Modulus-Argument (Polar) Form
How do I write a complex number in modulus-argument (polar) form?
- The Cartesian form of a complex number,
, is written in terms of its real part,
, and its imaginary part,
- If we let
and
, then it is possible to write a complex number in terms of its modulus,
, and its argument,
, called the modulus-argument (polar) form, given by...
- This is often written as z = r cis θ
- This is given in the formula book under Modulus-argument (polar) form and exponential (Euler) form
- It is usual to give arguments in the range
or
- Negative arguments should be shown clearly
- e.g.
- without simplifying
to either
or
- without simplifying
- The complex conjugate of r cis θ is r cis (-θ )
- If a complex number is given in the form
, then it is not in modulus-argument (polar) form due to the minus sign
- It can be converted by considering transformations of trigonometric functions
and
- So
- It can be converted by considering transformations of trigonometric functions
- To convert from modulus-argument (polar) form back to Cartesian form, evaluate the real and imaginary parts
- E.g.
becomes
- E.g.
How do I multiply complex numbers in modulus-argument (polar) form?
- The main benefit of writing complex numbers in modulus-argument (polar) form is that they multiply and divide very easily
- To multiply two complex numbers in modulus-argument (polar) form we multiply their moduli and add their arguments
- So if z1 = r1 cis (θ1) and z2 = r2 cis (θ2)
- z1 z2 = r1r2 cis (θ1 + θ2)
- Sometimes the new argument,
, does not lie in the range
(or
if this is being used)
- An out-of-range argument can be adjusted by either adding or subtracting
- E.g. If
and
then
- This is currently not in the range
- Subtracting
from
to give
, a new argument is formed
- This lies in the correct range and represents the same angle on an Argand diagram
- An out-of-range argument can be adjusted by either adding or subtracting
- The rules of multiplying the moduli and adding the arguments can also be applied when…
- …multiplying three complex numbers together,
, or more
- …finding powers of a complex number (e.g.
can be written as
)
- …multiplying three complex numbers together,
- The rules for multiplication can be proved algebraically by multiplying z1 = r1 cis (θ1) by z2 = r2 cis (θ2), expanding the brackets and using compound angle formulae
How do I divide complex numbers in modulus-argument (polar) form?
- To divide two complex numbers in modulus-argument (polar) form, we divide their moduli and subtract their arguments
- So if z1 = r1 cis (θ1) and z2 = r2 cis (θ2) then
- Sometimes the new argument,
, can lie out of the range
(or the range
if this is being used)
- You can add or subtract
to bring out-of-range arguments back in range
- You can add or subtract
- The rules for division can be proved algebraically by dividing z1 = r1 cis (θ1) by z2 = r2 cis (θ2) using complex division and the compound angle formulae
Exam Tip
- Remember that r cis θ only refers to
- If you see a complex number written in the form
then you will need to convert it to the correct form first
- Make sure you are confident with basic trig identities to help you do this
- If you see a complex number written in the form
Worked Example
Let and
a)
Find  , giving your answer in the form
, giving your answer in the form format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%223.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Er%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22102.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2225.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ecos%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math117e62166fc8586dfa4d1bc0e17%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2255.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2277.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eisin%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2294.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) where
where format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%224.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E0%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1256ce40170cc70401ebd74e53e%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2217.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x2264%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2229.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1256ce40170cc70401ebd74e53e%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26lt%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2255.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1256ce40170cc70401ebd74e53e%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2266.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)

b)
Find  , giving your answer in the form
, giving your answer in the form format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%223.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Er%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22102.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2225.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ecos%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math117e62166fc8586dfa4d1bc0e17%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2255.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2277.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eisin%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2294.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) where
where format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b555372f2a9945337bcb4f4828%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x2212%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b555372f2a9945337bcb4f4828%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2219.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b555372f2a9945337bcb4f4828%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2233.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x2264%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2245.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b555372f2a9945337bcb4f4828%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2259.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26lt%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1b555372f2a9945337bcb4f4828%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2273.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
Exponential (Euler's) Form
How do we write a complex number in Euler's (exponential) form?
- A complex number can be written in Euler's form as
- This relates to the modulus-argument (polar) form as
- This shows a clear link between exponential functions and trigonometric functions
- This is given in the formula booklet under 'Modulus-argument (polar) form and exponential (Euler) form'
- The argument is normally given in the range 0 ≤ θ < 2π
- However in exponential form other arguments can be used and the same convention of adding or subtracting 2π can be applied
How do we multiply and divide complex numbers in Euler's form?
- Euler's form allows for quick and easy multiplication and division of complex numbers
- If
and
then
- Multiply the moduli and add the arguments
- Divide the moduli and subtract the arguments
- Using these rules makes multiplying and dividing more than two complex numbers much easier than in Cartesian form
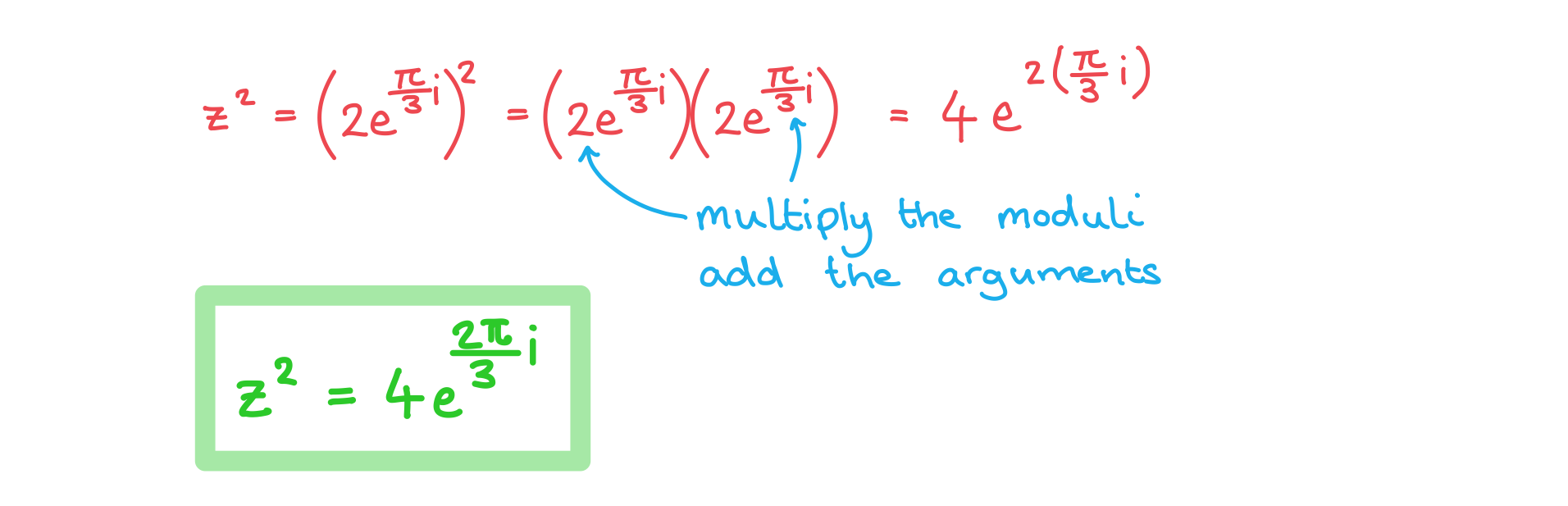
- When a complex number is written in Euler's form it is easy to raise that complex number to a power
- If
,
and
- If
What are some common numbers in exponential form?
- As
and
you can write:
- Using the same idea you can write:
- where k is any integer
- As
and
you can write:
- Or more commonly written as
- This is known as Euler's identity and is considered by some mathematicians as the most beautiful equation
- As
and
you can write:
Exam Tip
- Euler's form allows for easy manipulation of complex numbers, in an exam it is often worth the time converting a complex number into Euler's form if further calculations need to be carried out
- Familiarise yourself with which calculations are easier in which form, for example multiplication and division are easiest in Euler's form but adding and subtracting are easiest in Cartesian form
Worked Example
Consider the complex number . Calculate
giving your answer in the form
Conversion of Forms
Converting from Cartesian form to modulus-argument (polar) form or exponential (Euler's) form.
- To convert from Cartesian form to modulus-argument (polar) form or exponential (Euler) form use
- and
Converting from modulus-argument (polar) form or exponential (Euler's) form to Cartesian form.
- To convert from modulus-argument (polar) form to Cartesian form
- Write z = r (cosθ + isinθ ) as z = r cosθ + (r sinθ )i
- Find the values of the trigonometric ratios r sinθ and r cosθ
- You may need to use your knowledge of trig exact values
- Rewrite as z = a + bi where
- a = r cosθ and b = r sinθ
- To convert from exponential (Euler’s) form to Cartesian form first rewrite z = r eiθ in the form z = r cosθ + (r sinθ)i and then follow the steps above
Exam Tip
- When converting from Cartesian form into Polar or Euler's form, always leave your modulus and argument as an exact value
- Rounding values too early may result in inaccuracies later on
Worked Example
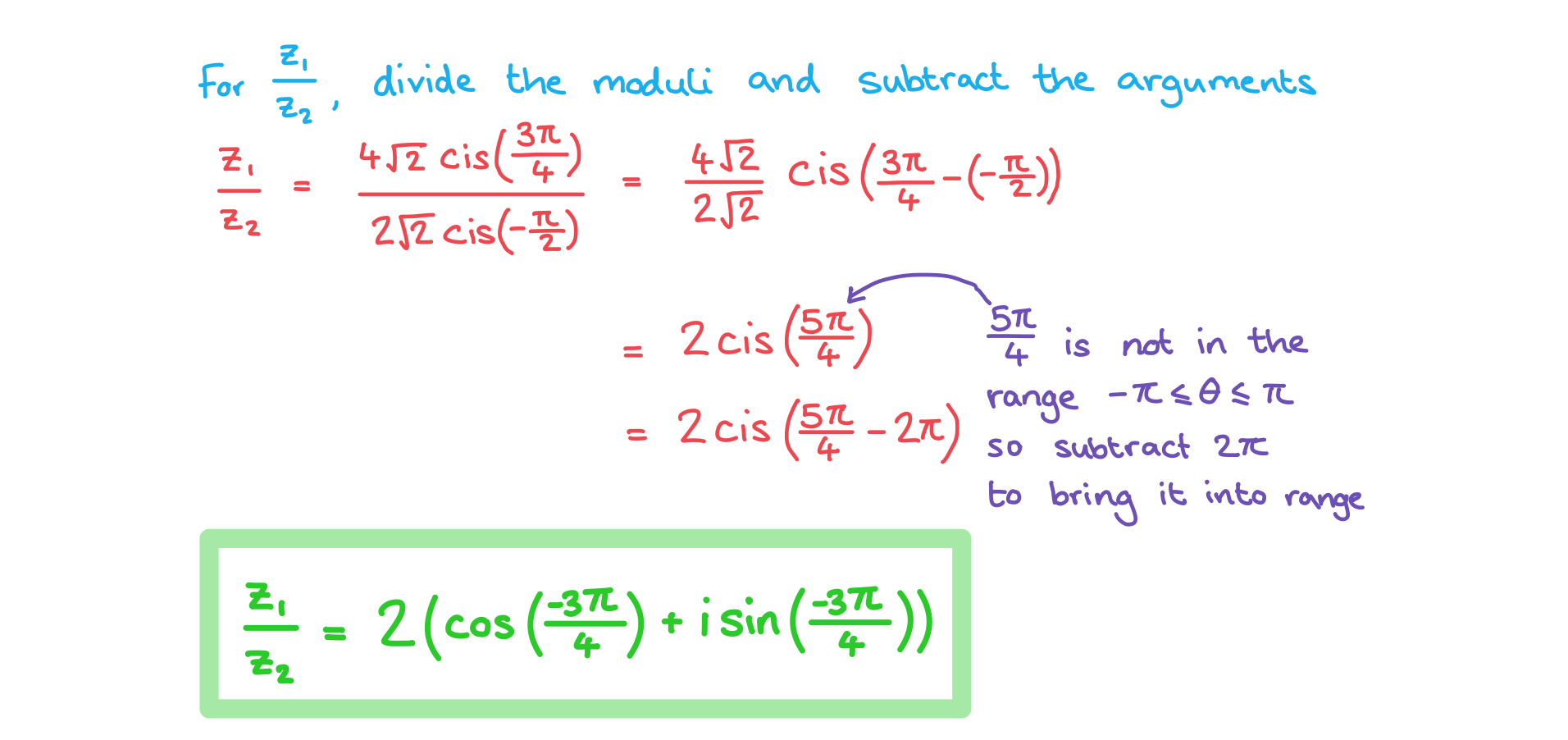
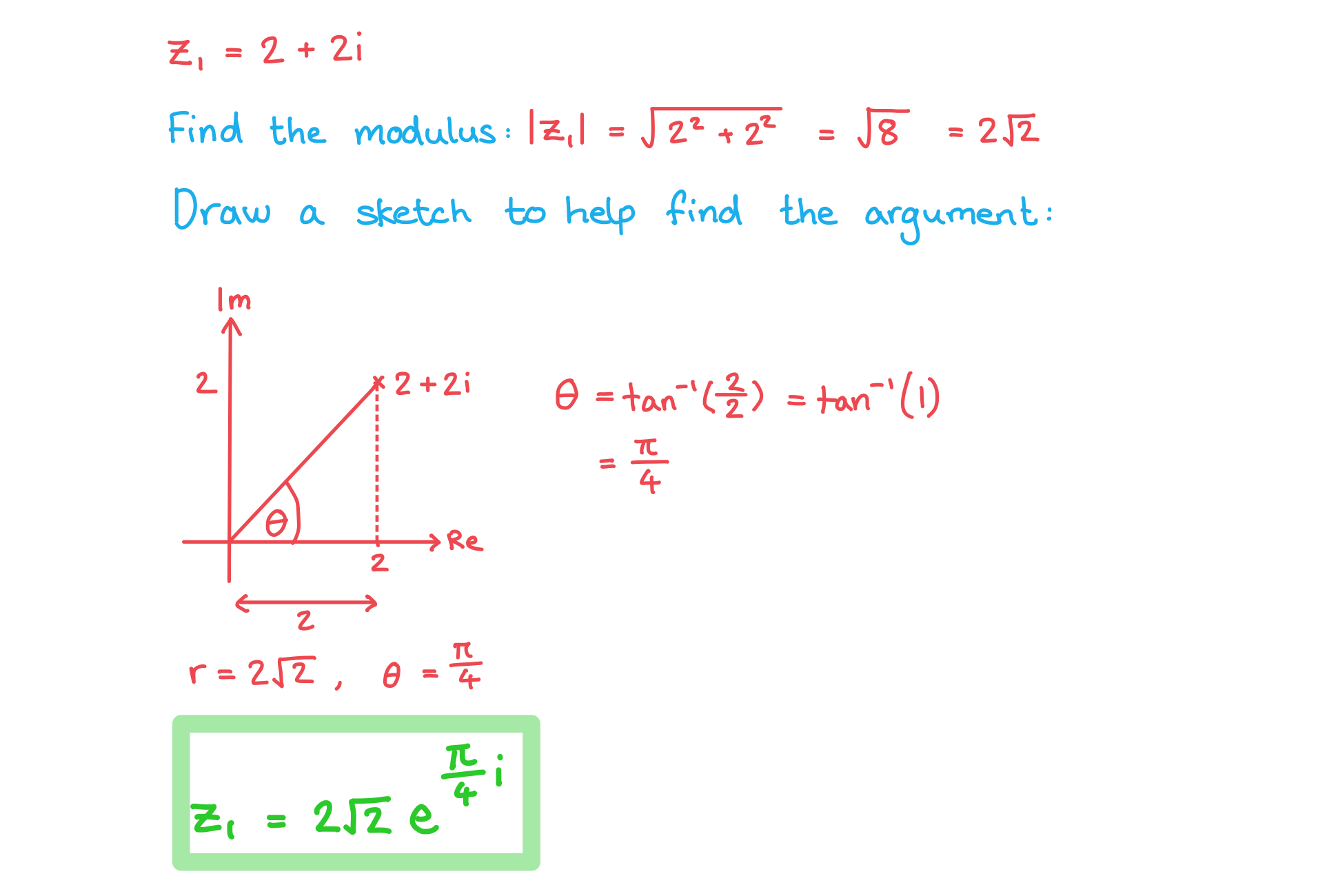
Two complex numbers are given by and
.
a)
Write  in the form
in the form  .
.
b)
Write  in the form
in the form format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%223.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Er%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22102.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2225.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ecos%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math117e62166fc8586dfa4d1bc0e17%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2255.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2277.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eisin%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2294.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3B8%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) and then convert it to Cartesian form.
and then convert it to Cartesian form.

