Aspirin & penicillin answers

 Answers to questions on Aspirin & penicillin
Answers to questions on Aspirin & penicillin
Answers to Aspirin & penicillin questions.
1. (a) An analgesic is a substance that reduces pain.
Mild analgesics work at the site of the injury by preventing particular enzymes (e.g. prostaglandin synthase) being formed. This prevents the formation of prostaglandins, which are responsible for swelling and the transmission of pain.
Strong analgesics work by acting temporarily with receptor sites in the brain so that pain signals within the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) are blocked.
(b) Carboxyl (accept carboxylic acid) and ester.
(c) Beneficial effect. One from:
Reduces fever, reduces risk of heart attack or stroke, thins the blood, effective for arthritis and rheumatism, anti-inflammatory. (Recently it has also been reported that it reduces the incidence of certain cancers).
Side effect. One from:
Causes bleeding to the stomach, Reye’s disease (in children under 12), allergic reaction, hearing loss, tinnitus, heartburn and nausea.
2. (a)
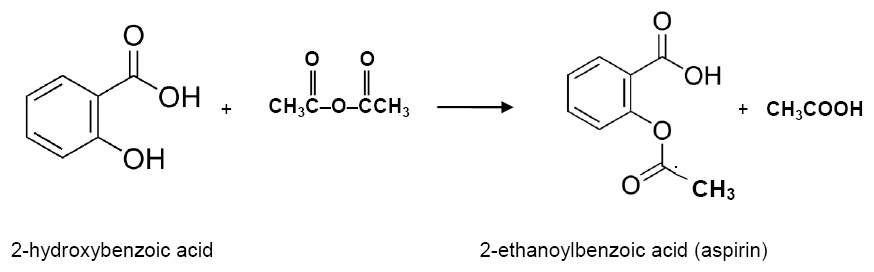

(b) Concentrated sulfuric acid
3. Although both carbonyl groups absorb infrared radiation in approximately the same region of the spectrum the precise frequency is determined by the other groups attached to the C=O group.
4. (a)
(b) Hydroxyl (accept alcohol or phenol), amide, carboxyl (accept carboxylic acid).
(c) It can be taken orally (penicillin G needed to be injected) / is not broken down easily in the stomach.
It is more resistant to the penicillinase enzyme.
(d) It interferes with the enzymes that bacteria need to make normal cell walls.
The cell walls are weakened and as the cell grows osmotic pressure causes the weakened cell wall to disintegrate and the bacterium dies.
(e) The Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium has developed resistance against normal penicillins and a cocktail of several different antibiotics is needed.
5. (a) Fleming was working as a bacteriologist on cultures of Staphylococcus aureus in London (actually St Mary’s Hospital, Paddington). He noticed that mould on an open petri dish was inhibiting the growth of the bacterium. He isolated a compound which he called penicillin which inhibited the growth but found it difficult to purify and stabilise. He published in 1929. Florey and Chain worked initially in Cambridge then in the USA. They overcame the problems with isolating and purifying penicillin and grew it in bulk using corn-steep liquor. They first tested it upon a policeman dying of blood poisoning (septicaemia).
(b) There are many other scientific discoveries where there is dispute about who made the discovery, e.g. the planet Neptune, the light bulb and oxygen gas. Many factors can contribute to the dispute. Observation versus theoretical deduction, nationalism and the triumph of publicity and tenacity to name but a few. In the case of penicillin it has been attributed to the presence of the newspaper mogul, Lord Beaverbrook, who was also on the governing body of St Mary’s Hospital, using his skill as a publicist and the prominence of the British Empire at the time.
6. It allows the bacteria to develop resistance and hence the penicillins become much less effective.
Download the Answers to Aspirin & penicillin questions ![]()

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team