Drug detection & analysis questions
 Questions on Drug detection and analysis
Questions on Drug detection and analysis
1. The structures of morphine, heroin, aspirin and ibuprofen are given in Section 37 of the data
booklet. Explain how infrared spectroscopy can be used to distinguish between:
(a) morphine and heroin.
(b) aspirin and ibuprofen.
2. Raoult’s law states that for an ideal solution the partial vapour pressure of each component equals the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction.
(a) Explain what is meant by an ideal solution.
(b) Explain what is meant by mole fraction.
(c) Explain how Raoult’s law can be applied to separate two liquids, which have quite similar boiling points.
3. Methyltestosterone is a banned synthetic steroid, which may be used illegally by athletes to enhance performance. The structures of testosterone, which occurs naturally, and methyltestosterone are shown below.
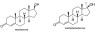
(a) State how much greater (in g mol-1) the molar mass of methyltestosterone will be compared to the molar mass of testosterone.
(b) Describe how the presence of methyltestosterone can be detected in the urine sample of an athlete.
4. In the television series ‘Breaking bad’, Walter White, a chemistry teacher, illegally mIB Docs (2) Teamfactures and sells a crystalline form of methamphetamine. Two compounds related to methamphetamine are ephedrone and its reduced form ephedrine.

(a) Distinguish between ephedrone and ephedrine in terms of the named functional groups they contain.
(b) Explain why ephedrine, unlike methamphetamine and ephedrone, can show diastereoisomerism.
(c) Knowing that a hydrogen atom bonded to a nitrogen atom does not usually affect the splitting patterns of adjacent hydrogen atoms due to hydrogen bonding explain why in their proton NMR spectrum all three compounds will show a singlet for one of the methyl groups whereas the signal for the other methyl group is split into a doublet.
(d) Explain how the number of signals and the relative areas under each signal in their proton NMR spectrum could be used to distinguish between the compounds.
(e) Explain how infrared spectroscopy could also be used to distinguish between the three compounds.
5. A simple ‘blow in the bag’ breathalyzer contains orange crystals of acidified potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7. It can be used to determine whether a motorist may be under the influence of alcohol.
(a) Explain why the crystals turn green if a motorist’s breath contains alcohol and give the two half-equations and the overall equation for the reaction that takes place.
(b) A more sophisticated breathalyzer contains a fuel cell. In this breathalyzer the ethanol is oxidized by oxygen on a platinum electrode. Give the half-equation for the reduction process that occurs.
Download the Drug detection & analysis questions ![]() to give to your students.
to give to your students.
To see the worked answers got to Drug detection & analysis answers.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team