Stereochemistry in biomolecules answers
 Answers to questions on Stereochemistry in biomolecules
Answers to questions on Stereochemistry in biomolecules
Answers to Stereochemistry in biomolecules questions
1. (a)
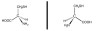
(b) The one on the left is the D- isomer and the one of the right, the L-configuration, is the one that occurs in proteins.
(c) Glycine (0), isoleucine (2), threonine (2)
2. (a) Cis/trans isomerisation and oxidation.
(b) Both have extended conjugation so absorb in the visible region. Only cis-retinal contains a carbonyl group (C=O), which absorbs at approximately 1700-1750 cm-1 in the infrared region of the spectrum.
(c) Cis-retinal can reversibly bind to opsin, a protein in the retina to form rhodopsin. When light falls on cis-retinal it is converted into trans-retinal, which changes the configuration of the protein. This triggers a response that sends an electrical signal to the brain. At the same time the trans-retinal detaches from the opsin and is converted back to cis-retinal by a series of enzymatic transformations so that the process (the visual cycle) can be repeated.
3. (a) Amylose and amylopectin are both formed from the condensation reaction between α-D-glucose molecules. Amylose is a linear (unbranched) polysaccharide containing up to 2000 glucose monomers joined by 1,4-glycosidic linkages. Due to the bond angles it forms a spiral, rather like a coiled spring. Amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide containing both 1,4- and 1,6- glycosidic linkages.
(b) Cellulose is also a linear polysaccharide made up from several thousand glucose molecules. It is formed from the condensation reaction between β-D-glucose molecules forming 1,4-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, it cannot be broken down by digestive enzymes and secretions of the gastrointestinal tract.
(c) It provides structure to plants (i.e. rigid cell walls).
It provides fibre (roughage) in the human diet, which helps to prevent constipation. It may also help to prevent colon cancer and cholesterol absorption.
4. (a) It is D-fructose as the –OH bonded to the last chiral carbon atom next to the aldose group (furthest from the aldehyde group) is on the right.
(b)

Download the Answers to Stereochemistry in biomolecules questions

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team