Energy Generation
- You need to know about the main ways of generating electricity:
- The equipment involved
- The advantages and disadvantages
- Calculate power obtained for different setups
- These revision notes cover:
- Nuclear Power
- Burning Fossil Fuels
- Wind Electricity Generators
- Hydroelectric Power
- Solar Power
Nuclear Power
Control Rods & Moderators:
- In a nuclear reactor, a chain reaction is required to keep the reactor running
- When the reactor is producing energy at the correct rate, two factors must be controlled:
- The number of free neutrons in the reactor
- The energy of the free neutrons
- To do this, nuclear reactors contain control rods and moderators
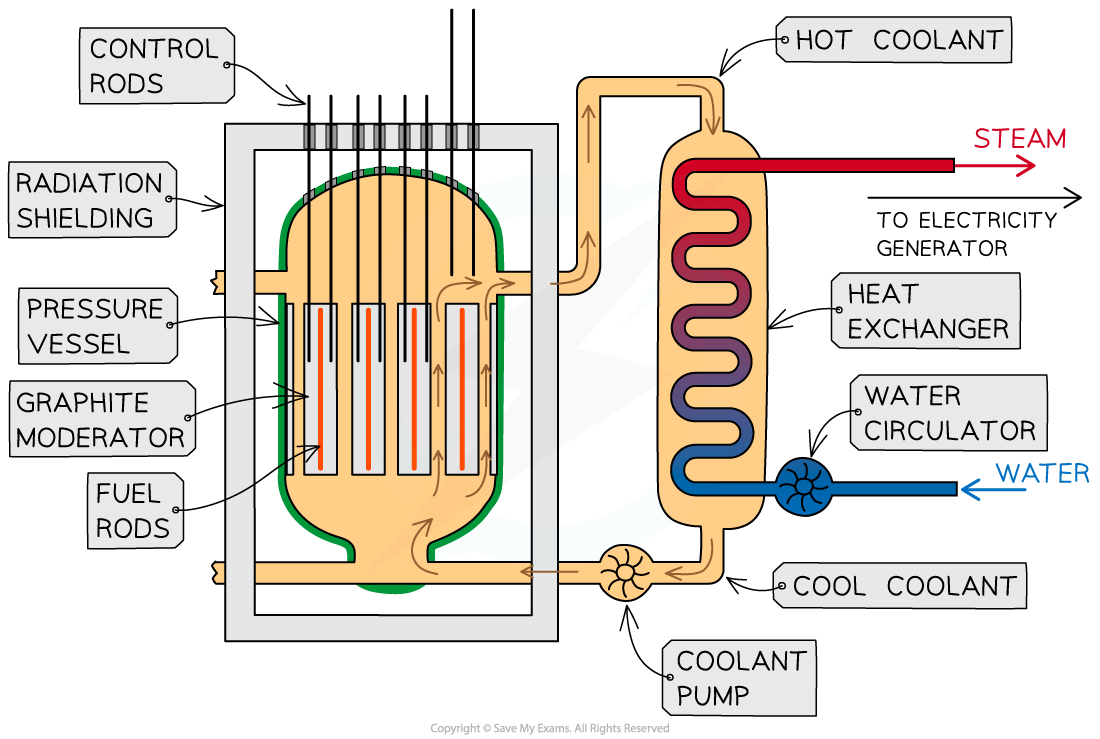
The overall purpose of a nuclear reactor is to collect the heat energy produced from nuclear reactions
Control Rods:
Purpose of a control rod: To absorb neutrons
- Control rods are made of a material which absorb neutrons without becoming dangerously unstable themselves
- The number of neutrons absorbed is controlled by varying the depth of the control rods in the fuel rods
- Lowering the rods further decreases the rate of fission, as more neutrons are absorbed
- Raising the rods increases the rate of fission, as fewer neutrons are absorbed
- This is adjusted automatically so that exactly one fission neutron produced by each fission event goes on to cause another fission
- In the event the nuclear reactor needs to shut down, the control rods can be lowered all the way so no reaction can take place
Moderator:
The purpose of a moderator: To slow down neutrons
- The moderator is a material that surrounds the fuel rods and control rods inside the reactor core
- The fast-moving neutrons produced by the fission reactions slow down by colliding with the molecules of the moderator, causing them to lose some momentum
- The neutrons are slowed down so that they are in thermal equilibrium with the moderator, hence the term ‘thermal neutron’
- This ensures neutrons can react efficiently with the uranium fuel
Shielding:
- The entire nuclear reactor is surrounded by shielding materials
- The purpose of shielding is to absorb hazardous radiation
- The daughter nuclei formed during fission, and the neutrons emitted, are radioactive
- The reactor is surrounded by a steel and concrete wall that can be nearly 2 metres thick
- This absorbs the emissions from the reactions
- It ensures that the environment around the reactor is safe
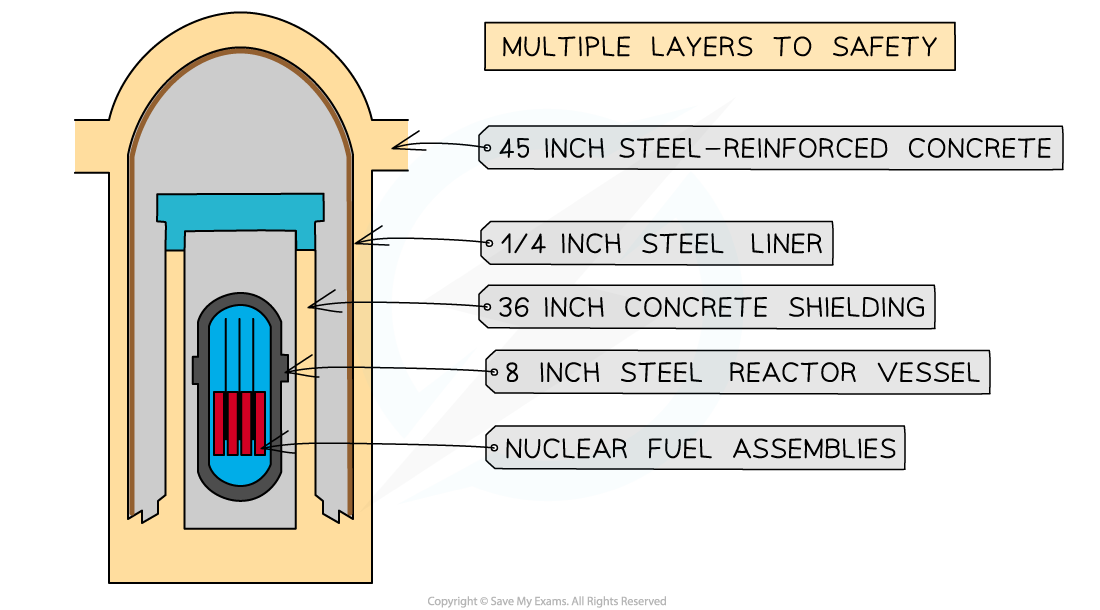
Shielding metals in a nuclear reactor
Advantages & Disadvantages of Nuclear Power
- Advantages of using nuclear power include:
- Extensive reserves of fissionable materials
- Increasingly refine technology available
- No greenhouse gases produced
- A large amount of power is produced
- Disadvantages of using nuclear power include:
- Hazardous radioactive waste materials produced
- Dangerous if the power plant goes significantly wrong
- Danger of misuse of nuclear material
- Problems with mining fuel
Burning Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, are used to produce energy on-demand when energy is needed
- This is done by burning the materials when the energy is required
- When fossil fuels are burned, it is used to heat water
- This water is heated until it becomes steam
- Steam is forced around the system and this turns a turbine
- The turbine spins and is connected to a generator which generates electricity
- This electricity is carried out of the system by electrical lines
- The steam within the turbine will cool and condense and then be pumped back into the boiler to repeat the process
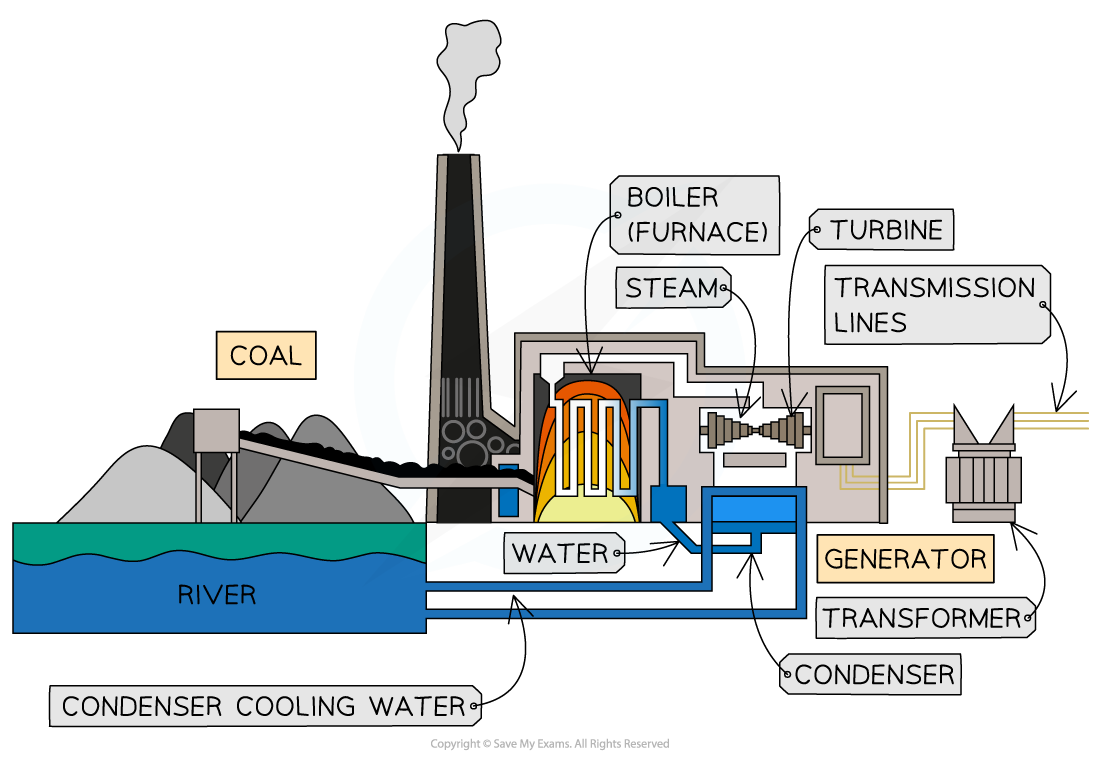
Diagram of a Fossil fuel based Reactor. The overall purpose of the reactor is to collect the heat energy produced from burning fossil fuels
- The approximate efficiency of fossil-fuel based power plants is approximately 40%
- Energy is lost to heat within exhaust gases, heat loss in the condenser process and friction within the system
Advantages & Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
- Advantages of using fossil fuel based power plants include:
- Extensive infrastructure in place
- High energy density of fuel
- Available energy at any time
- Well-known and developed technology
- Disadvantages of using fossil fuel based power plants include:
- Produces greenhouse gases
- Unsustainable (non-renewable)
- Produces pollution
Wind Electricity Generators
- Wind generators can be principally horizontally or vertically aligned
- The majority of modern designs use horizontally aligned designs
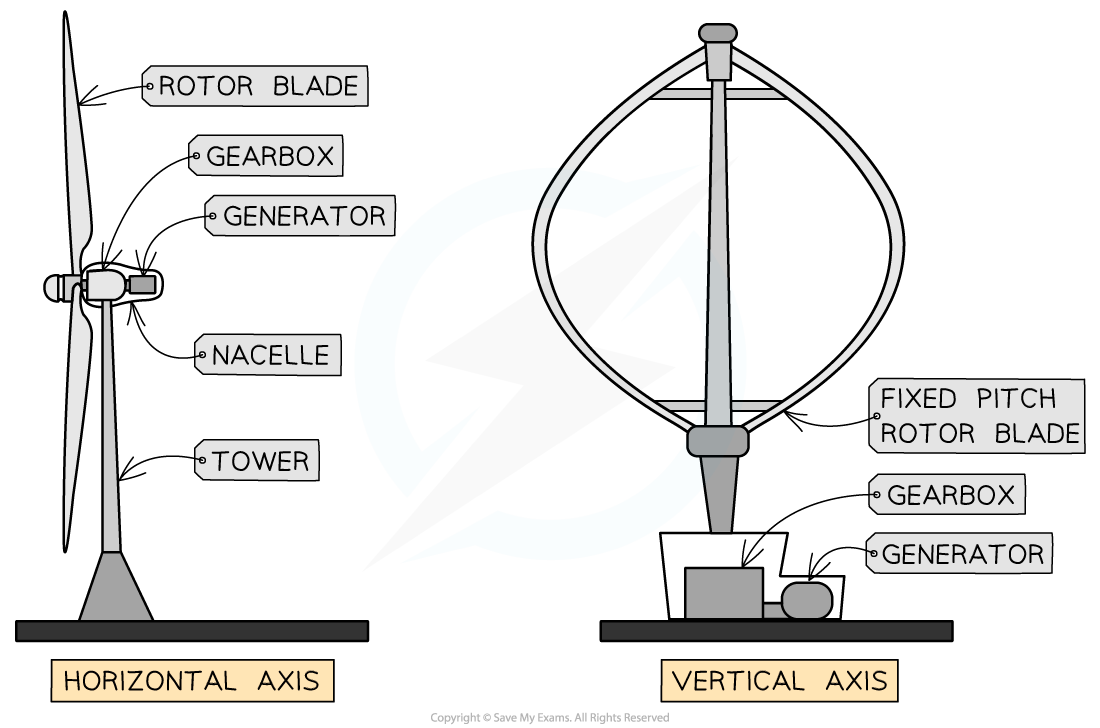
The two main designs of wind generators: horizontal and vertical alignment
- The approximate efficiency of wind generators is approximately 30%
- Energy is lost to aerodynamic limits, losses transferring the electricity to the grid and friction within the system
Advantages & Disadvantages of Wind Power
- Advantages of using wind-powered generators include:
- Clean (non-polluting) energy generation
- Freely available
- Is always sustainable and will never run out
- Disadvantages of using wind-powered generators include:
- Not consistent energy production
- Needs favourable local conditions to be placed in windy locations
- Can be visually unappealing
Hydroelectric Power
- Hydroelectric power using water stored at a height h, that mass of water m, is allowed to flow through turbines being pulled down by the acceleration due to gravity g
- The falling water has stored gravitational potential energy which is released when falling and used to spin turbines that generate electricity
- Energy can be stored for later use by pumping water back up to a higher location to be released to a lower location and spinning the turbines again when needed
- The approximate efficiency of hydroelectric power generation is approximately 90%
- Energy is lost to friction and other resistive forces
- The approximate maximum power that can be generated from a hydroelectric generator can be estimated by considering the rate of change of potential energy of the water falling through the turbines
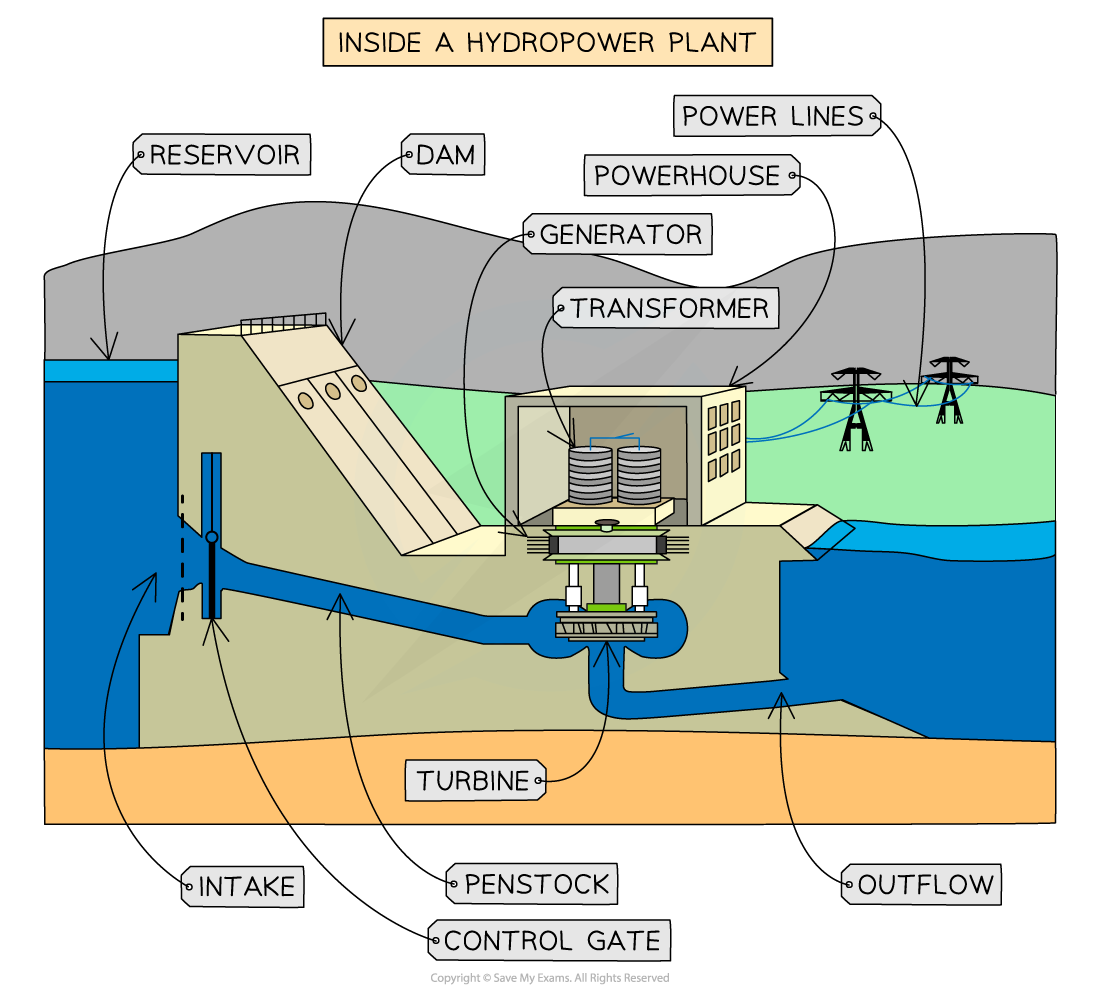
A hydroelectric power generation station. In off-peak hours water can be pumped back to the higher reservoir.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power
- Advantages of using hydroelectric generators include:
- Clean (non-polluting) energy generation
- Is sustainable
- Can be stored for when needed
- Disadvantages of using hydroelectric generators include:
- Large areas and changes to the environment are needed
- It relies on suitable locations
- A large initial investment is required
Calculating Energy Transformations
Wind Electricity Generators
- The approximate maximum power obtained per second that can be generated from a horizontal wind generator can be estimated by considering the blade radius and an incoming column of air
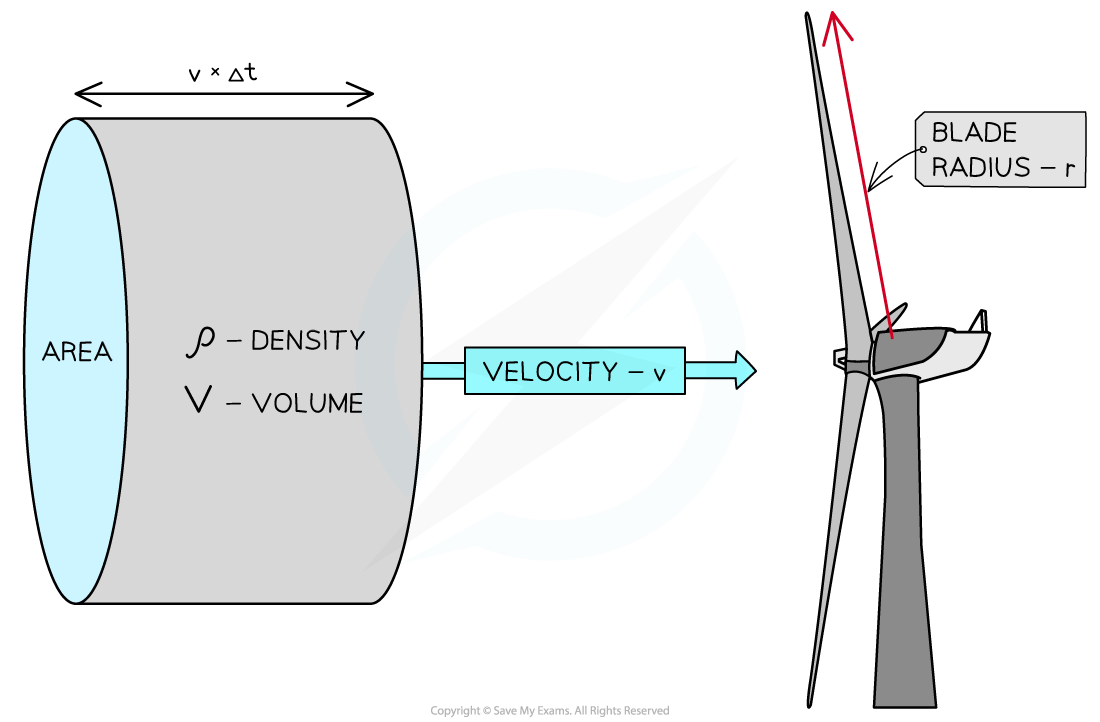
A column of air can provide only a limited amount of energy for a wind generator of blade radius r
- A column of air of density ρ can move through a cross-sectional area A which is determined by the blade radius r
- The amount of air that can move through this region is dependent on the velocity of the air v and the time considered t
- The kinetic energy of the air arriving at the turbine every second can be described by:
KE = ½ × mass × velocity2
- The mass, m, of the column of air can be described by using the equation
m = ρV = ρAL
- Where:
- ρ = density of the air (kg m−3)
- V = volume of the column (m3)
- A = cross-sectional area of the column (m2)
- L = length of the column (m)
- The length of the column can be described by
L = vt
- Where:
- v = velocity of the air (m s−1)
- t = time taken to travel the length of the column (s)
- Since the case is being considered for every second, time, t = 1 s
- Therefore, mass, in this case, will be:
m = ρvtA = ρvA
- This means power obtained per second can be described by:
P = ½ × (ρvA) × v2
P = ½ ρAv3
- This equation shows that the main variable that can impact power generated by wind is the wind's velocity
- If the wind's velocity remains the same, but the area covered by the blades doubles, then the theoretical power will double
- Yet, if the area covered by the blades remains the same and the wind velocity doubles, then the theoretical power available will increase eight-fold
- Typical values of quantities are useful to be aware of:
- Density of the air = 1.3 kgm−3 at standard temperature and pressure
- Velocity of the air required to turn the blades = 12 kmh−1 to get them turning and then 70 kmh−1 at full capacity
- Radius of the wind turbine blade = 50 - 150 m
Worked Example
Air moving at speed 9.5 m s-1 with a density of 1.15 kg m-3 is incident on a wind turbine. The length of the blades in the wind turbine are 14 m. After passing the wind turbine, the air is moving with a speed of 4.5 m s-1 and has a density of 1.30 kg m-3. Deduce the maximum power possible every second from this situation.
Step 1: List known values
-
- Air velocity before passing turbine: 9.5 m s-1
- Air density: 1.15 kg m-3
- Blade length: 14 m
- Air velocity after passing turbine: 4.5 m s-1
- Density: 1.30 kg m-3
Step 2: Find maximum power available
P = 0.5 × ρ × A × v3 = 0.5 × 1.15 × π × 142 × 9.53 = 3.04 × 105 W
Step 3: Find the remaining power within the air after passing the turbine
P = 0.5 × ρ × A × v3 = 0.5 × 1.15 × π × 142 × 4.53 = 3.64 × 104 W
Step 4: Find the power available for the turbine to use
P = (3.04 × 105) - (3.64 × 104) = 2.68 × 105 W
Step 5: State the final answer
-
- The maximum power available to the turbine is: 2.68 × 105 W every second
Hydroelectric Power
- Consider water of mass m stored at a height h, that is allowed to flow through turbines being pulled down by the acceleration due to gravity g
- The gravitational potential energy of the water is m × g × h
- Therefore, the change in energy (the power) will be:

- Where Δt = the time taken for the change in energy to occur
- This can be re-written in terms of volume and density rather than mass to consider the equation in terms of the volume flow rate
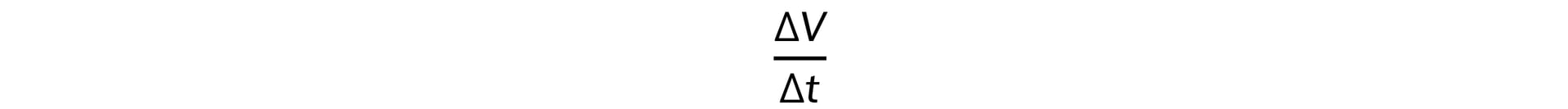
- Substituting this into the power equation gives:

- Therefore, to get large energy from hydroelectric power, large flow rates (ΔV ÷ Δt) and heights h are needed to maximise the energy produced
Worked Example
In a hydroelectric dam, water of density 1000 kg m−3 flows with a flow rate: 75 × 10−3 m3 s−1 goes through a turbine and descends approximately 22 m. Deduce the maximum power this will give if the efficiency of the turbine system is 85%.
Step 1: List the known quantities
- Flow rate, ΔV / Δt = 75 × 10−3 m3 s−1
- Height of water drop, h = 22 m
- Density of water, ρ = 1000 kg m−3
- Efficiency of turbine system, e = 85%
Step 2: State the relevant equation for hydroelectric power

- P = power (W)
- ρ = density (kg m-3)
- g = acceleration due to gravity (m s−2)
- h = height of falling water (m)
- ΔV / Δt = the flow rate (m3 s−1)
- e = efficiency [no units]
Step 3: Substitute in the values
P = (1000 × 9.8 × 22) × (75 × 10−3) × 0.85 = 1.37 x 104 W
Step 4: State final answer
- The approximate power available for the situation is: 1.37 × 104 W
