Lipids answers

 Answers to questions on Lipids
Answers to questions on Lipids
Answers to Lipids questions
1. (a) The first double bond occurs on the third carbon atom on the hydrocarbon chain counting from the opposite end to the carboxylic acid group.
(b) Esterification or condensation.
(c) 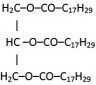
(d) It will be a liquid. It contains a high degree of unsaturation and the double bonds cause ‘kinks’ in the hydrocarbon chains so that the London dispersion forces between them are lower than for saturated hydrocarbon chains and hence the melting point will be lower.
(e) Mr for iodine (I2) = 2 x 126.9 = 253.8
25.38 g = 0.100 mol of I2
One mol of the triglyceride reacts with 9 mol of I2 (as it contains nine C=C double bonds)
Hence mass of triglyceride = (0.100 x 873.5) / 9 = 9.71 g
2. (a) It contains the typical four membered ring configuration present in all steroids.
(b) Add bromine (or iodine). Cholesterol will decolourise it rapidly as it contains a C=C double bond whereas estradiol does not contain a C=C double bond (so the Br2 or I2 cannot add to it). Note that the phenyl ring does not readily undergo addition reactions.
3. The first/upper structure is the cis- form and the second/lower is the trans- form.
They show cis/trans (or E/Z) isomerism.
The trans- form can be formed during the partial hydrogenation of polyunsaturated fattyacids.
It can increase LDL cholesterol, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
Download the Answers to Lipids questions

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team