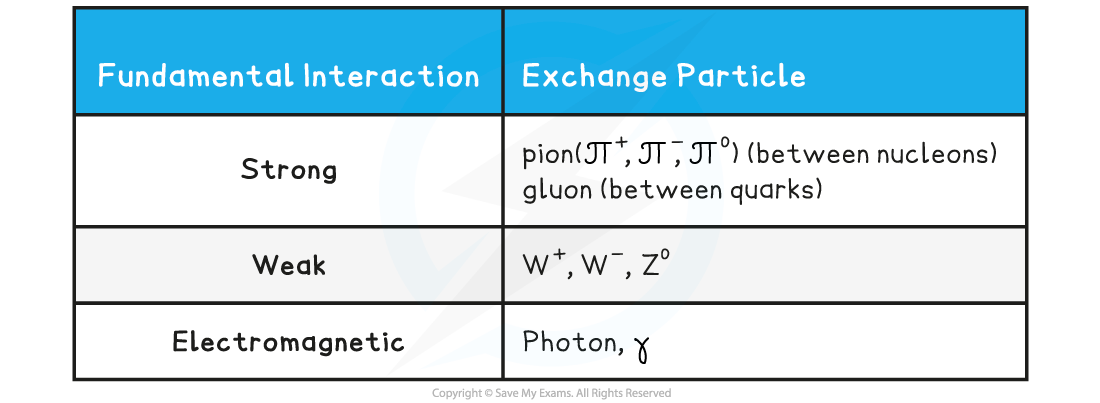
- The exchange particle of the strong interaction is either:
- The pion (between nucleons)
- The gluon (between quarks)
- This means that leptons cannot interact with the strong force, since they are not made up of quarks

Feynman diagram of the interaction between an up and down quark. The gluon is the exchange particle between them.
The Weak Nuclear Force
- The weak interaction is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms
- The exchange particle that carries this force is the W–, W+ or Z0 boson
- The type of exchange particle depends on the type of interaction
β decay
- β– and β+ decay are examples of the weak interaction in action
- In β– decay, a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and an anti-electron neutrino
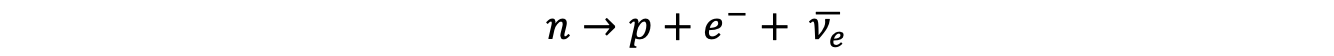
- The W– boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

Feynman diagram showing beta minus decay. The W– boson is the exchange particle
- In β+ decay, a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron and an electron neutrino
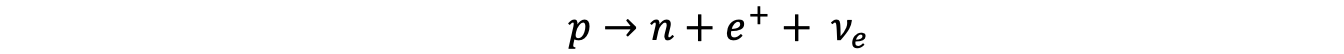
- The W+ boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

Feynman diagram showing beta plus decay. The W+ boson is the exchange particle
Electron Capture & Electron–Proton Collisions
- Electrons and protons are attracted to each other via the electromagnetic interaction
- However, when they interact with each other, it is the weak interaction that facilitates the collision
- Both electron capture and electron-proton collisions have the same decay equation
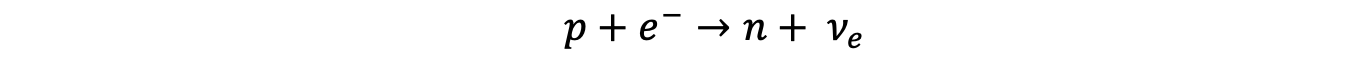
- Electron capture is when an atomic electron is absorbed by a proton in the nucleus resulting in the release of a neutron and an electron neutrino
- This decay is mediated by the W+ boson
- Electron-proton collisions are similar; when an electron collides with a proton, a neutron and an electron neutrino are emitted
- This decay is mediated by the W– boson

Feynman diagrams for electron capture and an electron-proton collision. These are equal except for the sign of the W boson
The Electromagnetic Force
- The electromagnetic force is only between charged particles
- The exchange particle that carries this force is the virtual photon, γ
- Properties of the photon are:
- It has no mass
- It has no charge
- It is its own antiparticle
- Electromagnetic interactions occur whenever two charged particles interact with each other
- For example, when two charged particles, such as electrons, are repelled by each other, a virtual photon is exchanged between them to produce this repulsion

Feynman diagram of electromagnetic repulsion between two electrons shown by the exchange of a virtual photon
- The electromagnetic force is also responsible for binding electrons to atoms
- This is due to the attractive force between the negative electrons and positive nucleus
The Gravitational Force
- The gravitational force acts only between particles with mass
- The exchange particle that carries this force is the theorized particle - the graviton
- Properties of the graviton are:
- It has no mass
- It has no charge
- It is its own antiparticle
- Gravitational interactions occur whenever two massive particles interact with each other
- The gravitational interaction is:
- only attractive, which means massive particles are pulled towards one another
- the weakest of the four forces, but also has an infinite range
- The gravitational force is usually ignored in particle interactions due to its weakness on such small mass scales
Exchange Particles
- When two particles interact, there cannot be instantaneous action at a distance
- This means one particle needs to "know" that the other is there
- This is the idea behind exchange (or virtual) particles.
- A definition of exchange particles is:
Exchange particles are virtual particles/bosons that mediate/carry/transmit the a fundamental force between interacting particles
-
- The phrase virtual boson can be used in place of virtual particles
- The words mediate or carry can be used in place of transmit
- When two particles exert a force on each other, a virtual particle is created
- Virtual particles only exist for a short amount of time and carry the fundamental force between each particle
- A force can be attractive or repulsive. An analogy of exchange particles would be:
- Two people are on skateboards and a ball is passed between them. Due to this, they start to move away from each other. The ball represents an exchange particle creating repulsion
- However, if one person throws a boomerang to the other, they will start to move closer together. The boomerang represents an exchange particle creating attraction
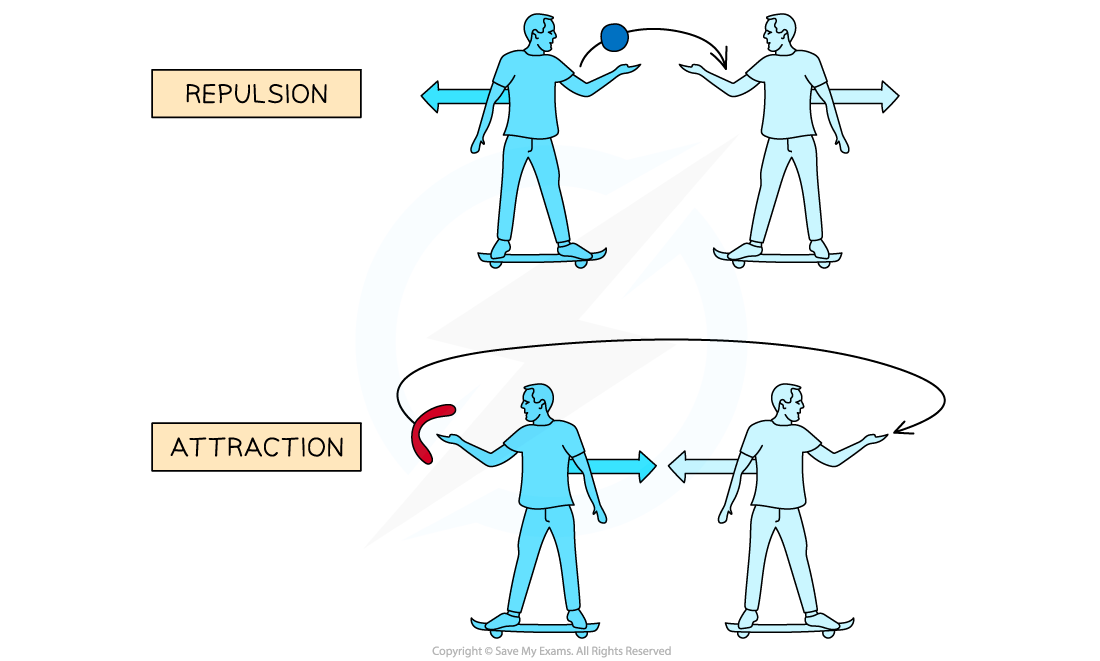
Both skateboarders can create repulsion or attraction by throwing a ball or boomerang between them. The ball and boomerang represent exchange particles.
- Each fundamental interaction is transmitted by its own exchange particle
- These are also called gauge bosons
Table of Exchange Particles
- Since gravity is so weak, it only has a noticeable effect on large masses, therefore, gravity does not play a part in particle interactions
- The theorised exchange particle for the gravitational force is the graviton, however, this has not yet been discovered
Exam Tip
You will be expected to remember which exchange particle mediates which fundamental interaction for your exam. This is particularly important when drawing Feynman diagrams, as the correct exchange particle will be expected to be on them.
Comparing Fundamental Forces
- There are four fundamental interactions, or fundamental forces, that exist. These are:
- Gravity
- Electromagnetism
- Strong Nuclear (or Strong Interaction)
- Weak Nuclear
- Gravity is the weakest of these forces, whilst the strong interaction is the strongest (hence the name)
- They also have different ranges:
- The electromagnetic and gravitational interactions have an infinite range
- The weak force has a range of up to 10–18 m
- The strong force has a range of ~ 10–15 m

The fundamental interactions in order of strength
- The gravitational interaction only affects particles with mass
- The electromagnetic interaction only affects particles with charge
- The weak interaction affects all particles
- The strong interaction only affects hadrons
