Conduction, Convection & Thermal Radiation
- Thermal energy transfers from hotter areas to cooler areas by the processes of:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
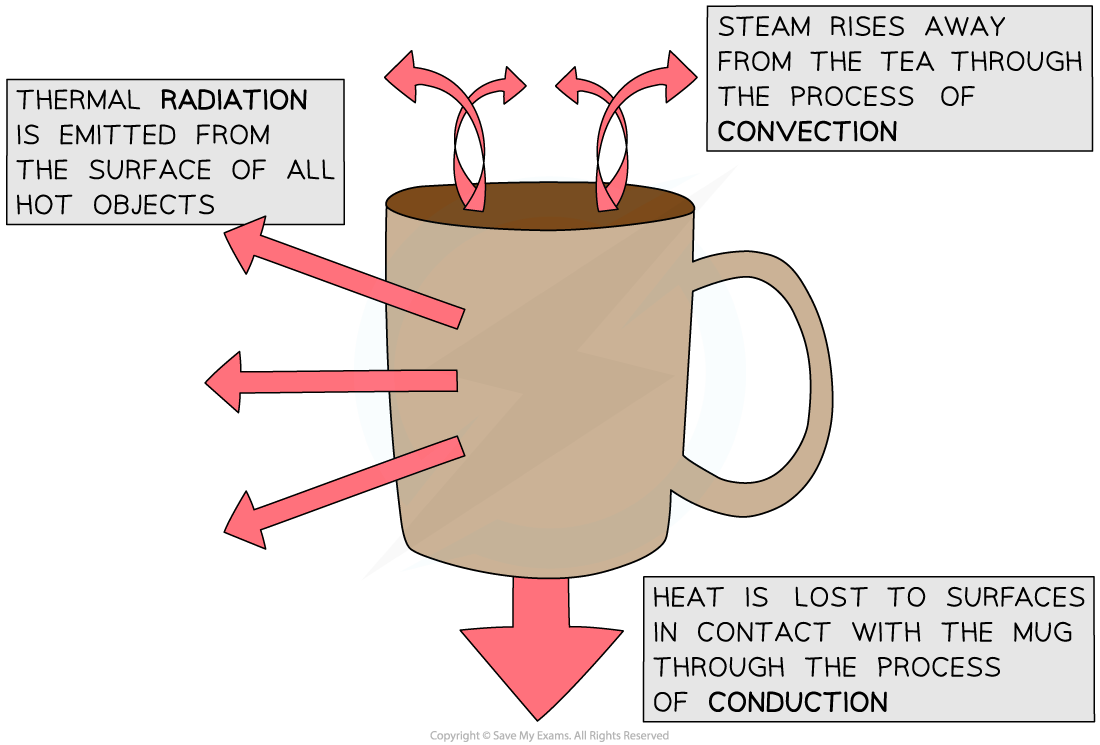
- Objects will always lose heat until they are in thermal equilibrium (same temperature) with their surroundings
- For example, a mug of hot tea will cool down until it reaches room temperature
Conduction
- Conduction is the main method of thermal energy transfer in solids
- Conduction occurs when:
Two solids of different temperatures come in contact with one another, thermal energy is transferred from the hotter object to the cooler object
- Metals are the best thermal conductors
- This is because they have a high number of free electrons
- Non-metals, such as plastic or glass, are poor at conducting heat
- Poor conductors of heat tend to be poor conductors of electricity
- This suggests a link between the mechanisms behind both types of conduction
- Liquids and gases are even poorer thermal conductors
- This is because the atoms are further apart, hence, the intermolecular forces are weaker
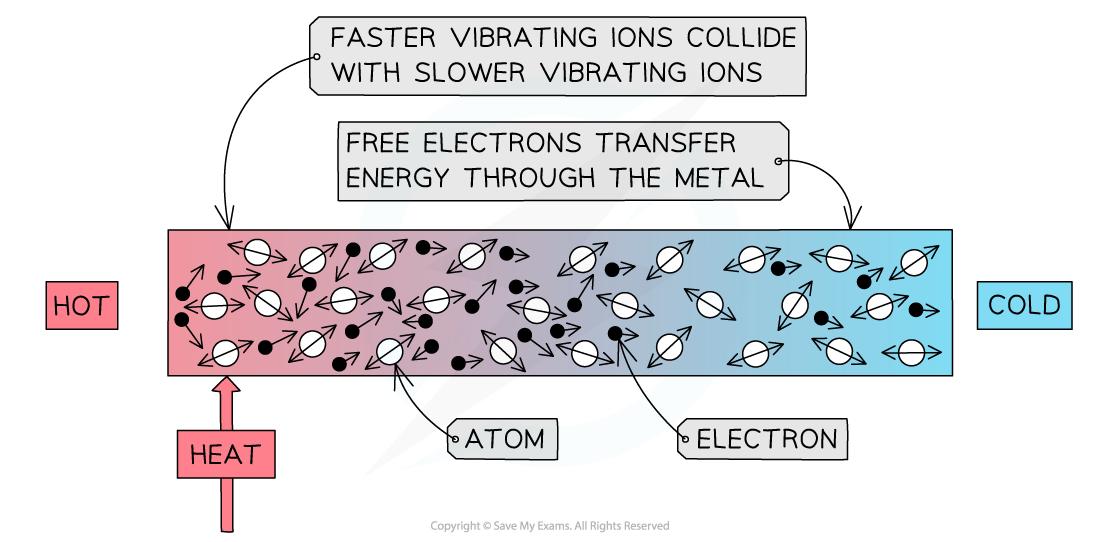
Conduction: the atoms in a solid vibrate and bump into each other
- Conduction can occur through two mechanisms:
- Atomic vibrations
- Free electron collisions
- When a substance is heated, the atoms, or ions, start to move around (vibrate) more
- The atoms at the hotter end of the solid will vibrate more than the atoms at the cooler end
- As they do so they bump into each other, transferring energy from atom to atom
- These collisions transfer internal energy until thermal equilibrium is achieved throughout the substance
- This occurs in all solids, metals and non-metals alike
- Metals are especially good at conducting heat due to their high number of delocalised electrons
- These can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material
- This, therefore, allows metals to achieve thermal equilibrium faster than non-metals
Worked Example
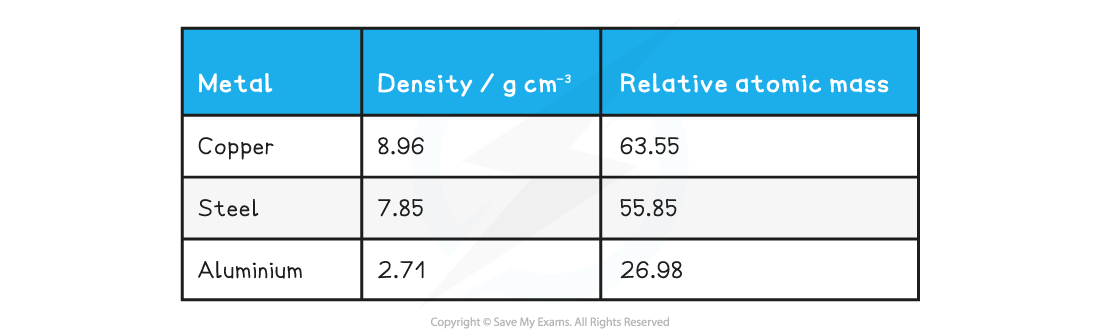
Determine which of the following metals is likely to be the best thermal conductor, and which is likely to be the worst.
You may take Avogadro's number to be 6.02 × 1023 mol−1 and you can assume each metal contributes one free electron per atom.
Step 1: Use dimensional analysis to determine the equation for the number of free electrons
- Units for number of free electrons per cubic centimetre, [n] = cm−3
- Units for density, [ρ] = g cm−3
- Units for Avogadro's number, [NA] = mol−1
- Units for relative atomic mass, [A] = g mol−1
[n]a = [ρ]b [NA]c [A]d
(cm−3)a = (g cm−3)b (mol−1)c (g mol−1)d
- The only unit present on both sides is cm−3, therefore:
a = b = 1
- No other units are present on both sides, so:
c + d = 0
b + d = 0
∴ d = −1, c = 1
Step 2: Write out the equation for the number of free electrons per cubic centimetre
[n]1 = [ρ]1 [NA]1 [A]−1
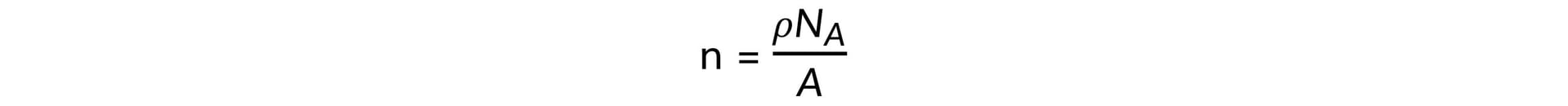
Step 3: Calculate the number of free electrons in each metal
- Copper:
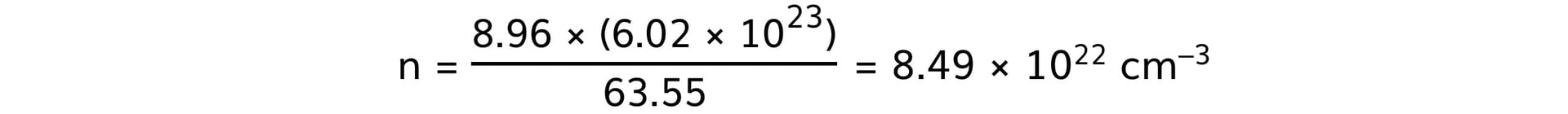
- Steel:
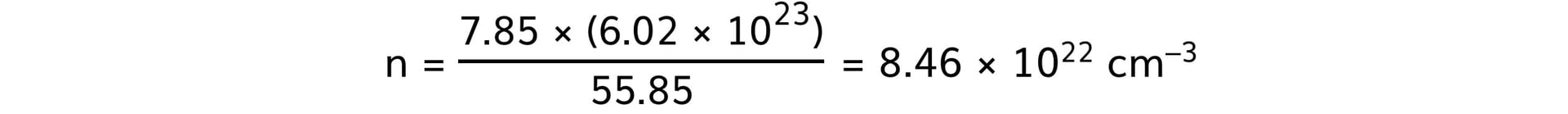
- Aluminium:
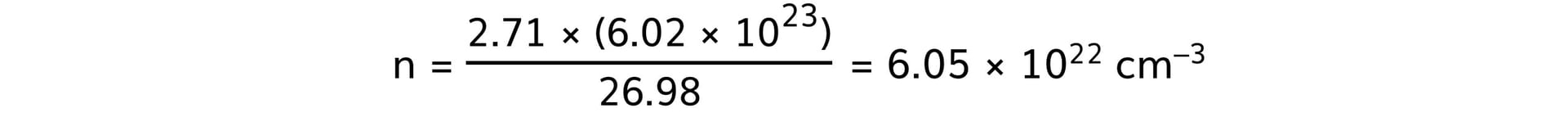
Step 4: Rank the metals from best thermal conductor to worst
- Best thermal conductor = copper (highest number of free electrons)
- Worst thermal conductor = aluminium (lowest number of free electrons)
Convection
- Convection occurs when:
A fluid is heated causing the movement of groups of atoms or molecules due to variations in density
- Convection is the main way that heat travels through liquids and gases
- Convection cannot occur in solids
- When a fluid (a liquid or a gas) is heated from below:
- The heated molecules gain kinetic energy and push each other apart, making the fluid expand
- This makes the hot part of the fluid less dense than the surrounding fluid
- The hot fluid rises, and the cooler (surrounding) fluid moves in to take its place
- Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again
- The resulting motion is called a convection current
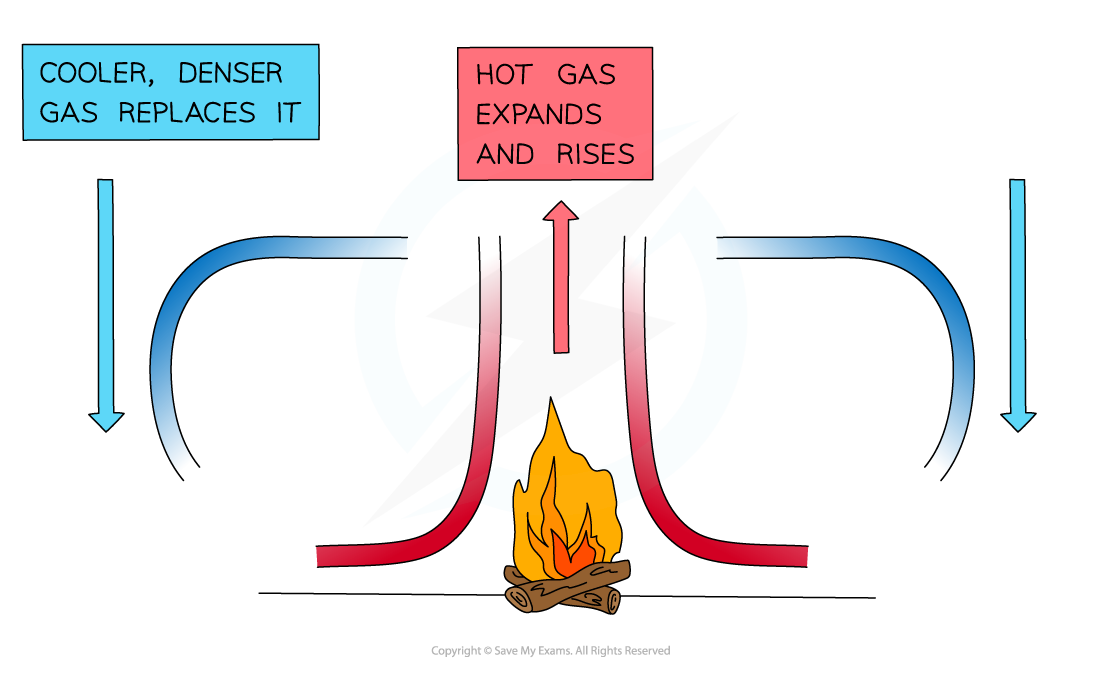
A convection current caused by the heat transfer from the fire
Worked Example
Discuss one example, in nature or in the lab, in which convection takes place.
Step 1: Draw a diagram to illustrate the convection currents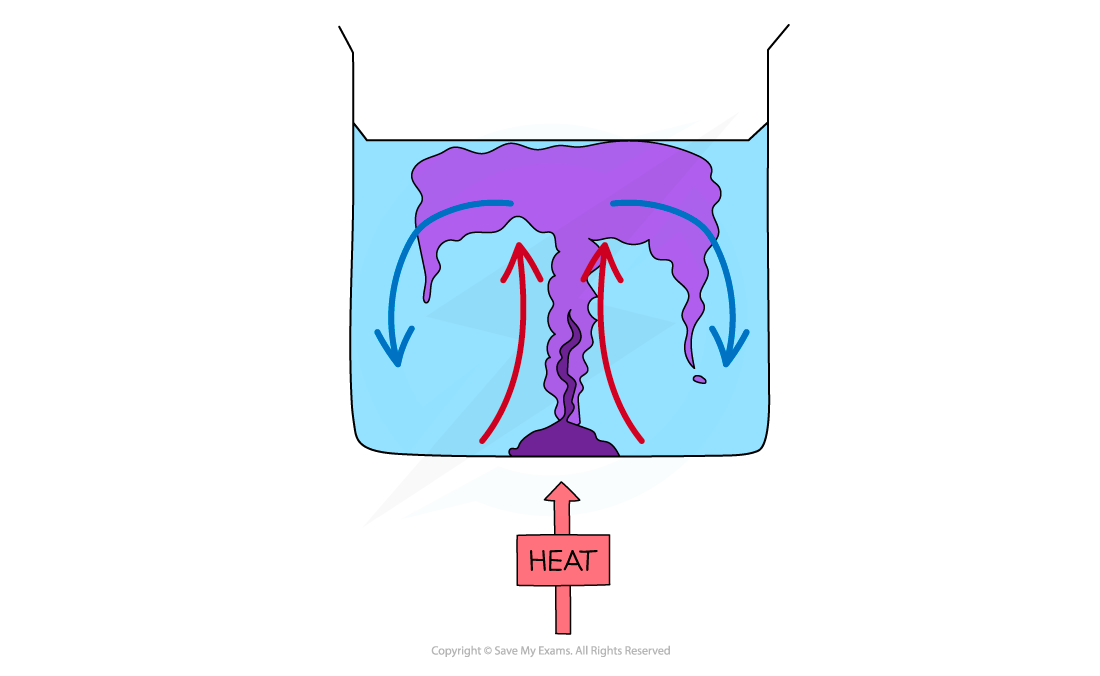 Step 2: Describe the situation
Step 2: Describe the situation
-
- One method of observing a convection current is by heating a beaker of water containing potassium permanganate crystals
- Heat is initially transferred through the glass wall of the beaker by conduction
- The water in the region of the Bunsen flame is heated and expands, becomes less dense and rises
- This causes the dissolved purple crystal to flow up with the water
- Meanwhile, when the water at the top of the beaker cools, it becomes denser again and falls
- The process continues which leads to a convection current where heat is transferred through the liquid
- The dissolved purple crystal follows this current which is what is observed during this experiment
-
- Other examples of convection include:
- Atmospheric convection / winds / sea breezes
- Thunderheads (a cloud that appears before a thunderstorm)
- Convection currents in the Earth's mantle (which can lead to continental drift)
- Ocean currents
- Solar conventions / sunspots / flares
- Other examples of convection include:
Thermal Radiation
- All bodies (objects), no matter what temperature, emit a spectrum of thermal radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves
- These electromagnetic waves usually lie in the infrared region of the spectrum
- Black-body radiation can also be emitted in the form of visible light or other wavelengths, depending on the temperature
- Thermal radiation is defined as:
Heat transfer by means of electromagnetic radiation normally in the infrared region
- The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time
- This is because atoms and molecules above absolute zero are in constant motion
- Electric charges within the atoms in a material vibrate causing electromagnetic radiation to be emitted
- Therefore, the higher the temperature, the greater the thermal motion of the atoms and the greater the rate of emission of radiation
- Thermal radiation is the only method of thermal energy transfer that does not require matter in order to move or propagate
- Therefore, thermal radiation is the only way heat can travel through a vacuum
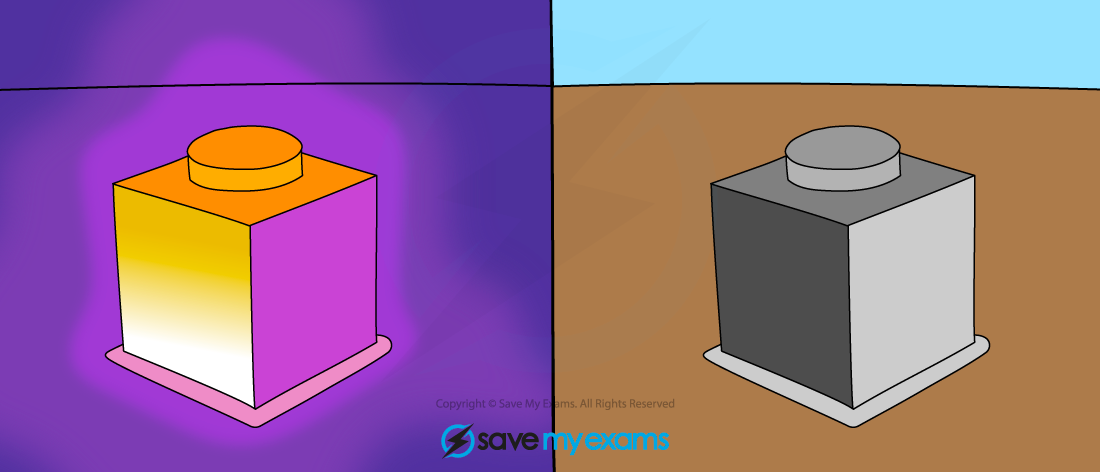
All objects above absolute zero emit infrared radiation
Worked Example
A hot meteorite hits the surface of the Moon.
Identify and discuss the principle means by which the meteorite can dissipate thermal energy.
Step 1: Identify the types of thermal energy transfer
- An object can lose energy through conduction, convection or radiation
- In this case, the hot meteorite will only be able to lose energy via conduction and radiation
Step 2: Explain these choices
- The meteorite can lose heat energy through conduction because it is in contact with the surface of the Moon
- The Moon does not have an atmosphere, so convection is not possible
- Infrared photons emitted by the meteorite are able to travel through a vacuum, so heat loss via radiation is possible
Exam Tip
If a question...
...mentions thermal energy transfers and metals, the answer will probably have something to do with conduction!
...refers to thermal energy transfers and a liquid or gas (that isn’t trapped) then make sure your answer mentions that convection currents will probably form!
...refers to the colour of something (black, white or shiny) then the answer will probably have something to do with thermal radiation!
...involves a vacuum (empty space) then mention radiation as it is the only way in which heat can travel through a vacuum as conduction and convection require particles to transfer heat!
