Taxol answers

 Answers to questions on Taxol - a chiral auxiliary case study
Answers to questions on Taxol - a chiral auxiliary case study
Answers to Taxol questions
1.
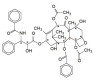
2. (a) The phenyl group and the hydroxyl group lie on opposite sides of the plane (in the enantiomer shown in the question the phenyl group is above the plane and the hydroxyl group is below the plane). If they were both on the same side the isomer would be the cis- isomer.
(b)
.jpg)
(c) A chiral auxiliary is a chiral molecule used during organic synthesis. It attaches to the organic reactant to force the stereochemistry of the reaction to follow a particular pathway so that only the desired enantiomeric product is formed. Once the product is formed the chiral auxiliary is removed and recycled.
(d) A pure enantiomer rotates the plane of plane-polarised light either clockwise or anti- clockwise by a fixed number of degrees. A polarimeter is used to measure the degree and direction of the rotation of the product. By using a calibration graph of degree of rotation against percentage composition the purity of the product can be determined by interpolation.
3. Both of the reactions occurring when the H of the –OH groups are replaced are esterification (or condensation) reactions.
Download the Answers to Taxol questions ![]()

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team