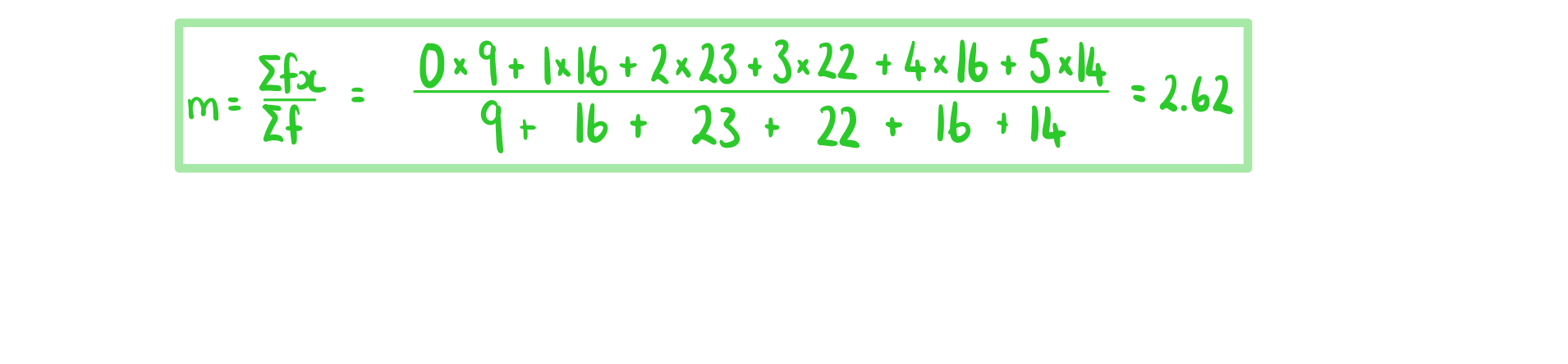Chi-Squared GOF: Uniform
What is a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a given distribution?
- A chi-squared (
) goodness of fit test is used to test data from a sample which suggests that the population has a given distribution
- This could be that:
- the proportions of the population for different categories follows a given ratio
- the population follows a uniform distribution
- This means all outcomes are equally likely
What are the steps for a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a given distribution?
- STEP 1: Write the hypotheses
- H0 : Variable X can be modelled by the given distribution
- H1 : Variable X cannot be modelled by the given distribution
- Make sure you clearly write what the variable is and don’t just call it X
- STEP 2: Calculate the degree of freedom for the test
- For k outcomes
- Degree of freedom is
- STEP 3: Calculate the expected frequencies
- Split the total frequency using the given ratio
- For a uniform distribution: divide the total frequency N by the number of outcomes k
- STEP 4: Enter the frequencies and the degree of freedom into your GDC
- Enter the observed and expected frequencies as two separate lists
- Your GDC will then give you the χ² statistic and its p-value
- The χ² statistic is denoted as
- STEP 5: Decide whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- If χ² statistic > critical value then reject H0
- If χ² statistic < critical value then accept H0
- OR compare the p-value with the given significance level
- If p-value < significance level then reject H0
- If p-value > significance level then accept H0
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- STEP 6: Write your conclusion
- If you reject H0
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the given distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data is not distributed as claimed
- If you accept H0
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the given distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data is distributed as claimed
- If you reject H0
Worked Example
A car salesman is interested in how his sales are distributed and records his sales results over a period of six weeks. The data is shown in the table.
|
Week |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
Number of sales |
15 |
17 |
11 |
21 |
14 |
12 |
A goodness of fit test is to be performed on the data at the 5% significance level to find out whether the data fits a uniform distribution.





Chi-Squared GOF: Binomial
What is a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a binomial distribution?
- A chi-squared (
) goodness of fit test is used to test data from a sample suggesting that the population has a binomial distribution
- You will either be given a precise binomial distribution to test
with an assumed value for p
- Or you will be asked to test whether a binomial distribution is suitable without being given an assumed value for p
- In this case you will have to calculate an estimate for the value of p for the binomial distribution
- To calculate it divide the mean by the value of n
- You will either be given a precise binomial distribution to test
What are the steps for a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a binomial distribution?
- STEP 1: Write the hypotheses
- H0 : Variable X can be modelled by a binomial distribution
- H1 : Variable X cannot be modelled by a binomial distribution
- Make sure you clearly write what the variable is and don’t just call it X
- If you are given the assumed value of p then state the precise distribution
- STEP 2: Calculate the expected frequencies
- If you were not given the assumed value of p then you will first have to estimate it using the observed data
- Find the probability of the outcome using the binomial distribution
- Multiply the probability by the total frequency
- You will have to combine rows/columns if any expected values are 5 or less
- STEP 3: Calculate the degrees of freedom for the test
- For k outcomes (after combining expected values if needed)
- Degree of freedom is
if you were given the assumed value of p
if you had to estimate the value of p
- STEP 4: Enter the frequencies and the degree of freedom into your GDC
- Enter the observed and expected frequencies as two separate lists
- Your GDC will then give you the χ² statistic and its p-value
- The χ² statistic is denoted as
- STEP 5: Decide whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- If χ² statistic > critical value then reject H0
- If χ² statistic < critical value then accept H0
- OR compare the p-value with the given significance level
- If p-value < significance level then reject H0
- If p-value > significance level then accept H0
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- STEP 6: Write your conclusion
- If you reject H0
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the binomial distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data does not follow
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the binomial distribution
- If you accept H0
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the binomial distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data follows
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the binomial distribution
- If you reject H0
Worked Example
A stage in a video game has three boss battles. 1000 people try this stage of the video game and the number of bosses defeated by each player is recorded.
|
Number of bosses defeated |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Frequency |
490 |
384 |
111 |
15 |
A goodness of fit test at the 5% significance level is used to decide whether the number of bosses defeated can be modelled by a binomial distribution with a 20% probability of success.




Chi-Squared GOF: Normal
What is a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a normal distribution?
- A chi-squared (
) goodness of fit test is used to test data from a sample suggesting that the population has a normal distribution
- You will either be given a precise normal distribution to test
with assumed values for μ and σ
- Or you will be asked to test whether a normal distribution is suitable without being given assumed values for μ and/or σ
- In this case you will have to calculate an estimate for the value of μ and/or σ for the normal distribution
- Either use your GDC or use the formulae
and
- You will either be given a precise normal distribution to test
What are the steps for a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a normal distribution?
· STEP 1: Write the hypotheses
-
- H0 : Variable X can be modelled by a normal distribution
- H1 : Variable X cannot be modelled by a normal distribution
- Make sure you clearly write what the variable is and don’t just call it X
- If you are given the assumed values of μ and σ then state the precise distribution
- STEP 2: Calculate the expected frequencies
- If you were not given the assumed values of μ or σ then you will first have to estimate them
- Find the probability of the outcome using the normal distribution
- Multiply the probability by the total frequency
- You will have to combine rows/columns if any expected values are 5 or less
- STEP 3: Calculate the degrees of freedom for the test
- For k class intervals (after combining expected values if needed)
- Degree of freedom is
if you were given the assumed values for both μ and σ
if you had to estimate either μ or σ but not both
if you had to estimate both μ and σ
- STEP 4: Enter the frequencies and the degree of freedom into your GDC
- Enter the observed and expected frequencies as two separate lists
- Your GDC will then give you the χ² statistic and its p-value
- The χ² statistic is denoted as
- STEP 5: Decide whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- If χ² statistic > critical value then reject H0
- If χ² statistic < critical value then accept H0
- OR compare the p-value with the given significance level
- If p-value < significance level then reject H0
- If p-value > significance level then accept H0
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- STEP 6: Write your conclusion
- If you reject H0
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the normal distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data does not follow
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the normal distribution
- If you accept H0
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the normal distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data follows
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the normal distribution
- If you reject H0
Worked Example
300 marbled ducks in Quacktown are weighed and the results are shown in the table below.
|
Mass (g) |
Frequency |
| 1 | |
| 9 | |
|
158 |
|
|
123 |
|
|
9 |
A goodness of fit test at the 10% significance level is used to decide whether the mass of a marbled duck can be modelled by a normal distribution with mean 520 g and standard deviation 30 g.





Chi-squared GOF: Poisson
What is a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a Poisson distribution?
- A chi-squared (χ²) goodness of fit test is used to test data from a sample suggesting that the population has a Poisson distribution
- You will either be given a precise Poisson distribution to test
with an assumed value for m
- Or you will be asked to test whether a Poisson distribution is suitable without being given an assumed value for m
- In this case you will have to calculate an estimate for the value of m for the Poisson distribution
- To calculate it just calculate the mean
- You will either be given a precise Poisson distribution to test
What are the steps for a chi-squared goodness of fit test for a Poisson distribution?
- STEP 1: Write the hypotheses
- H0 : Variable X can be modelled by a Poisson distribution
- H1 : Variable X cannot be modelled by a Poisson distribution
- Make sure you clearly write what the variable is and don’t just call it X
- If you are given the assumed value of m then state the precise distribution
- STEP 2: Calculate the expected frequencies
- If you were not given the assumed value of m then you will first have to estimate it using the observed data
- Find the probability of the outcome using the Poisson distribution
- Multiply the probability by the total frequency
- If a is the smallest observed value then calculate
- If b is the largest observed value then calculate
- If a is the smallest observed value then calculate
- You will have to combine rows/columns if any expected values are 5 or less
- STEP 3: Calculate the degrees of freedom for the test
- For k outcomes (after combining expected values if needed)
- Degree of freedom is
if you were given the assumed value of m
if you had to estimate the value of m
- STEP 4: Enter the frequencies and the degree of freedom into your GDC
- Enter the observed and expected frequencies as two separate lists
- Your GDC will then give you the χ² statistic and its p-value
- The χ² statistic is denoted as
- STEP 5: Decide whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- If χ² statistic > critical value then reject H0
- If χ² statistic < critical value then accept H0
- OR compare the p-value with the given significance level
- If p-value < significance level then reject H0
- If p-value > significance level then accept H0
- EITHER compare the χ² statistic with the given critical value
- STEP 6: Write your conclusion
- If you reject H0
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the Poisson distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data does not follow
- There is sufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the Poisson distribution
- If you accept H0
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the Poisson distribution
- Therefore this suggests that the data follows
- There is insufficient evidence to suggest that variable X does not follow the Poisson distribution
- If you reject H0
Worked Example
A parent claims the number of messages they receive from their teenage child within an hour can be modelled by a Poisson distribution. The parent collects data from 100 one hour periods and records the observed frequencies of the messages received from the child. The parent calculates the mean number of messages received from the sample and uses this to calculate the expected frequencies if a Poisson model is used.
|
Number of messages |
Observed frequency |
Expected frequency |
|
0 |
9 |
7.28 |
|
1 |
16 |
|
|
2 |
23 |
24.99 |
|
3 |
22 |
21.82 |
|
4 |
16 |
14.29 |
|
5 |
14 |
7.49 |
|
6 or more |
0 |
A χ² goodness of fit test at the 10% significance level is used to test the parent’s claim.